Abstract
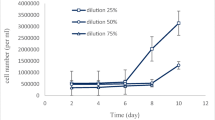
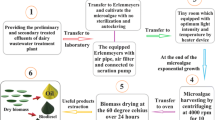
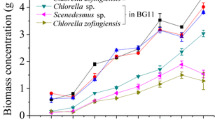
The present study focused on cost-effective production of microalgal biomass and lipid production on dairy effluent. The novel microalga, Chlorella sp. isolated from the dairy effluent showed high growth and lipid production on the undiluted and two-fold diluted dairy effluent which were four to five times higher than those of Chlorella vulgaris (control). The high growth of Chlorella sp. was thought to be possibly due to its heterotrophic growth capacity, high turbidity, COD, nutrients and trace elements. In contrast, C. vulgaris showed poor heterotrophic and photoautotrophic growth under the highly turbid conditions of dairy effluent. Both Chlorella sp. and C. vulgaris showed similar total FAME (mg FAME/g algal cells). The fatty acid composition analysis revealed that both Chlorella sp. and C. vulgaris possessed major C18 and C20 fatty acids which will be used for biodiesel production. Overall, the novel microalga, Chlorella sp. isolated from the dairy effluent showed high potential for cost-effective algal cultivation and lipid production on dairy effluent without any modification of process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skjånes, K., C. Rebours, and P. Lindblad (2013) Potential for green microalgae to produce hydrogen, pharmaceuticals and other high value products in a combined process. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 33: 172–215.
Unc, A., E. Monfet, A. Potter, M. Camargo-Valero, and S. Smith (2017) Note to Editor: Microalgae cultivation for wastewater treatment and biofuel production: a bibliographic overview of past and current trends. Algal Res. 24: A2–A7.
Ramsundar, P., A. Guldhe, P. Singh, and F. Bux (2017) Assessment of municipal wastewaters at various stages of treatment process as potential growth media for Chlorella sorokiniana under different modes of cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 227: 82–92.
Hena, S., N. Fatihah, S. Tabassum, and N. Ismail (2015) Three stage cultivation process of facultative strain of Chlorella sorokiniana for treating dairy farm effluent and lipid enhancement. Water Res. 80: 346–356.
Karapinar Kapdan, I. and S. Aslan (2008) Application of the Stover–Kincannon kinetic model to nitrogen removal by Chlorella vulgaris in a continuously operated immobilized photobioreactor system. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 83: 998–1005.
Chisti, Y. (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotech. adv. 25: 294–306.
Nam, K., H. Lee, S.-W. Heo, Y. K. Chang, and J.-I. Han (2017) Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris with swine wastewater and potential for algal biodiesel production. J. Appl. Phycol. 29: 1171–1178.
Hoh, D., S. Watson, and E. Kan (2016) Algal biofilm reactors for integrated wastewater treatment and biofuel production: a review. Chem. Eng. J. 287: 466–473.
Song, C., G. Chen, N. Ji, Q. Liu, Y. Kansha, and A. Tsutsumi (2015) Biodiesel production process from microalgae oil by waste heat recovery and process integration. Bioresour. Technol. 193: 192–199.
Gonçalves, A. L., J. C. Pires, and M. Simões (2017) A review on the use of microalgal consortia for wastewater treatment. Algal Res. 24: 403–415.
Wang, L., Y. Li, P. Chen, M. Min, Y. Chen, J. Zhu, and R. R. Ruan (2010) Anaerobic digested dairy manure as a nutrient supplement for cultivation of oil-rich green microalgae Chlorella sp. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 2623–2628.
Ding J., F. Zhao, Y. Cao, L. Xing, W. Liu, S. Mei, and S. Li (2015) Cultivation of microalgae in dairy farm wastewater without sterilization. Int. J. Phytoremediation. 17: 222–227.
Johnson, M. B. and Z. Wen (2010) Development of an attached microalgal growth system for biofuel production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85: 525–534.
Ummalyma, S. B., and R. K. Sukumaran (2014) Cultivation of microalgae in dairy effluent for oil production and removal of organic pollution load. Bioresour. Technol. 165: 295–301.
