Abstract
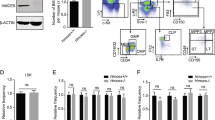
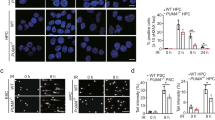
Dnmt1-associated protein 1 (Dmap1) is a core component of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex and the Swr1 chromatin-remodeling complex. However, the cellular function of Dmap1 remains largely unknown. We previously reported that Dmap1 plays a crucial role in DNA repair and is indispensable for the maintenance of chromosomal integrity of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. In this study, we examined the role of Dmap1 in self-renewing HSCs. Dmap1-knockdown induced by Dmap1-specific shRNA severely compromised the proliferative capacity of HSCs in vitro and long-term repopulating capacity of HSCs in recipient mice. Dmap1-knockdown in HSCs triggered DNA damage as evident by the formation of foci of γ-H2AX and activated p53-dependent cell cycle checkpoints. Deletion of p53 in HSCs abrogated the activation of p53-dependent cell cycle checkpoints, but did not restore the HSC function impaired by the knockdown of Dmap1. These findings suggest that Dmap1 is essential for the maintenance of genomic integrity of self-renewing HSCs and highlight DNA damage as one of the major stresses causing HSC depletion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Surani MA, Hayashi K, Hajkova P. Genetic and epigenetic regulators of pluripotency. Cell. 2007;128:747–62.
Morrison AJ, Shen X. Chromatin remodelling beyond transcription: the INO80 and SWR1 complexes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:373–84.
Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705.
Rountree MR, Bachmann KE, Baylin SB. DNMT1 binds HDAC2 and a new co-repressor, DMAP1, to form a complex at replication foci. Nat Genet. 2000;25:269–77.
Cai Y, Jin J, Tomomori-Sato C, et al. Identification of new subunits of the multiprotein mammalian TRRAP/TIP60-containing histone acetyltransferase complex. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:42733–6.
Conaway RC, Conaway JW. The INO80 chromatin remodeling complex in transcription, replication and repair. Trends Biochem Sci. 2009;34:71–7.
Boyer LA, Latek RR, Peterson CL. The SANT domain: a unique histone-tail-binding module? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:158–63.
Peterson CL, Côté J. Cellular machineries for chromosomal DNA repair. Genes Dev. 2004;18:602–16.
Auger A, Galarneau L, Altaf M, et al. Eaf1 is the platform for NuA4 molecular assembly that evolutionarily links chromatin acetylation to ATP-dependent exchange of histone H2A variants. Mol Cell Boil. 2008;28:2257–70.
Molofsky AV, Pardal R, Iwashita T, Park IK, Clarke MF, Morrison SJ. Bmi-1 dependence distinguishes neural stem cell self-renewal from progenitor proliferation. Nature. 2003;425:962–7.
Park IK, Qian D, Kiel M, et al. Bmi-1 is required for maintenance of adult self-renewing haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2003;423:302–5.
Iwama A, Oguro H, Masamitsu N, et al. Enhanced self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells mediated by the polycomb gene product Bmi-1. Immunity. 2004;21:843–51.
Negishi M, Saraya A, Miyagi S, et al. Bmi1 cooperates with Dnmt1-associated protein 1 in gene silencing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;353:992–8.
Negishi M, Chiba T, Saraya A, Miyagi S, Iwama A. DMAP1 is essential for the recruitment of PCNA to repair foci. Genes Cells. 2009;14:1347–57.
Rossi DJ, Jamieson CH, Weissman IL. Stems cells and the pathways to aging and cancer. Cell. 2008;132:681–96.
Rossi DJ, Seita J, Czechowicz A, Bhattacharya D, Bryder D, Weissman IL. Hematopoietic stem cell quiescence attenuates DNA damage response and permits DNA damage accumulation during aging. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:2371–6.
Nijnik A, Woodbine L, Marchetti C, et al. DNA repair is limiting for haematopoietic stem cells during ageing. Nature. 2007;449:288–91.
Osawa M, Hanada K, Hamada H, Nakauchi H. Long-term lymphohematopoietic reconstitution by a single CD34-low/negative hematopoietic stem cell. Science. 1996;273:242–5.
Sapountzi V, Logan IR, Robson CN. Cellular functions of TIP60. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38:1496–509.
Löbrich M, Jeggo PA. The impact of a negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer induction. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:861–9.
Srivastava N, Gochhait S, De Boer P, Bamezai RN. Role of H2AX in DNA damage response and human cancers. Mutat Res. 2009;681:180–8.
Murr R, Loizou JI, Yang YG, et al. Histone acetylation by Trrap-Tip60 modulates loading of repair proteins and repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:91–9.
Khanna KK, Jackson SP. DNA double-strand breaks: signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat Genet. 2001;27:247–54.
Fazzio TG, Huff JT, Panning B. An RNAi screen of chromatin proteins identifies Tip60-p400 as a regulator of embryonic stem cell identity. Cell. 2008;134:162–74.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Hiroyuki Miyoshi, RIKEN Bioresource Center for the CS-H1-shRNA-EF-1α-EGFP vector. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (#20052009) and the Global COE Program (Global Center for Education and Research in Immune System Regulation and Treatment), MEXT, Japan, a Grant-in-aid for Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST) from the Japan Science and Technology Corporation (JST) and a grant from the Takeda Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Koizumi, T., Negishi, M., Nakamura, S. et al. Depletion of Dnmt1-associated protein 1 triggers DNA damage and compromises the proliferative capacity of hematopoietic stem cells. Int J Hematol 91, 611–619 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0563-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0563-3