Abstract
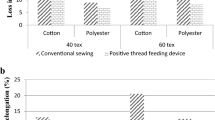
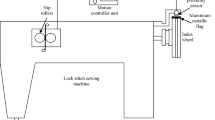
Sewing threads of different structures are analyzed for the loss in tensile properties of threads in sewing on a single needle lock stitch machine. The needle threads suffer greater loss in tensile properties than the bobbin threads in sewing, mainly due to abrasion at needle eye, which can cause structural damage to thread and fibre damage; both depend on the thread structure and inherent strength of fibres. The spun and core spun threads undergo both structural damage and rupture of surface fibres due to abrasion in sewing. The nylon filament threads, due to their better abrasion resistance suffer lesser loss in tenacity and breaking extension in sewing compared to polyester threads. The spun threads, having coarser fibres help in retaining the thread strength in sewing; whereas high tenacity filaments would be useful in the case of core spun and filament threads, Thread cyclic loading/dynamic tension on needle thread during sewing does not affect the strength of the threads under study significantly; however, it affects the initial modulus of few threads, especially the nylon and spun threads.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Sundaresan, P. K. Hari, and K. R. Salhotra, Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol., 9, 334 (1997).
R. M. Laing and C. Pearshouse, Text. Res. J., 57, 256 (1987).
G. Sundaresan, P. K. Hari, and K. R. Salhotra, Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol., 10, 64 (1998).
P. K. Hari, K. R. Salhotra, G. Sundaresan, and K. Chopra, “World Textile Conference”, University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, 1994.
A. Rudolf and J. Gersak, Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol., 13, 289 (2001).
R. M. Crow and N. H. Chamberlain, Clothing Institute Technological Report No. 21, The Clothing Institute, London, 1969.
J. Gersak, Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Tech., 7, 71 (1995).
J. Gersak and B. Knez, Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Tech., 3, 6 (1991).
M. J. Schick, Ed., “Surface Characteristics of Fibres and Textiles”, p.206, Marcel and Dekker Inc., New York, 1975.
G. Sundaresan, Ph.D. Dissertation, IIT Delhi, India, 1996.
G. Sundaresan, P. K. Hari, and K. R. Salhotra, J. Text. Inst., 89, 422 (1998).
Amefird, http://www.amefird.com/technical-tools/threadsize/ fabric-weight/ (2010).
Sunstar, KM 250 Series Sewing Machines, Sunstar Machinery Co. Ltd., Korea, 2005.
V. K. Midha, A. Mukhopadhyay, R. Chattopadhyay, and V. K. Kothari, Text. Res. J., 79, 1155 (2009).
V. K. Midha, A. Mukhopadhyay, R. Chattopadhyay, and V. K. Kothari, Text. Res. J., 80, 491 (2010).
J. W. S. Hearle, B. Lomas, and W. D. Cooke, “Atlas of Fibre Fracture and Damage to Textiles”, 2nd ed., Woodhead Publishing Limited, 1998.
Amefird, http://www.amefird.com/technical-tools/threadeducation/ thread-logic/, American & Efird Inc., 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samuel Wesley, D., Rengasamy, R.S. Changes in tensile properties of needle thread in lock stitch sewing. Fibers Polym 18, 390–399 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-1026-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-1026-8