Chokshi, K., I. Pancha, A. Ghosh, and S. Mishra (2016) Microalgal biomass generation by phycoremediation of dairy industry wastewater: an integrated approach towards sustainable biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 221: 455–460.
Hena S., H. Znad, K. Heong, and S. Judd (2018) Dairy farm wastewater treatment and lipid accumulation by Arthrospira platensis. Water Res. 128: 267–277.
Tam, N. F. Y. and Y. S. Wong (1996) Effect of ammonia concentrations on growth of Chlorella vulgaris and nitrogen removal from media. Bioresour. Technol. 57: 45–50.
Kobayashi, N., E. A. Noel, A. Barnes, A. Watson, J. N. Rosenberg, G. Erickson, and G. A. Oyler (2013) Characterization of three Chlorella sorokiniana strains in anaerobic digested effluent from cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 150: 377–386.
Bligh, E. G. and W. J. Dyer (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Phys. 37: 911–917.
Kim, Y.-H., Y.-K. Choi, J. Park, S. Lee, Y.-H. Yang, H. J. Kim, T.-J. Park, Y. H. Kim, and S. H. Lee (2012) Ionic liquid-mediated extraction of lipids from algal biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 109: 312–315.
Griffiths, M. J., C. Garcin, R. P. van Hille, and S. T. Harrison (2011) Interference by pigment in the estimation of microalgal biomass concentration by optical density. J. Microbiol. Methods. 85: 119–123.
Choi, Y.-K., R. S. Kumaran, H. J. Jeon, H.-J. Song, Y.-H. Yang, S. H. Lee, K.-G. Song, K. J. Kim, V. Singh, and H. J. Kim (2015) LED light stress induced biomass and fatty acid production in microalgal biosystem, Acutodesmus obliquus. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 145: 245–253.
Jeon, H. J., Y.-K. Choi, K.-G. Song, S. H. Lee, Y.-H. Yang, H. Kim, S. Kim, R. Kumaran, S. W. Hong, and H. J. Kim (2013) Development of a photoelectrochemical sensor for monitoring algal biomass (Chlorella vulgaris). Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 185: 405–410.
Wang, L., M. Min, Y. Li, P. Chen, Y. Chen, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, and R. Ruan (2010) Cultivation of green algae Chlorella sp. in different wastewaters from municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl, Biochem. Biotechnol. 162: 1174–1186.
Bohutskyi, P., K. Liu, B. A. Kessler, T. Kula, Y. Hong, E. J. Bouwer, M. J. Betenbaugh, and F. T. Allnutt (2014) Mineral and non-carbon nutrient utilization and recovery during sequential phototrophic-heterotrophic growth of lipid-rich algae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98: 5261–5273.
Yang, J., J. Cao, G. Xing, and H. Yuan (2015) Lipid production combined with biosorption and bioaccumulation of cadmium, copper, manganese and zinc by oleaginous microalgae Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341. Bioresour. Technol. 175: 537–544.
Franklin, N. M., J. L. Stauber, R. P. Lim, and P. Petocz (2002) Toxicity of metal mixtures to a tropical freshwater alga (Chlorella sp.): the effect of interactions between copper, cadmium, and zinc on metal cell binding and uptake. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 21: 2412–2422.
Zhu, L., Z. Wang, Q. Shu, J. Takala, E. Hiltunen, P. Feng, and Z. Yuan (2013) Nutrient removal and biodiesel production by integration of freshwater algae cultivation with piggery wastewater treatment. Water Rese. 47: 4294–4302.
Shen, L., J. D. Ndayambaje, T. Murwanashyaka, W. Cui, E. Manirafasha, C. Chen, Y. Wang, and Y. Lu (2017) Assessment upon heterotrophic microalgae screened from wastewater microbiota for concurrent pollutants removal and biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 245: 386–393.
Chen, M., H. Tang, H. Ma, T. C. Holland, K. Y. S. Ng, and S. O. Salley (2011) Effect of nutrients on growth and lipid accumulation in the green algae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 1649–1655.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, YK., Jang, H.M. & Kan, E. Microalgal Biomass and Lipid Production on Dairy Effluent Using a Novel Microalga, Chlorella sp. Isolated from Dairy Wastewater. Biotechnol Bioproc E 23, 333–340 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0094-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0094-y