Abstract
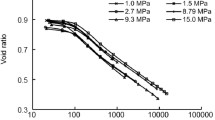
Ultra-soft soils have high water content, low strength, and high compressibility. Staged preloading has been commonly used in China to improve ultra-soft soils during land reclamation before highways and other structures are constructed. In this study, seven series of one-dimensional consolidation tests were performed on undisturbed, remolded, or reconstituted specimens of three types of soils subjected to simulated, staged loading. Test results showed that the compression curves had two straight lines, which intersected at a yield stress. Burland’s concept of the intrinsic compression line was adopted to present the compression curves of reconstituted clays at different initial water contents. The intrinsic compression line was modified to better fit the test data for the stresses lower than 40 kPa. The coefficient of soil consolidation increased with an increase of the effective vertical stress as a result of the rate of increase in constrained modulus higher than that of decrease in permeability. The maximum coefficient of secondary consolidation, Cámax, was correlated with the ratio of the initial void ratio to the void ratio at yield stress by a unique curve, which was proposed to distinguish the pre-yield stress from the post-yield stress state. Test results showed that the secondary compression characteristics depended on the applied stress and the initial void ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berilgen, S. A., Berilgen, M. M., and Ozaydin, I. K. (2006). “Compression and permeability relationships in high water content clays.” Applied Clay Science, Vol. 31, Nos. 3–4, pp. 249–261, DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2005.08.002.
Bo, M. W., Arulrajah, A., and Choa, V. (1997). “Large deformation of slurry-like soil.” Deformation and Progressive Failure in Geomechanics, Asaoka, A., Adachi, T, and Oka, F. (eds.), Balkema, pp. 437–442.
Bo, M. W., Choa, V., Wong, K. S., and Arulrajah, A. (2011). “Laboratory validation of ultra-soft soil deformation model.” Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 65–74, DOI: 10.1007/s10706-010-9351-3.
Bo, M. W., Wong, K. S., and Choa, V. (2008). “Constant rate of displacement test on ultra-soft soil.” Geotechnical Engineering, Vol. 161, pp. 129–135, DOI: 10.1680/geng.2008.161.3.129.
Burland, J. B. (1990). “On the compressibility and shear strength of natural clays.” Geotechnique, Vol. 40, No. 3, pp. 329–378. DOI: 10.1680/geot.1990.40.3.329.
Cao, Y. P. (2007). “Relationship of Coefficients of secondary consolidation with moisture content of saturated cohesive soil.” China Harbor Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 3, pp. 21–23, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2007.03.006.
Cao, Y. H., Li, W., and Liu, T. Y. (2011). “Surface-layer improvement technology for ultra soft soil by vacuum preloading.” Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering (supplement), Vol. 33, No. 1, pp. 234–238.
Casagrande, A. and Fadum, R. E. (1940). “Notes on soil testing for engineering purpose.” Harvard Soil Mechanics Series, Cambridge Massachusetts: Harvard University, Graduate School of Engineering, Vol. 8, pp. 36–39.
Cheng, Y. X., Du, D. J., and Li, Z. L. (2011). “The structural constitution of hydraulic fill in Tianjin Binhai New Area.” Journal of Engineering Geology, Vol. 19, No. Suppl, pp. 256–260.
Chu, J., Bo, M. W., and Choa, V. (2006). “Improvement of ultra-soft soil using prefabricated vertical drains.” Geotextiles and Geomembranes, Vol. 24, No. 6, pp. 339–348, DOI: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2006.04.004.
Dong, Z. L., Zhang, G. X., Zhou, Q., Luo, Y., Qiu, Q. C., and Li, Y. (2011). “Research and application of improvement technology of shallow ultra-soft soil formed by hydraulic reclamation in Tianjin Binhai new area.” Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, Vol. 30, No. 5, pp. 1073–1080.
Duncan, J. M. (1993). “Limitation of conventional analysis of consolidation settlement.” Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, Vol. 119, No. 9, pp. 1333–1359, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1993)119:9(1333).
Fox, P. J. and Baxter, C. D. P. (1997). “Consolidation properties of soil slurries from hydraulic consolidation test.” Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, Vol. 123, No. 8, pp. 770–776, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1997)123:8(770).
Gao, Y. B., Zhu, H. H., Ye, G. B., and Xu, C. (2004). “The investigation of the coefficient of secondary compression Ca in odometer tests.” Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 459–463, DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.04.006.
