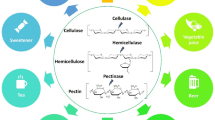
Abstract
Enzymes constitute a major monetary cost in the bioconversion of holocellulose to ethanol. Identifying enzyme inhibitors and moderating their effects is one approach that may help to overcome this issue. Most inhibitors that reduce the hydrolysis activity of holocellulases are released as the holocellulosic biomass is broken down in the pretreatment and hydrolysis steps. Recent reports in the literature have shown that the major inhibitors or deactivators of cellulases are phenols and xylooligosaccharides. The bioconversion of hemicelluloses by hemicellulases also has important practical applications in various agro-industrial processes in addition to the conversion of hemicellulosic biomass to fuels and chemicals. Hemicellulases, such as β-xylosidases, may also help alleviate the inhibitory effect of xylooligosaccharides to cellulases. However, compared to cellulases, less is known about the inhibition or deactivation of hemicellulases and pectinases, especially for inhibitors that are generated during pre-treatment and the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic substrates. Considering the importance of such enzymes for the complete degradation of lignocellulosic substrates, this review provides a broad view of the effect of inhibitors of holocellulases (cellulases, hemicellulases, and pectinases).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Goukh AA, Greve LC, Labavitch JM (1983) Purification and partial characterization of ‘Bartlett’ pear fruit polygalacturonase inhibitors. Physiol Plant Pathol 23:111–122
Andreaus J, Filho EXF, Bon EPS (2008) A review on biotechnology of holocellulose-degrading enzymes. In: Hou CT, Shaw JF (eds) Biocatalysis and bioenergy. Wiley, New Jersey, pp 1–41
Arantes V, Jack N, Saddler JN (2010) Access to cellulose limits the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis: the role of amorphogenesis. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:4
Bae HD, McAllister TA, Yanke J, Cheng KJ, Muir AD (1993) Effects of condensed tannins on endoglucanase activity and filter paper digestion by Fibrobacter succinogenes S85. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2132–2138
Balestrieri C, Castaldo D, Giovane A, Quagliuolo L, Servillo L (1990) A glycoprotein inhibitor of pectin methylesterase in kiwi fruit (Actinidia chinensis). Eur J Biochem 193:183–187
Barmore CR, Nguyen TK (1985) Polygalacturonase inhibition in rind of Valencia orange infected with Diplodia natalensis. Phytopathol 75:446–449
Bezerra RMF, Dias AA (2005) Enzymatic kinetic of cellulose hydrolysis inhibition by ethanol and cellobiose. Appl Biochem Biotech 126:49–59
Bezerra RMF, Dias AA, Fraga I, Pereira AN (2006) Simultaneous ethanol and cellobiose inhibition of cellulose hydrolysis studied with integrated equations assuming constant or variable substrate concentration. Appl Biochem Biotech 134:27–38
Borjesson J, Engqvist M, Sipos B, Tjerneld F (2007) Effect of poly(ethylene glycol) on enzymatic hydrolysis and adsorption of cellulase enzymes to pretreated lignocelluloses. Enz Microb Technol 41:186–195
Borneman WS, Ljungdahl LG, Hartley RD, Akin DE (1993) Feruloyl and p-coumaroyl esterases from the anaerobic fungus Neocallimastix strain MC-2: properties and functions in plant cell wall degradation. In: Coughlan MP Hazlewood GP (eds) Hemicellulose and hemicellulases. Portland, London, pp 85–102
Boukari I, O’Donohue M, Rémond C, Chabbert B (2011) Probing a family GH11 endo-β-1,4-xylanase inhibition mechanism by phenolic compounds: role of functional phenolic groups. J Mol Cat B: Enzymatic 72:130–138
Bugbee WM (1993) A pectin lyase inhibitor protein from cell walls of sugar beet. Phytopathol 83:63–68
Can HK, Guner A (2006) Investigation of adsorption-desorption dynamism of bovine serum albumin on crosslinked N, N-diethylaminoethyl dextran microbeads: solution phase. J Appl Polym Sci 99:2288–2299
Celestino SMC, de Freitas SM, Medrano FJ, de Souza MV, Filho EXF (2006) Purification and characterization of a novel pectinase from Acrophialophora nainiana with emphasis on its physicochemical properties. J Biotechnol 123:33–42
Cervone F, De Lorenzo G, Degra L, Salvi G, Bergami M (1987) Purification and characterization of a polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein from Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol 85:631–637
Coughlan MP, Thuohy MG, Filho EXF, Puls J, Claeyssens M, Vrsanská M et al. (1993) Enzymological aspects of microbial hemicellulases with emphasis on fungal systems. In: Coughlan MP Hazlewood GP (eds) Hemicellulose and hemicellulases. Portland, London, pp 53–84
D’hallewin G, Schirra M, Powell ALT, Greve C, Labavitch JM (2004) Properties of a polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein isolated from “Oroblanco” grapefruit. Physiol Plantarum 120:395–404
