Abstract
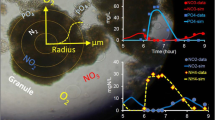
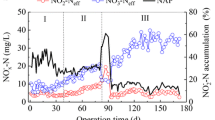
In this study, the characteristics partial nitrifying biomass in the Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) for aerobic granulation was investigated based on experiments and simulation modeling. The reactor operation was carried out at high concentration of ammonium (200~850 mg N/L) which favored Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB) growth over Nitrite-Oxidizing Bacteria (NOB) growth. In partial nitrifying granulation, both Free Ammonia (FA) and Free Nitrous Acid (FNA) simultaneously influenced the activity of NOB much more than that of AOB. According to the simulation results, thE Dissolved Oxygen (DO) concentration and oxygen affinity affect the growth competition and can influence the species that are predominant in the reactor. Both AOB and NOB can have growth potential under toxicants (FA and FNA) inhibition and limited oxygen condition. The AOB growth forms inner part of granule’s biofilm, but the NOB growth does not engage in the formation of granules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav, S. S., Lee, D. J., Show, K. Y., and Tay, J. H. (2008). “Aerobic granular sludge: Recent advances.” Biotechnol. Adv., Vol. 26, No. 5, pp. 411–423, DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.05.002.
Anthonisen, A. C., Loehr, R. C., Prakasam, T. B. S., and Srinath, E. G. (1976). “Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous-acid.” J. Water. Pollut. Control. Fed., Vol. 48, No. 5, pp. 835–852.
APHA (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st ed. American Public Health Association, Washington DC, USA.
Belmonte, M., Vazquez-Padin, J. R., and Figueroa, M. (2009). “Characteristics of nitrifying granules developed in an air pulsing SBR.” Process. Biochem., Vol. 44, No. 5, pp. 602–606, DOI: 10.1016/j.procbio.2009.02.019.
Beun, J. J., Hendriks, A., Van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., Morgenroth, E., Wilderer, P. A., and Heijnen, J. J. (1999). “Aerobic granulation in a sequencing batch reactor.” Water Res., Vol. 33, No. 10, pp. 2283–2290, DOI: 10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00463-1.
Blackburne, R., Yuan, Z., and Keller, J. (2008). “Partial nitrification to nitrite using low dissolved oxygen concentration as the main selection factor.” Biodegrad., Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 303–312, DOI: 10.1007/s10532-007-9136-4.
Cui, F., Lee, S., and Kim, M. (2011). “Removal of organics and nutrients from food wastewater using combined thermophilic two-phase anaerobic digestion and shortcut biological nitrogen removal.” Water Res., Vol. 45, No. 16, pp. 5279–5286, DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2011. 07.030.
Cui, F., Park, S., and Kim, M. (2014). “Characteristics of aerobic granulation at mesophilic temperatures in wastewater treatment.” Bioresour. Technol., Vol. 151, pp. 78–84, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.025.
Hellinga, C., Schellen, A. A. J. C., Mulder, J. W., van Loosdrechet, M. C. M., and Heijnen, J. J. (1998). “The SHARON process: An innovative method for nitrogen removal from ammonia-rich wastewater.” Water. Sci. Technol., Vol. 37, No. 9, pp. 135–142, DOI: 10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00281-9.
Li, A. J., Li, X. Y., Quan, X. C., and Yang, Z. F. (2013). “Aerobic sludge granulation for partial nitrification of ammonia-rich inorganic wastewater.” Environ. Eng. Manag. J., Vol. 12, No. 7, pp. 1375–1380.
Liu, Q. S., Tay, J. H., and Liu, Y. (2003). “Substrate concentrationindependent aerobic granulation in sequential aerobic sludge blanket reactor.” Environ. Technol., Vol. 24, No. 10, pp. 1235–1242, DOI: 10.1080/09593330309385665.
Liu, Y. and Tay, J. H. (2004). “State of the art of biogranulation technology for wastewater treatment.” Biotechnol. Adv., Vol. 22, No. 7, pp. 533–563, DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2004.05.001.
Mosquera-Corral, A., Gonzalez, F., Campos, J. L., and Mendez, R. (2005). “Partial nitrification in a SHARON reactor in the presence of salts and organic carbon compounds.” Process. Biochem., Vol. 40, No. 9, pp. 3109–3118, DOI: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.03.042.
Nielsen, P. H. (1996). “Adsorption of ammonia to activated sludge.” Water Res., Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 762–764, DOI: 10.1016/0043-1354(95)00222-7.
Okabe, S., Oshiki, M., Takahashi, Y., and Satoh, F. (2011). “Development of long-term stable partial nitrification and subsequent anammox process.” Bioresour. Technol., Vol. 102, No. 13, pp. 6801–6807, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.011.
Pambrun, V., Paul, E., and Spérandio, M. (2006). “Modelling the partial nitrification in sequencing batch reactor for biomass adapted to high ammonia concentrations.” Biotechnol. Bioeng., Vol. 95, No. 1, pp. 120–131, DOI: 10.1002/bit.21008.