Gao, Z. Y., Zhang, M. Y., and Liu, L. Y. (2000). “Laboratory model test of vacuum preloading in combination with electro-osmotic consolidation.” China Harbor Engineering, Vol. 10, No. 5, pp. 58–61, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3688.2000.05.014.
Gibson, R. E., England, G. L., and Hussey, M. J. L. (1967). “The theory of one-dimensional consolidation of saturated clays.” Geotechnique, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 261–273, DOI: 10.1680/geot.1967.17.3.261.
Hong, Z. and Tsuchida, T. (1999). “On compression characteristics of Ariake clays.” Canadian Geotechnical Journal, Vol. 36, No. 5, pp. 807–814, DOI: 10.1139/t99-058.
Hong, Z. S, Zeng, L. L., Cui, Y. J., Cai, Y. Q., and Lin, C. (2012). “Compression behaviour of natural and reconstituted clays.” Geotechnique, Vol. 62, No. 4, pp. 291–301, DOI: 10.1680/geot.10.P.046.
Hong, Z., Shen, S., Deng, Y., and Negami, T. (2007). “Loss of soil structure for natural sedimentary clays.” Geotechnical Engineering, Vol. 160, No. 3, pp. 153–159, DOI: 10.1680/geng.2007.160.3.153.
Hong, Z.-S., Yin, J., and Cui, Y.-J. (2010). “Compression behavior of reconstructed soils at high initial water contents.” Geotechnique, Vol. 60, No. 9, pp. 691–700, DOI: 10.1680/geot.09.P.059.
Huerta, A., Kriegsmann, G. A., and Krizek, R. J. (1988). “Permeability and compressibility of slurries from seepage-induced consolidation.” Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, Vol. 114, No. 5, pp. 614–627, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1988)114:5(614).
Kamon, M., Gu, H. D., and Masahiro, I. (2001). “Improvement of mechanical properties of ferrum lime stabilized soil with the addition of aluminum sludge.” Materials Science Research International, Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 47–53, DOI: 10.2472/jsms.50.3Appendix_47.
Kenneth, W. and Cargill, M. (1984). “Prediction of consolidation of very soft soil.” Journal Geotechnical Engineering, Vol. 110, No. 6, pp. 775–795, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1984)110:6(775).
Lei, H. Y. and Xiao, S. F. (2002). “Study on secondary-consolidation deformation characteristics of soft soil in Tianjin.” Journal of Engineering Geology, Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 385–389, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2002.04.007.
Ling, P., Xu, Z. H., and Zeng, L. S. (2003). “Research on coefficient of consolidation of soft clay under compression.” Rock and Soil Mechanics, Vol. 24, No. 1, pp. 106–108, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2003.01.018.
Liu, P. H., Wang, Q., and Dong, J. X. (2005). “Microstructure experimental investigation of indoor reinforced dredger fill.” Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 21–23, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.04.006.
Liu, Y., Wang, Q., and Xiao, D. F. (2003b). “The comparative research on fundamental properties of dredger fill in different areas.” Geotechnical Engineering Technique, Vol. 4, No. 00, pp. 197–200. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2003.04.003.
Liu, Y., Xiao, S. F., and Wang, Q. (2003a). “Mechanism analysis of increase in structural strength of solidified dredger fill.” Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), Vol. 31, No. 11, pp. 1295–1298. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2003.01.018.
Mesri, G. and Feng, T. W. (1991). “Surcharging to reduce secondary settlements.” Proceedings, International Conference on Geotechnical Engineering for Coastal Development, Yokohama, Vol. 1, No. 00, pp. 359–364, DOI: 10.1016/0148-9062(93)90902-P.
Mikasa, M. (1963). The consolidation of soft clay — a new consolidation theory and its application, Kajima Institution Publishing Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan.
Miller, P. G. and Tsugawa, P. R. (2000). “Influence of soil type on stabilization with cement kiln dust.” Construction and Building Materials, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 89–97, DOI: 10.1016/S0950-0618(00)00007-6.
Ministry of Transportation, PRC (JTS147-1-2010) (2010). Code for soil foundations of ports, Beijing, China.
Mitchell, K. (1993). Fundamentals of Soil Behavior, 2nd edition. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons.
Nagaraj, T. S., Srinivasa, M. B. R., Vatsala, A., and Joshi, R. C. (1990). “Analysis of compressibility of sensitive soils.” Journal of Geotechnical Engineering Division, ASCE, Vol. 116, No. 1, pp. 105–118, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1990)116:1(105).
