Abstract
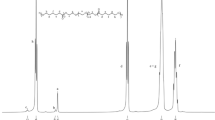
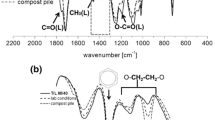
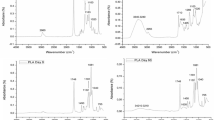
Polyesteramides based on ɛ-caprolactam and ɛ-caprolactone differing in the content of ester-amide structural units were subjected to biodegradation — composting in a big compost pile under controlled conditions (controlled composting) and in small composters at a steady temperature of 60 °C (isothermal composting). Both types of composting resulted in degradation of the polyesteramides depending on copolymer composition, isothermal composting being more robust. The contribution of abiotic hydrolysis to the degradation of polyesteramides was studied at 60 °C in buffer solutions with pH 5.4, 7.4 and 8.4. The prevailing effect of abiotic hydrolysis over biological one was shown at 60 °C. Ester bonds in polyestramide chains were preferentially cleaved; therefore, the scope of degradation increased with the content of ester units in the copolymer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AH:
-
abiotic hydrolysis
- CLA:
-
ɛ-caprolactam
- IC:
-
isothermal composting at 60 °C
- CC:
-
controlled composting
- CLO:
-
ɛ-caprolactone
- PEA:
-
poly(esteramide)
References
Cajthaml T., Bhatt M., Šašek V., Matějů V.: Bioremediation of PAH-contaminated soil by composting: a case study. Folia Microbiol. 47, 696–700 (2002).
Chromcová D., Bernášková A., Brožek J, Prokopová I., Roda J., Náhlík J., Šašek V.: Degradation of polyesteramides prepared by the anionic polymerization of ɛ-caprolactam in the presence of poly(ɛ-caprolactone). Polym.Degrad.Stab. 90, 546–554 (2005).
Chromcová D., Baslerová L., Roda J., Brožek J.: Polymerization of lactams. Preparation of polyesteramides by the anionic copolymerization of ɛ-caprolactam and ɛ-caprolactone. Eur.Polym.J. 44, 1733–1742 (2008).
Dubourguier H.C.: From laboratory to industrial scale: composting of polluted soils from former coal industry and gas plants: future research needs, pp. 267–283 in V. Šašek, J.A. Glaser, Ph. Baveye (Eds): The Utilization of Bioremediation to Reduce Soil Contamination: Problems and Solutions. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht-Boston-London 2003.
Fermor T.R., Smith J.F., Spencer D.M.: The microflora of experimental mushroom composts. J.Hortic.Sci. 54, 137–147 (1979).
Šašek V., Bhatt M., Cajthaml T., Malachová K., Lednická D.: Compost-mediated removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from contaminated soil. Arch.Environ.Contam.Toxicol. 44, 336–342 (2003).
Šašek V., Vitásek J., Chromcová D., Prokopová I., Brožek J., Náhlík J.: Biodegradation of synthetic polymers by composting and fungal treatment. Folia Microbiol. 51, 425–430 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brožek, J., Šašek, V., Prokopová, I. et al. Degradation of polyesteramides during composting under standard and isothermal conditions. Folia Microbiol 54, 451–456 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0063-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0063-0