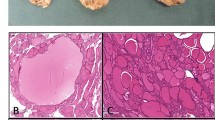
Abstract
Follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTCs) are the second most common malignant neoplasia of the thyroid and in general its prognosis is quite favorable. However, the occurrence of metastases or non-responsiveness to radioiodine therapy worsens the prognosis considerably. We evaluated immunohistochemically the expression of hypoxia-associated proteins by hypoxia-induced factor 1α (HIF-1α), the stroma-remodeling marker Tenascin C, as well as markers for the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), namely E-cadherin and slug in a series of 59 sporadic FTCs. In addition, various clinicopathologic parameters were assessed like TNM-staging, age, tumor size as well as tumor characteristics like desmoplasia, necrosis, and calcification. Overexpression of HIF-1α was seen in 29 of 59 tumors (49.2%) including 21 (35.6%) FTC with strong expression of tumor cell groups. HIF-1α correlated significantly with metastasis (p < 0.001; Mann-Whitney U test), degree of desmoplasia (p = 0.042, Kruskal-Wallis test), tenascin C expression (p = 0.042, Kruskal-Wallis test), calcification (p < 0.025, Kruskal–Wallis test), necrosis (p = 0.002), age (p = 0.011, Kruskal-Wallis test) and tumor stage UICC (p = 0.022, Kruskal-Wallis test). Furthermore, metastasis was associated with the degree of desmoplasia (p = 0.014; Fisher’s exact test), calcification (p = 0.008, Fisher’s exact test), necrosis (p = 0.042, Fisher’s exact test), tumor size (p = 0.015, Mann-Whitney U test), and age (p = 0.001, Mann-Whitney U test). In a Cox proportional hazards model, only metastasis remained as an independent risk factor for overall survival (hazard rate: 10.2 [95% CI, 02.19 to 47.26]; p = 0.003). Our data suggest that HIF-1α plays a critical role in the remodeling of the extracellular matrix as well as metastasizing process of follicular thyroid carcinoma and targeting hypoxia-associated and -regulated proteins may be considered as potential targets for personalized medicine.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA (2010) Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 10:9–22. doi:10.1038/nrc2748
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M (2010) Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140:883–899. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025
Birner P, Schindl M, Obermair A, Plank C, Breitenecker G, Oberhuber G (2000) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is a marker for an unfavorable prognosis in early-stage invasive cervical cancer. Cancer Res 60:4693–4696
Kitada T, Seki S, Sakaguchi H, Sawada T, Hirakawa K, Wakasa K (2003) Clinicopathological significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in human pancreatic carcinoma. Histopathology 43:550–555
Maxwell PH, Dachs GU, Gleadle JM, Nicholls LG, Harris AL, Stratford IJ, Hankinson O, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (1997) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8104–8109
Pugh CW, Gleadle J, Maxwell PH (2001) Hypoxia and oxidative stress in breast cancer. Hypoxia signalling pathways. Breast Cancer Res: BCR 3:313–317
Schindl M, Schoppmann SF, Samonigg H, Hausmaninger H, Kwasny W, Gnant M, Jakesz R, Kubista E, Birner P, Oberhuber G, Group ABaCCS (2002) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in lymph node-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8:1831–1837
Zalatnai A (2006) Molecular aspects of stromal-parenchymal interactions in malignant neoplasms. Curr Mol Med 6:685–693
De Wever O, Mareel M (2003) Role of tissue stroma in cancer cell invasion. J Pathol 200:429–447. doi:10.1002/path.1398
Yoshida T, Akatsuka T, Imanaka-Yoshida K (2015) Tenascin-C and integrins in cancer. Cell Adhes Migr 9:96–104. doi:10.1080/19336918.2015.1008332
Dong W, Qin G, Shen R (2016) Rab11-FIP2 promotes the metastasis of gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer 138:1680–1688. doi:10.1002/ijc.29899
Huang CH, Yang WH, Chang SY, Tai SK, Tzeng CH, Kao JY, Wu KJ, Yang MH (2009) Regulation of membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase by SLUG contributes to hypoxia-mediated metastasis. Neoplasia 11:1371–1382
Rankin EB, Giaccia AJ (2016) Hypoxic control of metastasis. Science 352:175–180. doi:10.1126/science.aaf4405
