Abstract
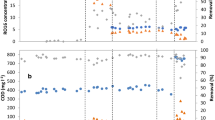
Complete mineralization of dye effluent was realized through sequential anaerobic followed by aerobic processes. The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the degradation of wastewater of four remazol dyes with integrated anaerobic/aerobic (SBR1) and aerobic (SBR2) processes under sequencing batch reactor operation. The ORP profiles show that the SBR1 was in anaerobic condition during the 15 h React mode and turned to aerobic condition through air aeration for 3 h. The SBR1 and SBR2 achieved almost similar performance in the removal of organic compounds with average 95% COD removal. The SBR1 performed better in the color removal with 93% removal efficiency while the SBR2 only attained 50% removal efficiency. The biodegradation rate of the remazol dyes was well described by the first-order kinetic model with the sequence degradation rate remazol pink > remazol violet > remazil yellow > remazol green.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonakdarpour B, Vyrides I, Stuckey DC (2011) Comparison of the performance of one stage and two stage sequential anaerobic–aerobic biological processes for the treatment of reactive-azo-dye-containing synthetic wastewaters. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65(4):591–599
Carliell CM, Barclay SJ, Naidoo N, Buckley CA, Mulholland DA, Senior E (1995) Microbial decolourasition of a reactive azo dye under anaerobic conditions. Water SA 21(1):61–69
Chu HC, Chen KM (2002) Reuse of activated sludge biomass: II. The rate processes for the adsorption of basic dyes on biomass. Process Biochem 37(10):1129–1134
El-Sheekh MM, Farghl AA, Galal HR, Bayoumi HS (2016) Bioremediation of different types of polluted water using microalgae. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 27(2):401–410
El-Zaher EHFA, Abou-Zeid AM, Mostafa AA, Arif DM (2016) Industrial oil wastewater treatment by free and immobilized Aspergillus niger KX759617 and the possibility of using it in crop irrigation. Rend Fis Acc Lincei. doi:10.1007/s12210-016-0578-7
Gnanapragasam G, Senthilkumar M, Arutchelvan V, Velayutham T, Nagarajan S (2011) Bio-kinetic analysis on treatment of textile dye wastewater using anaerobic batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 102(2):627–632
Işık M, Sponza DT (2006) Biological treatment of acid dyeing wastewater using a sequential anaerobic/aerobic reactor system. Enzyme Microb Technol 38(7):887–892
Khalid A, Arshad M, Crowley DE (2009) Biodegradation potential of pure and mixed bacterial cultures for removal of 4-nitroaniline from textile dye wastewater. Water Res 43(4):1110–1116
Ong SA, Toorisaka E, Hirata M, Tadashi H (2008) Combination of adsorption and biodegradation processes for textile effluent treatment using a granular activated carbon-bioflm confgured packed column system. J Environ Sci 20(8):952–956
Ong SA, Ho LN, Wong YS, Raman K (2012) Performance and kinetic study on bioremediation of diazo dye (reactive black 5) in wastewater using spent GAC-biofilm sequencing batch reactor. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(4):1615–1623
Ong SA, Ho LN, Wong YS, Komalathevi R, Bahari R (2013) Mineralization of Methyl Orange-containing wastewater by integrated anaerobic and aerobic processes using spent granular activated carbon-biofilm under sequencing batch reactor operation. Desalination Water Treat 51(13–15):2813–2819
Sirianuntapiboon S, Srisornsak P (2007) Removal of disperse dyes from textile wastewater using bio-sludge. Biores Technol 98(5):1057–1066
Sirianuntapiboon S, Sadahiro O, Salee P (2007) Some properties of a granular activated carbon-sequencing batch reactor (GAC-SBR) system for treatment of textile wastewater containing direct dyes. J Environ Manage 85(1):162–170
Spagni A, Grilli S, Casu S, Mattioli D (2010) Treatment of a simulated textile wastewater containing the azo-dye reactive orange 16 in an anaerobic-biofilm anoxic–aerobic membrane bioreactor. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 64(7):676–681
Sponza DT, Işık M (2004) 0. Decolorization and inhibition kinetic of Direct Black 38 azo dye with granulated anaerobic sludge. Enzyme Microb Technol 34(2):147–158
Suthersan SS (2002) Natural and enhanced remediation systems. Acradis, Lewis Publisher, Washington, DC
Van der Zee EP, Lettinga G, Field JA (2001) Azo dye decolorization by anaerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 44:1169–1176
Venkata Mohan S, Chandrasekhara Rao N, Sarma PN (2007) Simulated acid azo dye (Acid black 210) wastewater treatment by periodic discontinuous batch mode operation under anoxic–aerobic–anoxic microenvironment conditions. Ecol Eng 31(4):242–250
Wijetunga S, Li XF, Jian C (2010) Effect of organic load on decolourization of textile wastewater containing acid dyes in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. J Hazard Mater 177(1–3):792–798
Yaacob NS, Mohamad R, Ahmad SA, Abdullah H, Ibrahim AL, Ariff AB (2016) The influence of different modes of bioreactor operation on the efficiency of phenol degradation by Rhodococcus UKMP-5M. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 27(4):749–760
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ong, SA., Ho, LN., Wong, YS. et al. Comparative study on the biodegradation of mixed remazol dyes wastewater between integrated anaerobic/aerobic and aerobic sequencing batch reactors. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 28, 497–501 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-017-0622-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-017-0622-2