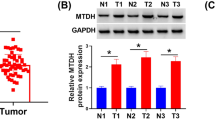
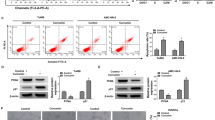
Abstract
S100 proteins, a family of Ca2+-binding proteins, have been linked to several human diseases in recent years. Deregulated expression of S100 proteins, including S100A9 and its partner S100A8, was reported to be associated with neoplastic disorders. In our previous study using serial analysis of gene expression, we identified decreased expressions of S100A9 and S100A8 in human cervical squamous cell carcinoma. To investigate the functions of S100A8 and S100A9 in cervical cancer, we purified recombinant S100A8 and S100A9 proteins and treated CaSki human cervical cancer cells with these proteins. We found that S100A8/A9 induced apoptosis and inhibited migration of CaSki cells; S100A8/A9 also reduced the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 in CaSki cells. In summary, this study suggests that S100A8 and S100A9 have inhibitory effects on the proliferation of CaSki carcinoma cells by inducing cell apoptosis and on the invasiveness of CaSki cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Walboomers JM, Jacobs MV, Manos MM et al (1999) Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J Pathol 189(1):12–19
Hinchliffe SA, van Velzen D, Korporaal H et al (1995) Transience of cervical HPV infection in sexually active, young women with normal cervicovaginal cytology. Br J Cancer 72(4):943–945
Martin CM, Astbury K, O’Leary JJ (2006) Molecular profiling of cervical neoplasia. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 6(2):217–229
Polyak K, Riggins GJ (2001) Gene discovery using the serial analysis of gene expression technique: implications for cancer research. J Clin Oncol 19(11):2948–2958
Kang HW, Geng L, Zhao L et al (2004) Gene expression profile in human normal cervical squamous epithelium. Chin J Reprod Health 15(5):303–305
Zimmer DB, Cornwall EH, Landar A et al (1995) The S100 protein family: history, function, and expression. Brain Res Bull 37(4):417–429
Donato R (2003) Intracellular and extracellular roles of S100 proteins. Microsc Res Tech 60(6):540–551
Heizmann CW, Fritz G, Schafer BW (2002) S100 proteins: structure, functions and pathology. Front Biosci 7:d1356–d1368
Yui S, Nakatani Y, Mikami M (2003) Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9), an inflammatory protein complex from neutrophils with a broad apoptosis-inducing activity. Biol Pharm Bull 26(6):753–760
Wang J, Cai Y, Hao Xu et al (2004) Expression of MRP14 gene is frequently down-regulated in Chinese human esophageal cancer. Cell Res 14(1):46–53
Roesch Ely M, Nees M, Karsai S et al (2005) Transcript and proteome analysis reveals reduced expression of calgranulins in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cell Biol 84(2–3):431–444
Arai K, Teratani T, Kuruto-Niwa R et al (2004) S100A9 expression in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: S100A9 expression in adenocarcinoma is closely associated with poor tumour differentiation. Eur J Cancer 40(8):1179–1187
Arai K, Teratani T, Nozawa R et al (2001) Immunohistochemical investigation of S100A9 expression in pulmonary adenocarcinoma: S100A9 expression is associated with tumor differentiation. Oncol Rep 8(3):591–596
Ryckman C, Vandal K, Rouleau P et al (2003) Proinflammatory activities of S100: proteins S100A8, S100A9, and S100A8/A9 induce neutrophil chemotaxis and adhesion. J Immunol 170(6):3233–3242
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326(Pt 1):1–16
Haemmerlin G, Sträuli P (1981) In vitro motility of cells from human epidermoid carcinoma: a study by phase-contrast and reflection-contrast cinematography. Int J Cancer 27(5):603–610
Cramer LP, Mitchison TJ (1995) Myosin is involved in postmitotic cell spreading. J Cell Biol 131(1):179–189
John A, Tuszynski G (2001) The role of matrix metalloproteinases in tumor angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Pathol Oncol Res 7(1):14–23
Mitra A, Chakrabarti J, Chattopadhyay N et al (2003) Membrane-associated MMP-2 in human cervical cancer. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 22(2):93–100
Juuti A, Lundin J, Nordling S et al (2006) Epithelial MMP-2 expression correlates with worse prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Oncology 71(1-2):61–68
Shim KN, Jung SA, Joo YH et al (2007) Clinical significance of tissue levels of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 42(2):120–128
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30571939 and 10772007). We wish to thank Dr. Philippe A. Tessier of University of Laval, Quebec, Canada for providing vectors pET28a-S100A8 and pET28a-S100A9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30571939 and 10772007).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, F., Song, Y., Li, Z. et al. S100A8/A9 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis of CasKi Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 16, 353–360 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9225-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9225-2