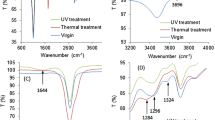
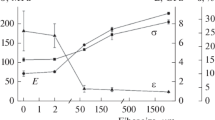
Abstract
For nearly half a century textile prostheses have been intensively used in vascular surgery. They have saved millions of human lives, but they are not yet perfect. Graft failures have been, in part, attributed to the prostheses finishing processes, generally based on thermal treatments. These treatments permit to reduce fabric porosity and fix the wavy form of prosthetic tube walls involved by crimping process. Four tubular fabrics have been woven with different polyethylene terephthalate (PET) yarns spun under different industrial processes: Setila, Dacron, Diolen and Viscosuisse. Three heat setting techniques were investigated for prostheses crimping: dry heat, vapor heat and autoclaving. Crystallinity index and crystal growth in the equatorial directions have been calculated from Wide Angle X-ray Scattering scans. The aim was to analyze physical structural changes of PET fibers after thermal finishing processes applied to textile vascular prostheses and highlight fiber morphological evolutions related to these treatments. Viscosuisse yarns held the largest crystalline domains built up of numerous crystals but smaller than Dacron ones. However, the best crystalline configurations for the overall yarns were generally obtained for dry heat processes. Compromise regions of treatment conditions for prosthetic Dacron tubes were also obtained to optimize crystal development for the different crimping processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Voorhees, J. A. Jaretzki, and A. H. Blakemore, Ann. Surg., 135, 332 (1952).
E. Michael, Artif. Organs, 32, 661 (2008).
C. D. Etz, T. Homann, D. Silovitz, C. A. Bodian, M. Luehr, G. D. Luozzo, K. A. Plestis, and R. B. Griepp, Ann. Thorac. Surg., 84, 1206 (2007).
S. Ben Abdessalem, B. Durand, S. Akesbi, N. Chakfe, and J.-G. Kretz, J. Text. Inst., 96, 117 (2005).
N. Blanchemain, T. Laurent, F. Chai, C. Neut, S. Haulon, V. Krump-Konvalinkova, M. Morcellet, B. Martel, C. J. Kirkpatrick, and H. F. Hildebrand, Acta Biomater., 4, 1725 (2008).
A. Cardon, N. Chakfe, F. Thaveau, E. Gagnon, O. Hartung, S. Aillet, Y. Kerdiles, Y.-M. Dion, J.-G. Kretz, and C.-J. Doillon, Ann. Vasc. Surg., 14, 543 (2000).
N. Yasuharu, Y. Yoshihisa, O. Takafumi, T. Yasuko, and T. Eiji, Jap. J. Artif. Organs, 28, 547 (1999).
M. W. King, Z. Zhang, and R. Guidoin, J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag., 1, 1 (2001).
“Medical”, Technical Usage Textiles A., 40, 36 (2001).
K. Berger and L. R. Sauvage, Ann. Surg., 193, 477 (1981).
N. Lheureux, L. Germain, R. Labbe, and F. Auger, J. Vasc. Surg., 17, 499 (1993).
L. E. Niklason, Science, 286, 1493 (1999).
R. Smeets, A. Bozkurt, M. S. Harwoko, U. Wiesemann, C. Apel, F. Budillon, T. Gries, D. Riediger, and M. Wöltie, Technical Textiles, 3, 27 (2005).
H. Van Damme, M. Deprez, E. Creemers, and R. Limet, Acta Chir. Belg., 105, 249 (2005).
S. Ben Abdessalem, I. Zbali, N. Litim, and S. Mokhtar, Iranian Polym. J., 18, 15 (2009).
R. Guidoin, M. King, X. Deng, E. Paris, and Y. Douville, Rev. Eur. Biomed. Tech., 4, 13 (1982).
M. Feldstein and B. Pourdeyhimi, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 9, 1061 (1990).
B. Pourdeyhimi and C. Text, J. Biomater. Appl., 2, 163 (1987).
B. Pourdeyhimi, Text. Prog., 15, 1 (1986).
M. S. Ellison, P. E. Lopes, and W. T. Pennington, J. Engineered Fibers Fabrics, 3, 10 (2008).
S. K. Mukhopadhyay, E. M. O. Bebbington, and P. W. Foster, Text. Res. J., 62, 403 (1992).
M. Azaiez, I. Zbali, and S. Ben Abdessalem, Iranica J. Energy & Environ., 2, 79 (2011).
H. Khlif, S. Ben Abdessalem, S. Dhouib, and F. Sakli, Trends Applied Sci. Res., ISSN 1819-3579 / DOI 10.3923/tasr.2011, 2011.
H. Khlif and S. Ben Abdessalem, Res. J. Text. Appar., 15, 2011.
BASF, “Dyeing and Finishing of Polyester Fibers”, pp.138–141, BASF Editions, Germany, 1990.
H. M. Heuvel and R. Huisman, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 22, 2229 (1978).
M. Sotton, A. M. Arniaud, and C. Rabourdin, ITF Scientific Bulletin, 7, 265 (1978).
V. B. Gupta and S. Kumar, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 26, 1865 (1981).
J. Radhakrishnan, U. P. Kanitkar, and V. B. Gupta, J. Society Dyers & Colourists, 113, 59 (1997).
P. L. Davies, U. Gather, M. Meise, D. Mergel, and T. Mildenberger, Ann. Appl. Stat., 2, 861 (2008).
V. B. Gupta, J. Text. Inst., 86, 299 (1995).
R. Huisman and H. M. Heuvel, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 37, 595 (1989).
I. Zbali, Ph. D. Dissertation, University of Haute Alsace, France, 2004.
C. Le Clerc, Ph. D. Dissertation, University of Paris Mines, France, 2006.
F. Dieval, D. Mathieu, and B. Durand, Text. Res. J., 73, 200 (2003).
F. Dieval, D. Mathieu, and B. Durand, J. Text. Inst., 95, 131 (2004).
G. Vassilatos, “Dynamics, Structure Development and Fiber Properties in High-Speed Spinning of Polyethylene Terephthalate” in “High Speed Fiber Spinning” (A. Ziabicki and H. Kawai Eds.), pp.421–423, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1985.
J. Gacen, J. M. Canal, A. Naik, and F. Bernal, ITF Scientific Bulletin, 14, 35 (1985).
K. V. Datye and A. A. Vaidya, “Chemical Processing of Synthetic Fibers and Blends”, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1984.
R. Huisman and H. M. Heuvel, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 22, 943 (1978).
M. P. W Wilson, Polymer, 15, 277 (1974).
P. Bouriot, J. Jacquemart, and M. Sotton, ITF Scientific Bulletin, 6, 9 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khlif, H., Dhouib, S., Ben Abdessalem, S. et al. The impacts of thermal treatments on the physical properties of textile vascular prostheses. Fibers Polym 13, 68–78 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0068-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0068-1