Abstract
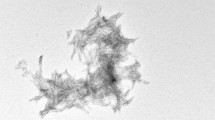
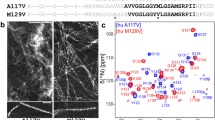
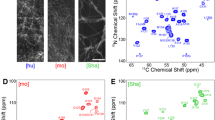
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. Aggregation of amyloid β (Aβ), a peptide of 39−43 residues length, into insoluble fibrils is considered to initiate the disease. Determination of the molecular structure of Aβ fibrils is technically challenging and is a significant goal in AD research that may lead to design of effective therapeutical inhibitors of Aβ aggregation. Here, we present chemical-shift assignments for fibrils formed by highly pure recombinant Aβ1−40 with the Osaka E22Δ mutation that is found in familial AD. We show that that all regions of the peptide are rigid, including the N-terminal part often believed to be flexible in Aβ wt.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertini I, Gonnelli L, Luchinat C, Mao J, Nesi A (2011) A new structural model of Aβ40 fibrils. J Am Chem Soc 133(40):16013–16022
Böckmann A, Gardiennet C, Verel R, Hunkeler A, Loquet A, Pintacuda G, Emsley L, Meier BH, Lesage A (2009) Characterization of different water pools in solid-state NMR protein samples. J Biomol NMR 45(3):319–327
Castellani F, van Rossum B, Diehl A, Rehbein K, Oschkinat H (2003) Determination of solid-state NMR structures of proteins by means of three-dimensional N-15-C-13-C-13 dipolar correlation spectroscopy and chemical shift analysis. Biochemistry 42(39):11476–11483
Debelouchina GT, Platt GW, Bayro MJ, Radford SE, Griffin RG (2010) Magic angle spinning NMR analysis of beta2-microglobulin amyloid fibrils in two distinct morphologies. J Am Chem Soc 132(30):10414–10423
Fändrich M, Schmidt M, Grigorieff N (2011) Recent progress in understanding Alzheimer’s β-amyloid structures. Trends Biochem Sci:1–8
Franks W, Wylie B, Frericks Schmidt H, Nieuwkoop A, Mayrhofer R-M, Shah G, Graesser D, Rienstra CM (2008) Dipole tensor-based atomic-resolution structure determination of a nanocrystalline protein by solid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:4621–4625
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297(5580):353–356
Irie K, Murakami K, Masuda Y, Morimoto A, Ohigashi H, Ohashi R, Takegoshi K, Nagao M, Shimizu T, Shirasawa T (2005) Structure of beta-amyloid fibrils and its relevance to their neurotoxicity: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Biosci Bioeng 99(5):437–447
Levy-Lahad E, Wasco W, Poorkaj P, Romano DM, Oshima J, Pettingell WH, Yu CE, Jondro PD, Schmidt SD, Wang K (1995) Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer’s disease locus. Science 269(5226):973–977
Lopez del Amo J-M, Schmidt M, Fink U, Dasari M, Fändrich M, Reif B (2012) An asymmetric dimer as the basic subunit in Alzheimer's disease amyloid β fibrils. Angew Chem Int Ed 51(25):6136–6139
Loquet A, Bardiaux B, Gardiennet C, Blanchet C, Baldus M, Nilges M, Malliavin T, Böckmann A (2008) 3D Structure Determination of the Crh Protein from Highly Ambiguous Solid-State NMR Restraints. J Am Chem Soc 130(11):3579–3589
Manolikas T, Herrmann T, Meier BH (2008) Protein structure determination from 13C spin-diffusion solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 130(12):3959–3966
Ovchinnikova OY, Finder VH, Vodopivec I, Nitsch RM, Glockshuber R (2011) The Osaka FAD mutation E22Δ leads to the formation of a previously unknown type of amyloid β fibrils and modulates Aβ neurotoxicity. J Mol Biol 408(4):780–791
Schuetz A, Wasmer C, Habenstein B, Verel R, Greenwald J, Riek R, Böckmann A, Meier BH (2010) Protocols for the sequential solid-state NMR spectroscopic assignment of a uniformly labeled 25 kDa protein: HET-s(1−227). ChemBioChem 11(11):1543–1551
Shen Y, Delaglio F, Cornilescu G, Bax A (2009) TALOS plus: a hybrid method for predicting protein backbone torsion angles from NMR chemical shifts. J Biomol NMR 44(4):213–223
Stevens TJ, Fogh RH, Boucher W, Higman VA, Eisenmenger F, Bardiaux B, van Rossum B-J, Oschkinat H, Laue ED (2011) A software framework for analysing solid-state MAS NMR data. J Biomol NMR 51(4):437–447
Tomiyama T, Nagata T, Shimada H, Teraoka R, Fukushima A, Kanemitsu H, Takuma H, Kuwano R, Imagawa M, Ataka S, Wada Y, Yoshioka E, Nishizaki T, Watanabe Y, Mori H (2008) A new amyloid beta variant favoring oligomerization in Alzheimer’s-type dementia. Ann Neurol 63(3):377–387
Tycko R (2006) Molecular structure of amyloid fibrils: insights from solid-state NMR. Q Rev Biophys 39(1):1–55
Tycko R (2011) Solid-state NMR studies of amyloid fibril structure. Annu Rev Phys Chem 62(1):279–299
Van Melckebeke H, Wasmer C, Lange A, Ab E, Loquet A, Böckmann A, Meier BH (2010) Atomic-resolution three-dimensional structure of HET-s(218-289) amyloid fibrils by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 132(39):13765–13775
Vranken WF, Boucher W, Stevens TJ, Fogh RH, Pajon A, Llinas M, Ulrich EL, Markley JL, Ionides J, Laue ED (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59(4):687–696
Wang Y, Jardetzky O (2002) Probability-based protein secondary structure identification using combined NMR chemical-shift data. Protein Sci 11(4):852–861
Wasmer C, Lange A, van Melckebeke H, Siemer AB, Riek R, Meier BH (2008) Amyloid fibrils of the HET-s(218-289) prion form a beta solenoid with a triangular hydrophobic core. Science 319(5869):1523–1526
Wishart DS, Sykes BD (1994) The 13C chemical-shift index: a simple method for the identification of protein secondary structure using 13C chemical-shift data. J Biomol NMR 4(2):171–180
Zech SG, Wand AJ, McDermott AE (2005) Protein structure determination by high-resolution solid-state NMR spectroscopy: application to microcrystalline ubiquitin. J Am Chem Soc 127(24):8618–8626
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Andreas Hunkeler for technical support and Hiang Dreher-Teo for providing TEV protease. This work was supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-12-BS08-0013-01), the ETH Zurich, the Swiss National Science Foundation (Grants 200020_124611, 200020_146757) and the NCCR program “Neural Plasticity and Repair” and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. We also acknowledge support from the European Commission under the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7), contract Bio-NMR 261863.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Matthias Huber and Oxana Yu. Ovchinnikova have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huber, M., Ovchinnikova, O.Y., Schütz, A.K. et al. Solid-state NMR sequential assignment of Osaka-mutant amyloid-beta (Aβ1−40 E22Δ) fibrils. Biomol NMR Assign 9, 7–14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-013-9535-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-013-9535-x