Serrano-Gomez SJ, Maziveyi M, Alahari SK (2016) Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol Cancer 15:18
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression nature reviews. Cancer 2:442–454. doi:10.1038/nrc822
Chow SM, Law SC, Mendenhall WM, Au SK, Yau S, Yuen KT, Law CC, Lau WH (2002) Follicular thyroid carcinoma: prognostic factors and the role of radioiodine. Cancer 95:488–498. doi:10.1002/cncr.10683
Ito Y, Hirokawa M, Masuoka H, Yabuta T, Fukushima M, Kihara M, Higashiyama T, Takamura Y, Kobayashi K, Miya A, Miyauchi A (2013) Distant metastasis at diagnosis and large tumor size are significant prognostic factors of widely invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma. Endocr J 60:829–833
Ito Y, Miyauchi A, Tomoda C, Hirokawa M, Kobayashi K, Miya A (2013) Prognostic significance of patient age in minimally and widely invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma: investigation of three age groups. Endocr J 61:265–271
DeLellis RA (2006) Pathology and genetics of thyroid carcinoma J Surg Oncol 94:662–669. doi:10.1002/jso.20700
Sobin L, Gospodarowicz M, Wittekind C (2009) TNM classification of malignant tumours. Wiley-Blackwell, New York
Ghossein RA, Hiltzik DH, Carlson DL, Patel S, Shaha A, Shah JP, Tuttle RM, Singh B (2006) Prognostic factors of recurrence in encapsulated Hurthle cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: a clinicopathologic study of 50 cases. Cancer 106:1669–1676. doi:10.1002/cncr.21825
Lang W, Choritz H, Hundeshagen H (1986) Risk factors in follicular thyroid carcinomas. A retrospective follow-up study covering a 14-year period with emphasis on morphological findings. Am J Surg Pathol 10:246–255
Burrows N, Resch J, Cowen RL, von Wasielewski R, Hoang-Vu C, West CM, Williams KJ, Brabant G (2010) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in thyroid carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:61–72. doi:10.1677/ERC-08-0251
Ito Y, Miyauchi A, Tomoda C, Hirokawa M, Kobayashi K, Miya A (2014) Prognostic significance of patient age in minimally and widely invasive follicular thyroid carcinoma: investigation of three age groups. Endocr J 61:265–271
Koperek O, Akin E, Asari R, Niederle B, Neuhold N (2013) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in papillary thyroid carcinoma is associated with desmoplastic stromal reaction and lymph node metastasis. Virchows Archiv : Int J Pathol 463:795–802. doi:10.1007/s00428-013-1484-3
Koperek O, Bergner O, Pichlhöfer B, Oberndorfer F, Hainfellner JA, Kaserer K, Horvat R, Harris AL, Niederle B, Birner P (2011) Expression of hypoxia-associated proteins in sporadic medullary thyroid cancer is associated with desmoplastic stroma reaction and lymph node metastasis and may indicate somatic mutations in the VHL gene. J Pathol 225:63–72
Semenza G (2012) Hypoxia-inducible factors: mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 33:207–214
Birner P, Gatterbauer B, Oberhuber G, Schindl M, Rössler K, Prodinger A, Budka H, Hainfellner JA (2001) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in oligodendrogliomas: its impact on prognosis and on neoangiogenesis. Cancer 92:165–171
Cleven AHG, van Engeland M, Wouters BG, de Bruïne AP (2007) Stromal expression of hypoxia regulated proteins is an adverse prognostic factor in colorectal carcinomas. Cell Oncol 29:229–240
Schoppmann SF, Fenzl A, Schindl M, Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Nagy K, Gnant M, Horvat R, Jakesz R, Birner P (2006) Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha correlates with VEGF-C expression and lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 99:135–141
Bertout JA, Patel SA, Simon MC (2008) The impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8:967–975. doi:10.1038/nrc2540
Dery M, Michaud M, Richard D (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulation by hypoxic and non-hypoxic activators. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:535–540
Erler JT, Giaccia AJ (2006) Lysyl oxidase mediates hypoxic control of metastasis. Cancer Res 66:10238–10241. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3197
Hockel M, Vaupel P (2001) Tumor hypoxia: definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:266–276
Sullivan R, Graham CH (2007) Hypoxia-driven selection of the metastatic phenotype. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26:319–331. doi:10.1007/s10555-007-9062-2