Park, S. and Bae, W. (2009). “Modeling kinetics of ammonium oxidation and nitrite oxidation under simultaneous inhibition by free ammonia and free nitrous acid.” Process Biochem., Vol. 44, No. 6, pp. 631–640, DOI: 10.1002/bit.21008.
Peng, D., Bernet, N., Delgenes, J. P., and Moletta, R. (1999). “Aerobic granular sludge-A case report.” Water Res., Vol. 33, No. 3, pp. 890–893, DOI: 10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00443-6.
Ruiz, G., Jeison, D., and Chamy, R. (2003). “Nitrification with high nitrite accumulation for the treatment of wastewater with high ammonia concentration.” Water Res., Vol. 37, No. 6.pp. 1371–1377, DOI: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00475-X.
Schmidt, I., Sliekers, O., Schmid, M., Bock, E., Fuerst, J., Kuenen, J. G., Jetten, M. S. M., and Strous, M. (2003). “New concepts of microbial treatment processes for the nitrogen removal in wastewater.” FEMS Microbiol. Rev., Vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 481–492, DOI: 10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00039-1.
Sinha, B. and Annachhatre, A. P. (2007). “Partial nitrification-operational parameters and microorganisms involved.” Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol., Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 285–313, DOI: 10.1007/s11157-006-9116-x.
Song, Y., Ishii, S., Rathnayake, L., Ito, T., Satoh, H., and Okabe, S. (2013). “Development and characterization of the partial nitrification aerobic granules in a sequencing batch airlift reactor.” Bioresour. Technol., Vol. 139, pp. 285–291, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.018.
Tsuneda, S., Ejiri, Y., Nagano, T., and Hirata, A. (2004). “Formation mechanism of nitrifying granules observed in an Aerobic Upflow Fluidized Bed (AUFB) reactor.” Water. Sci. Technol., Vol. 49, No. 11–3, pp. 27–34, DOI: 10.1007/s10098-011-0355-3.
Tsuneda, S., Nagano, T., Hoshino, T., Ejiri, Y., Noda, N., and Hirata, A. (2003). “Characterization of nitrifying granules produced in an aerobic upflow fluidized bed reactor.” Water Res., Vol. 37, No. 20, pp. 4965–4973, DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2003.08.017.
Van der Star, W. R. L., Abma, W. R., Bolmmers, D., Mulder, J., Tokutomi, T., Strous, M., Picioreanu, C., and van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. (2007). “Startup of reactors for anoxic ammonium oxidation: Experiences from the first full-scale Anammox reactor in Rotterdam.” Water Res., Vol. 41, No. 18, pp. 4149–4163, DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.03.044.
Van Dongen, U., Jetten, M. S. M., and van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. (2001). “The SHARON((R))-Anammox((R)) process for treatment of ammonium rich wastewater.” Water Sci. Technol., Vol. 44, No. 1, pp. 153–160, DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00047.
Van Hulle, S. W. H., Vandeweyer, H. J. P., Meesschaert, B. D., Vanrolleghem, P. A., Dejans, P., and Dumoulin, A. (2010). “Engineering aspects and practical application of autotrophic nitrogen removal from nitrogen rich streams.” Chem. Eng. J., Vol. 162, No. 1, pp. 1–20, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.05.037.
Villaverde, S., Fdz-Polanco, F., and Garcia, P. A. (2000). “Nitrifying biofilms acclimation to free ammonia in submerged biofilters: Start-up influence.” Water Res., Vol. 34, No. 2, pp. 602–610, DOI: 10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00175-X.
Wan, C. L., Sun, S. P., Lee, D. J., Liu, X., Wang, L., Yang, X., and Pan, X. L. (2013). “Partial nitrification using aerobic granules in continuousflow reactor: Rapid startup.” Bioresour. Technol., Vol. 142, pp. 517–522, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.120.
Wang, X. H., Jiang, L. X., Shi, Y. J., Gao, M. M., Yang, S., and Wang, S. G. (2012). “Effects of step-feed on granulation processes and nitrogen removal performances of partial nitrifying granules.” Bioresour. Technol., Vol. 123, pp. 375–381, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.07.080.
Wiesmann, U. (1994). “Biological nitrogen removal from wastewater. In: Fiechter., A., editor. Advanced in biochemical engineering/biotechnology.” Berlin: Springer-Verlag Berling Heidelberg, Vol. 5, pp. 113–154.
Wilen, B. M., Gapes, D., and Keller, J. (2004). “Determination of external and internal mass transfer limitation in nitrifying microbial aggregates.” Biotechnol. Bioeng., Vol. 86, No. 4, pp. 445–457, DOI: 10.1002/bit.20058.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, F., Park, S., Mo, K. et al. Experimentation and mathematical models for partial nitrification in aerobic granular sludge process. KSCE J Civ Eng 21, 127–133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0506-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0506-5