Qing, Y. S., Li, Z. Y., Cao, D. Z., Gu, L. J., and Sun, Y. J. (1999). “Consolidation of soft soil foundation by vacuum-pumping in low level position.” GeoScience, Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 471–477.
Shenbaga, R. K. and Havanagi, V. G. (1999). “Compressive strength of cement stabilized flyash-soil mixtures.” Cement and Concrete Research, Vol. 29, No. 5, pp. 673–677, DOI: 10.1016/S0008-8846(99)00018-6.
Sivapullaiah, P. V., Prashanth, J. P., Sridharan, A., and Narayana, B. V. (1998). “Reactive silica and strength of flashes.” Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, Vol. 16, No. 3, pp. 239–250, DOI: 10.1023/A:1008889326269.
Tang, Y. Q. and Zhou, L. Q. (2007). Environment Engineering Geology of Soft Soil, Transportation Press, Beijing.
Taylor, D. W. (1942), Research on Consolidation of Clays, Serial 85, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Cambridge: Depart. Of Civil and Sanitary Engineering.
Terzaghi, K. and Peck, R. B. (1967). Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice, John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Tohari, A., Nishigaki, M., and Komatsu M. (2007). “Laboratory rainfallinduced slope failure with moisture content measurement.” Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, Vol. 133, No. 5, pp. 575–587, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:5(575).
Weber, W. G. (1969). “Performance of embankments constructed over peat.” Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, ASCE 95(SM 1), pp. 53–76.
Wen, H. J. and Zhang, Y. X. (2002). “Analysis of mechanism of drain and consolidation of super soft soil.” Journal of Chongqing University, Vol. 25, No. 9, pp. 82–85, DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2002.09.023.
Wen, H. J., Yan, C. F., and Wang, D. Y. (1999). “Some engineering properties of the dredger fill.” Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University, Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 79–83, DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1674-4764.1999.02.017.
Yin, J. H. (1999). “Non-linear creep of soils in oedometer tests.” Geotechnique, Vol. 49, No. 5, pp. 699–707.
Yin, J. H. and Graham, J. (1996). “Elastic visco-plastic modelling of one-dimensional consolidation.” Geotechnique, Vol. 46, No. 3, pp. 515–527, DOI: 10.1680/geot.1996.46.3.515.
Yin, Z. Z., Zhang, H. B., Zhu, J. G., and Li, G. W. (2003). “Secondary consolidation of soft soil.” Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, Vol. 25, No. 5, pp. 521–526, DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2003.05.001.
Yu, X. J., Yin, Z. Z., and Dong, W. J. (2007). “Influence of load on secondary consolidation deformation of soft soils.” Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, Vol. 29, No. 6, pp. 913–916. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2007.06.021.
Zeng, L. L., Hong, Z. S., Cai, Y. Q., and Han, J. (2011). “Change of hydraulic conductivity during compression of undisturbed and remolded clays.” Applied Clay Science, Vol. 51, Nos. 1–2, pp. 86–93, DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.11.005.
Zeng, L. L., Hong, Z. S., Liu, S. Y., Zhang, D. W., and Du, Y. J. (2011). “A method for predicting deformation caused by secondary consolidation for naturally sedimentary structural clays.” Rock and Soil Mechanics, Vol. 32, No. 10, pp. 3136–3142, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.10.041.
Zhang, C. S. (2005). Study of the properties of deformation and consolidation of marine clay at shenzhen houhai Bay, PhD Dissertation, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry.
Zhang, M., Zhao, Y. M., Gong, L., and Hu, R. H. (2010). “Test study of coefficient of consolidation of fresh hydraulic fill ultra-soft in Shenzhen bay.” Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, Vol. 29, No. Supp.1, pp. 3157–3161.
Zhou, Q. J. and Chen, X. P. (2006). “Test study on properties of secondary consolidation of soft soil.” Rock and Soil Mechanics, Vol. 27, No. 3, pp. 404–408, DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.03.013.
Zhu, Y. T., Zheng, A. R., and Li, W. (2008). “Laboratory tests for the consolidation property of dredger fill in the Shenzhen area.” Journal of Hunan University, Vol. 35, No. 11, pp. 120–123.
Znidarcic, D. and Liu, J. C. (1989). “Consolidation characteristics determination for dredged materials.” Proc., 22nd Annual Dredging Seminar. for dredged Studies, Texas A&M Univ., College Station, Texas, pp. 45–65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, H., Wang, X., Chen, L. et al. Compression characteristics of ultra-soft clays subjected to simulated staged preloading. KSCE J Civ Eng 20, 718–728 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0343-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0343-y