Dekker RFH (1986) Kinetic, inhibition, and stability properties of a commercial β-D-glucosidase (cellobiase) preparation from Aspergillus niger and its suitability in the hydrolysis of lignocelluloses. Biotechnol Bioeng 28:1438–1442
El Modafar C, El Boustani E (2001) Cell wall-bound phenolic acid and lignin contents in date palm as related to its resistance to Fusarium oxysporum. Biol Plantarum 44:125–130
Eriksson T, Borjesson J, Tjerneld F (2002) Mechanism of surfactant effect in enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Enzyme MicrobTechnol 31:353–364
Fang X, Shen Y, Zhao J, Bao X, Qu Y (2010) Status and prospect of lignocellulosic bioethanol from China. Biores Technol 101:4814–4819
Fenske JJ, Griffin DA, Penner MH (1998) Comparison of aromatic monomers in lignocellulosic biomass prehydrolysates. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 20:364–368
Gamble GR, Snook ME, Henriksson G, Akin DE (2000) Phenolic constituents in the bast tissue and inhibition of cellulose and pectinase. Biotechnol 22:741–746
Goldstein JL, Swain T (1956) The inhibition of enzymes by tannins. Phytochem 4:185–192
Gong CS, Ladisch MR, Tsao GT (1977) Cellobiase from Trichoderma viride: purification, properties, kinetics, and mechanism. Biotechnol Bioeng 19:959–981
Gruno M, Väljamä P, Petterson G, Johansson G (2004) Inhibition of the Trichoderma reesei cellulases by cellobiose is strongly dependent on the nature of the substrate. Biotechnol Bioeng 86:503–511
Gustavson KH (1956) The chemistry of tannins processes. Academic, New York
Hodge DB, Karim MN, Schell DJ, McMillan JD (2008) Soluble and insoluble solids contributions to high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Biores Technol 99:8940–8948
Jing X, Zhang X, Bao J (2009) Inhibition performance of lignocellulose degradation products on industrial cellulase enzymes during cellulose hydrolysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 159:696–707
Kawakubo T, Karita S, Araki Y, Watanabe S, Oyadomari M et al. (2010) Analysis of exposed cellulose surfaces in pretreated wood biomass using carbohydrate-binding module (CBM)–cyan fluorescent protein (CFP). Biotechnol Bioeng 105:49–508
Keskar SS, Srinivasan MC, Deshpande VV (1989) Chemical modification of a xylanase from a thermotolerant Streptomyces. Evidence for essential tryptophan and cysteine residues at the active site. Biochem J 261:49–55
Kim HJ, Kang SO, Yung CH (1993) Purification and characterization of xylanase I from Trichoderma koningii ATCC 26113. Korean J Microbiol 31:63–71
Kim Y, Ximenes EA, Mosier NS, Ladisch MR (2011) Soluble inhibitors/deactivators of cellulase enzymes from lignocellulosic biomass. Enz Microbial Technol 48:408–415
Kristensen JB (2009) Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose substrate interactions and high solids loadings. In: Faculty of Life Sciences, Vol. Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), University of Copenhagen, Frederiksberg, p 130
Kumar R, Wyman CE (2009) Effect of additives on the digestibility of corn stover solids following pretreatment by leading technologies. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1544–1557
Ladisch MR, Gong C-S, Tsao GT (1977) Corn crop residues as a potential source of single cell protein: kinetics of Trichoderma viride cellobiase action. Dev Ind Microbiol Ser 18:157–168
Ladisch M, MosierN KY, Ximenes EA, Hogsett D (2010) Conversion of cellulose to biofuels. Chem Eng Progress 106:56–63
Lagaert S, Beliën T, Volckaert G (2009) Plant cell walls: protecting the barrier from degradation by microbial enzymes. Sem Cell Develop Biol 20:1064–1073
Mandels M, Reese ET (1965) Inhibition of cellulases. Annu Rev Phytopathol 3:85–102
McNeil M, Darvill AG, Fry SC, Albersheim P (1984) Structure and function of the primary cell walls of plants. Annu Rev Biochem 53:625–663
McAllister TA, Bae HD, Yanke LJ, Cheng KJ (1994) Effect of condensed tannins from birdsfoot trefoil on endoglucanase activity and the digestion of cellulose filter paper by ruminal fungi. Can J Microbiol 40:298–305
McMillan JD (1994) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. In: Himmel ME, Baker JO, Overend RP (eds) Enzymatic conversion of biomass for fuels production. ACS symposium series, vol. 566. ACS, Washington, DC, pp 292–324
Mohamed SA, Farid NM, Hossiny EN, Bassuiny RI (2006) Biochemical characterization of an extracellular polygalacturonase from Trichoderma harzianum. J Biotechnol 127:54–64
Mohana S, Shah A, Divecha J, Madamwar D (2008) Xylanase production by Burkholderia sp. DMAX strain under solid state fermentation using distillery spent wash. Biores Technol 99:7553–7564
Moreira LRS, Filho EXF (2008) An overview of mannan structure and mannan-degrading enzyme systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:165–178
Mosier N, Wyman C, Dale B, Elander R, Lee YY, Holtzapple M et al. (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Biores Technol 96:673–686
Panagiotou G, Olsson L (2007) Effect of compounds released during pretreatment of wheat straw on microbial growth and enzymatic hydrolysis rates. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:250–258