Rapisarda A, Shoemaker RH, Melillo G (2009) Antiangiogenic agents and HIF-1 inhibitors meet at the crossroads. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 8:4040–4043
Burrows N, Babur M, Resch J, Ridsdale S, Mejin M, Rowling EJ, Brabant G, Williams KJ (2011) GDC-0941 inhibits metastatic characteristics of thyroid carcinomas by targeting both the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) pathways. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 96:E1934–E1943. doi:10.4061/2011/762905
Manalo D, Rowan A, Lavoie T, Natarajan L, Kelly B, Ye S, Garcia J, Semenza G (2005) Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial cell responses to hypoxia by HIF-1. Blood 105:659–669
Chen S, Chen JZ, Zhang JQ, Chen HX, Yan ML, Huang L, Tian YF, Chen YL, Wang YD (2016) Hypoxia induces TWIST-activated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in nude mice. Cancer Lett 383:73–84. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.09.027
Lan L, Luo Y, Cui D, Shi BY, Deng W, Huo LL, Chen HL, Zhang GY, Deng LL (2013) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition triggers cancer stem cell generation in human thyroid cancer cells. Int J Oncol 43:113–120. doi:10.3892/ijo.2013.1913
Giannoni E, Bianchini F, Calorini L, Chiarugi P (2011) Cancer associated fibroblasts exploit reactive oxygen species through a proinflammatory signature leading to epithelial mesenchymal transition and stemness. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:2361–2371
Zhu GH, Huang C, Feng ZZ, Lv XH, Qiu ZJ (2013) Hypoxia-induced snail expression through transcriptional regulation by HIF-1α in pancreatic cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci 58:3503–3515
Chiquet-Ehrismann R, Tucker RP (2004) Connective tissues: signalling by tenascins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1085–1089. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2004.01.007
Elvidge GP, Glenny L, Appelhoff RJ, Ratcliffe PJ, Ragoussis J, Gleadle JM (2006) Concordant regulation of Gene expression by hypoxia and 2-Oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase inhibition: the role of HIF-1, HIF-2, and other pathways. J Biol Chem 281:15215–15226
Colpaert C, Vermeulen P, van Beest P, Goovaerts G, Weyler J, Van Dam P, Dirix L, Van Marck E (2001) Intratumoral hypoxia resulting in the presence of a fibrotic focus is an independent predictor of early distant relapse in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. Histopathology 39:416–425
Couvelard A, O'Toole D, Leek R, Turley H, Sauvanet A, Degott C, Ruszniewski P, Belghiti J, Harris AL, Gatter K, Pezzella F (2005) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factors is correlated with the presence of a fibrotic focus and angiogenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Histopathology 46:668–676
Takacova M, Bullova P, Simko V, Skvarkova L, Poturnajova M, Feketeova L, Babal P, Kivela AJ, Kuopio T, Kopacek J, Pastorek J, Parkkila S, Pastorekova S (2014) Expression pattern of carbonic anhydrase IX in medullary thyroid carcinoma supports a role for RET-mediated activation of the HIF pathway. Am J Pathol 184:953–965 doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.01.002
Faam B, Ghaffari MA, Ghadiri A, Azizi F (2015) Epigenetic modifications in human thyroid cancer. Biomed Reports 3:3–8. doi:10.3892/br.2014.375
Nikiforov YE (2011) Molecular analysis of thyroid tumors. Mod Pathol : Off J U S Can Acad Pathol, Inc 24:S34. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.167
Ebos JML, Lee CR, Cruz-Munoz W, Bjarnason GA, Christensen JG, Kerbel RS (2009) Accelerated metastasis after short-term treatment with a potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 15:232–239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by the Medical Scientific Fund of the Mayor of the City of Vienna (project # 10069).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klaus, A., Fathi, O., Tatjana, TW. et al. Expression of Hypoxia-Associated Protein HIF-1α in Follicular Thyroid Cancer is Associated with Distant Metastasis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 24, 289–296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0232-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0232-4