Abstract
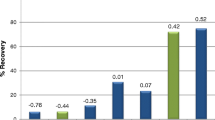
A rapid, sensitive, and reproducible high-performance liquid chromatographic procedure for the determination of nine biogenic amines in non-alcoholic beers was developed by an optimized benzoylation procedure. A Plackett–Burman factorial design was used in order to screen the statistically significant variables. The significant factors of biogenic amine benzoylation, reagent volume and pH, were optimized by a complete factorial response surface design, and optimal reaction conditions were generated. The optimized method showed good linearity (correlation coefficients > 0.997) and good recoveries (from 88.6 to 104.7 %). The repeatability and reproducibility of method were >3.9 and >4.6 %, respectively. Moreover, the detection limits of biogenic amines were calculated between 0.05 and 0.15 μg/ml in wine samples. The optimized method has been applied to the determination of biogenic amine contents of non-alcoholic beers consumed in Iran. Their values ranged from 0 to 2.56 mg/l, no significant differences (p > 0.05) were observed between the analyzed samples, and none of these samples surpass the toxic levels reported in the literature.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida C, Fernandes JO, Cunha SC (2012) A novel dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) method for the determination of eighteen biogenic amines in beer. Food Control 25(1):380–388
Branyik T, Silva DP, Baszczynski M, Lehnert R, Almeida e Silva JB (2012) A review of methods of low alcohol and alcohol-free beer production. J Food Eng 108(4):493–506
Chang W-Y, Wang C-Y, Jan J-L, Lo Y-SWu C-H (2012) Vortex-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with derivatization for the fluorometric determination of aliphatic amines. J Chromatogr A 1248:41–47
Costantini A, Cersosimo M, Del Prete V, Garcia-Moruno E (2006) Production of biogenic amines by lactic acid bacteria: screening by PCR, thin-layer chromatography, and high-performance liquid chromatography of strains isolated from wine and must. J Food Prot 69(2):391–396
De Borba BM, Rohrer JS (2007) Determination of biogenic amines in alcoholic beverages by ion chromatography with suppressed conductivity detection and integrated pulsed amperometric detection. J Chromatogr A 1155(1):22–30
De Mey E, Drabik-Markiewicz G, De Maere H, Peeters MC, Derdelinckx G, Paelinck H, Kowalska T (2012) Dabsyl derivatisation as an alternative for dansylation in the detection of biogenic amines in fermented meat products by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem 130(4):1017–1023
Favaro G, Pastore P, Saccani G, Cavalli S (2007) Determination of biogenic amines in fresh and processed meat by ion chromatography and integrated pulsed amperometric detection on Au electrode. Food Chem 105(4):1652–1658
Fernandes JO, Ferreira MA (2000) Combined ion-pair extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of diamines, polyamines and aromatic amines in Port wine and grape juice. J Chromatogr A 886(1–2):183–195
Goria M, Beatriz AIzquierdo-Pulido M (1999) Levels and significance of biogenic amines in Brazilian beers. J Food Compos Anal 12(2):129–136
Hernández-Cassou S, Saurina J (2011) Derivatization strategies for the determination of biogenic amines in wines by chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques. J Chromatogr B 879(17–18):1270–1281
Hernández-Orte P, Peña-Gallego A, Ibarz MJ, Cacho J, Ferreira V (2006) Determination of the biogenic amines in musts and wines before and after malolactic fermentation using 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate as the derivatizing agent. J Chromatogr A 1129(2):160–164
Hornero M, Ndez D, Garrido F, Ndez A (1997) Rapid high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of biogenic amines in fermented vegetable brines. J Food Prot 60(4):414–419
Hwang D-F, Chang S-H, Shiua C-YTuu-jyi C (1997) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of biogenic amines in fish implicated in food poisoning. J Chromatogr B 693(1):23–30
Kalac P, Hlavata V, Krizek M (1997) Concentrations of five biogenic amines in Czech beers and factors affecting their formation. Food Chem 58(3):209–214
Kelly MT, Blaise ALarroque M (2010) Rapid automated high performance liquid chromatography method for simultaneous determination of amino acids and biogenic amines in wine, fruit and honey. J Chromatogr A 1217(47):7385–7392. doi:7310.1016/j.chroma.2010.7309.7047
Keow CM, Abu Bakar F, Salleh AB, Heng LY, Wagiran R, Bean LS (2007) An amperometric biosensor for the rapid assessment of histamine level in tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon) spoilage. Food Chem 105(4):1636–1641
Kovács Á, Simon-Sarkadi L, Ganzler K (1999) Determination of biogenic amines by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 836(2):305–313
Křı́žek M, Pelikánová T (1998) Determination of seven biogenic amines in foods by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. J Chromatogr A 815(2):243–250
Kung H-F, Chien L-T, Liao H-J, Lin C-S, Liaw E-T, Chen W-CTsai Y-H (2008) Chemical characterisation and histamine-forming bacteria in salted mullet roe products. Food Chem 110(2):480–485
Lange J, Thomas K, Wittmann C (2002) Comparison of a capillary electrophoresis method with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of biogenic amines in various food samples. J Chromatogr B 779(2):229–239
Lapa-Guimarães J, Pickova J (2004) New solvent systems for thin-layer chromatographic determination of nine biogenic amines in fish and squid. J Chromatogr A 1045(1–2):223–232