Qing Q, Yang B, Wyman CE (2010) Impact of surfactants on pretreatment of corn stover. Biores Technol 101:5941–5951
Qing Q, Yang B, Wyman CE (2010) Xylooligomers are strong inhibitors of cellulose hydrolysis by enzymes. Biores Technol 101:9624–9630
Qing Q, Wyman CE (2011) Supplementation with xylanase and β-xylosidase to reduce xylooligomer and xylan inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose and pretreated corn stover. Biotechnol Biofuels 4:18
Ryan SE, Nolan K, Thompson R, Gubitz GM, Savage AV, Tuohy MG (2003) Purification and characterization of a new low molecular weight endoxylanase from Penicillium capsulatum. Enz Microb Technol 33:775–785
Saha B (2003) Hemicellulose bioconversion. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:279–291
Sineiro J, Dominguez H, Núñez MJ, Lema JM (1997) Inhibition of cellulase activity by sunflower polyphenols. Biotechnol Lett 19:521–524
Siqueira FG, Filho EXF (2010) Plant cell wall as substrate for the production of enzymes with industrial applications. Mini-Rev Org Chem 7:54–60
Szengyel Z, Zacchi G, Varga A, Réczey K (2000) Cellulase production of Trichoderma reesei Rut C30 using steam-pretreated spruce. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 84–86:679–691
Takagi M (1984) Inhibition of cellulase by fermentation products. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:1506–1507
Teixeira RSS, Siqueira FG, Souza MV, Filho EXF, Bon EPS (2010) Purification and characterization studies of a thermostable β-xylanase from Aspergillus awamori. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:1041–1051
Tejirian A, Xu F (2011) Inhibition of enzymatic cellulolysis by phenolic compounds. Enz Microb Technol 48:239–247
Thakur A, Pahwa R, Singh S, Gupta R (2010) Production, purification and characterization of polygalacturonase from Mucor circinelloides ITCC 6025. Enz Res 2010:1–7
Tu M, Pan X, Saddler JN (2009) Adsorption of cellulase on cellulolytic enzyme lignin from lodgepole pine. J Agric Food Chem 57:7771–7778
Väljamäe P, Sild V, Petterson G, Johansson G (1998) The initial kinetics of hydrolysis by cellobiohydrolases I and II is consistent with a cellulose surface—erosion model. Eur J Biochem 253:469–475
Várnai A, Siika-aho M, Viikari L (2010) Restriction of the enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-pretreated spruce by lignin and hemicelluloses. Enz Microb Technol 46:185–193
Vieira WB, Moreira LRS, Monteiro Neto A, Filho EXF (2007) Production and characterization of an enzyme complex from a new strain of Clostridium thermocellum with emphasis on its xylanase activity. Braz J Microbiol 38:237–242
Walton JD (1994) Deconstructing the cell wall. Plant Physiol 104:1113–1118
Wu Z, Lee YY (1997) Inhibition of the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose by ethanol. Biotechnol Lett 19:977–979
Wu HS, Luo J, Raza W, Liu YX, Gu M, Chen G et al. (2009) Effect of exogenously added ferulic acid on in vitro Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Niveum. Sci Horticul 124:448–453
Xiao Z, Zhang X, Gregg D, Saddler J (2004) Effects of sugar inhibition on cellulases and β-glucosidase during enzymatic hydrolysis of softwood substrates. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 115:1115–1126
Ximenes EA, Kim Y, Mosier N, Dien B, Ladisch M (2010) Inhibition of cellulases by phenols. Enz Microb Technol 46:170–176
Ximenes EA, Kim Y, Mosier N, Dien B, Ladisch M (2011) Deactivation of cellulases by phenol. Enz Microb Technol 48:54–60
Yang B, Wyman CE (2006) BSA treatment to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose in lignin containing substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:614–617
Yang B, Willies DM, Wyman CE (2006) Changes in the enzymatic hydrolysis rate of Avicel cellulose with conversion. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:1122–1128
Zhang YHP, Himmel ME, Mielenz JR (2006) Outlook for cellulase improvement: screening and selection strategies. Biotechnol Adv 24:452–481
Acknowledgments
E.X.F. acknowledges the receipt of a research fellowship from the Brazilian Research Council (CNPq). P.M.D.J. and L.R.S.M acknowledge the receipt of a postgraduate maintenance scholarship from CNPq and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education, respectively. This work is funded by CNPq (research grants 563260/2010-6 and 563823/2010-0), Foundation for Research Support of Federal District (Brazil, Pronex Program) and National Institute of Science and Technology of Bioethanol. The authors would like to thank Dr. Eduardo de Aquino Ximenes for proofreading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duarte, G.C., Moreira, L.R.S., Jaramillo, P.M.D. et al. Biomass-Derived Inhibitors of Holocellulases. Bioenerg. Res. 5, 768–777 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-012-9182-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-012-9182-6