Abstract
Purpose
The main aim of the present study was to formulate Donepezil Hydrochloride (DH)–loaded ethosomal intranasal gel to increase the transport of the drug through the blood–brain barrier (BBB), thus decreasing plasma fluctuation and also decreasing the oral side effects associated with the drug.
Methods
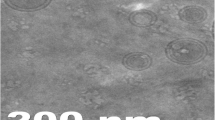
DH-loaded ethosomes were prepared by ethanol injection method. Nine ethosomal formulations were prepared containing three different concentrations of Phospholipon 90G and ethanol in combination and were evaluated for vesicle size, %entrapment efficiency, and drug content. The optimized ethosomal formulation was incorporated into the gelling base containing Poloxamer 407 (18%) and Poloxamer 188 (6%) as thermosensitive polymers and Carbopol 934 (0.1–0.5%) as mucoadhesive polymer. The prepared gels were further evaluated for gelation temperature, gelation time, drug content, mucoadhesive strength, viscosity, in vitro drug release, and ex vivo drug permeation study through the sheep nasal mucosa.
Results
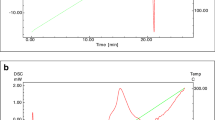
The optimized ethosomal formulation F4 showed a vesicle size of 110.06 ± 1.910 and a % entrapment efficiency of 70.02 ± 0.353. The mucoadhesive strength and gelation temperature were found to be 3332 ± 4.314 and 31.7 ± 0.033 in the case of optimized gel formulation. The in vitro and ex vivo drug permeation from the optimized gel formulation was almost 100% after a period of 24 h.
Conclusion
Formulated DH-loaded ethosomal intranasal gel could serve as the better alternative for the brain targeting via the intranasal route.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- DH:
-
Donepezil Hydrochloride
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s Disease
- CNS:
-
Central Nervous System
- KBr:
-
Potassium Bromide
- FTIR:
-
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
References
Harilal S, Jose J, Grace D, Parambi T, Kumar R, Elizabeth G. Advancements in nanotherapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease: current perspectives. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019.
Hansen RA, Gartlehner G, Webb AP, Morgan LC, Moore CG, Jonas DE. Efficacy and safety of donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine for the treatment of Alzheimer’ s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Interv Aging. 2008;3:211–25.
Jelic V, Darreh-shori T. Donepezil: a review of pharmacological characteristics and role in the management of Alzheimer disease. Clin Med Insights Ther. 2010;2:771–88.
Bryson HM, Benfield P. Donepezil : new drug profile. Drugs Aging. 1997;10:234–9.
Sozio P, Cerasa LS, Marinelli L, Di Stefano A. Transdermal donepezil on the treatment of Alzheimer’ s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2012;8:361–8.
Bragagni M, Mennini N, Maestrelli F, Cirri M, Bragagni M, Mennini N, et al. Comparative study of liposomes, transfersomes and ethosomes as carriers for improving topical delivery of celecoxib ethosomes as carriers for improving topical delivery of celecoxib. Drug Deliv. 2012;19:354–61.
Aggarwal D, Nautiyal U. Ethosomes: a review. Int J Pharm Med Res. 2016;4:354–63.
Raja Azalea D, Mohambed M, Joji S, Sankar C. Design and evaluation of chitosan nanoparticles as novel drug carriers for the delivery of donepezil. Iran J Pharm Sci. 2012;8:155–64.
Wang Z, Xiong G, Tsang WC, Schätzlein AG, Uchegbu IF. Nose-to-brain delivery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;370:593–601.
Shelke S, Shahi S, Jadhav K, Dhamecha D, Tiwari R, Patil H. Thermoreversible nanoethosomal gel for the intranasal delivery of eletriptan hydrobromide thermoreversible nanoethosomal gel for the intranasal delivery of eletriptan hydrobromide. J Mater Sci Mater Med. Springer US; 2016.
Shelke S, Pathan I, Shinde G, Agrawal G, Damale M, Chouthe R. Poloxamer-based in situ nasal gel of naratriptan hydrochloride deformable vesicles for brain targeting. Bionanoscience BioNanoScience. 2020;10:633–48.
Peram MR, Jalalpure S, Kumbar V, Patil S, Bhat K, Diwan P. Factorial design based curcumin ethosomal nanocarriers for the skin cancer delivery: in vitro evaluation. J Liposome Res [Internet]. Taylor & Francis. 2019;29:291–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/08982104.2018.1556292.
Shelke S, Shahi S, Jalalpure S, Dhamecha D. Poloxamer 407-based intranasal thermoreversible gel of zolmitriptan-loaded nanoethosomes: formulation, optimization, evaluation and permeation studies. J Liposome Res. 2016;1–11.
Joshi M, Bolmal U, Dandagi P. Formulation and evaluation of cefuroxime axetil sol gel for periodontits. Int J Pharm Sci. 2014;6:498–503.
Bhagya R. Formulation and characterization of atorvastatin ethosomal gel. J Drug Dev Deliv. 2018;1:13–20.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank KLE College of Pharmacy, Belagavi, Karnataka, for providing facilities to conduct this research work. The authors are also thankful to Wockhardt Research Centre, Aurangabad (Maharashtra, India), and Lipoid (Germany) for providing gift sample of donepezil hydrochloride and Phospholipon 90G respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have equal contribution to this research work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gangopadhyay, A., Dandagi, P.M. & Sutar, K.P. Development and Evaluation of Thermoreversible Ethosomal Gel of Donepezil Hydrochloride for Intranasal Delivery. J Pharm Innov 18, 238–246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-022-09636-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-022-09636-y