Lasekan OO, Lasekan WO (2000) Biogenic amines in traditional alcoholic beverages produced in Nigeria. Food Chem 69(3):267–271
Lavizzari T, Teresa Veciana-Nogués M, Bover-Cid S, Mariné-Font A, Carmen Vidal-Carou M (2006) Improved method for the determination of biogenic amines and polyamines in vegetable products by ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1129(1):67–72
Lee S, Eom H-S, Yoo M, Cho Y, Shin D (2011) Determination of biogenic amines in Cheonggukjang using ultra high pressure liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Food Sci Biotechnol 20(1):123–129
Lonvaud-Funel A (2001) Biogenic amines in wines: role of lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 199(1):9–13
Loret S, Deloyer P, Dandrifosse G (2005) Levels of biogenic amines as a measure of the quality of the beer fermentation process: data from Belgian samples. Food Chem 89(4):519–525
Loukou Z, Zotou A (2003) Determination of biogenic amines as dansyl derivatives in alcoholic beverages by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection and characterization of the dansylated amines by liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 996(1–2):103–113
Mayer HK, Fiechter G, Fischer E (2010) A new ultra-pressure liquid chromatography method for the determination of biogenic amines in cheese. J Chromatogr A 1217(19):3251–3257
Moret S, Bortolomeazzi R, Lercker G (1992) Improvement of extraction procedure for biogenic amines in foods and their high-performance liquid chromatographic determination. J Chromatogr 591(1–2):175–180
Myers R, Montgomery D, Anderson-Cook C (2009) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments (Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics). Wiley, New York
Ngim KK, Ebeler SE, Lew ME, Crosby DG, Wong JW (2000) Optimized procedures for analyzing primary alkylamines in wines by pentafluorobenzaldehyde derivatization and GC–MS. J Agric Food Chem 48(8):3311–3316
Önal A (2007) A review: current analytical methods for the determination of biogenic amines in foods. Food Chem 103(4):1475–1486
Ozdestan O, Uren A (2009) A method for benzoyl chloride derivatization of biogenic amines for high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 78(4–5):1321–1326
Özyurt G, Kuley E, Özkütük S, Özogul F (2009) Sensory, microbiological and chemical assessment of the freshness of red mullet (Mullus barbatus) and goldband goatfish (Upeneus moluccensis) during storage in ice. Food Chem 114(2):505–510
Paleologos EK, Chytiri SD, Savvaidis IN, Kontominas MG (2003) Determination of biogenic amines as their benzoyl derivatives after cloud point extraction with micellar liquid chromatographic separation. J Chromatogr A 1010(2):217–224
Plackett RL, Burman JP (1946) The design of optimum multifactorial experiments. Biometrika 33(4):305–325
Proestos C, Loukatos P, Komaitis M (2008) Determination of biogenic amines in wines by HPLC with precolumn dansylation and fluorimetric detection. Food Chem 106(3):1218–1224
Reddy DS, Venkatarangan L, Chien B, Ramu K (2005) A high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry assay of the androgenic neurosteroid 3α-androstanediol (5α-androstane-3α,17β-diol) in plasma. Steroids 70(13):879–885
Redmond JW, Tseng A (1979) High-pressure liquid chromatographic determination of putrescine, cadaverine, spermidine and spermine. J Chromatogr 170:479–481
Restuccia D, Spizzirri UG, Puoci F, Cirillo G, Curcio M, Parisi OI, Iemma F, Picci N (2011) A new method for the determination of biogenic amines in cheese by LC with evaporative light scattering detector. Talanta 85(1):363–369
Santos MHS (1996) Biogenic amines: their importance in foods. Int J Food Microbiol 29(2–3):213–231
Šimat V, Dalgaard P (2011) Use of small diameter column particles to enhance HPLC determination of histamine and other biogenic amines in seafood. LWT - Food Sci Technol 44(2):399–406
Stalikas CD, Pilidis GA (2000) Development of a method for the simultaneous determination of phosphoric and amino acid group containing pesticides by gas chromatography with mass-selective detection: optimization of the derivatization procedure using an experimental design approach. J Chromatogr A 872(1–2):215–225
Tang T, Shi T, Qian K, Li P, Li J, Cao Y (2009) Determination of biogenic amines in beer with pre-column derivatization by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 877(5–6):507–512
Vidal-Carou MC, Lahoz-Portolés F, Bover-Cid S, Mariné-Font A (2003) Ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of biogenic amines and polyamines in wine and other alcoholic beverages. J Chromatogr A 998(1–2):235–241
Yen G-C, Hsieh C-L (1991) Simultaneous analysis of biogenic amines in canned fish by HPLC. J Food Sci 56(1):158–160
Yongmei L, Xin L, Xiaohong C, Mei J, Chao L, Mingsheng D (2007) A survey of biogenic amines in Chinese rice wines. Food Chem 100(4):1424–1428
Zhijun L, Yongning W, Gong Z, Yunfeng Z, Changhu X (2007) A survey of biogenic amines in chinese red wines. Food Chem 105(4):1530–1535
Conflict of Interest
Fereydoon Aflaki declares that he has no conflict of interest. Vanik Goulipour declares that he has no conflict of interest. Nader Saemian declares that he has no conflict of interest. Shahab Sheibani declares that he has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aflaki, F., Ghoulipour, V., Saemian, N. et al. Biogenic Amine Contents in Non-alcoholic Beers: Screening and Optimization of Derivatization. Food Anal. Methods 7, 713–720 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9746-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9746-x