Abstract
Objective
To assess the plasma Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) concentrations in obese children and to investigate the relationship between PTX3 levels and metabolic syndrome (MS) components.
Methods
Seventy-seven obese patients aged 10–16 y (38 girls, 39 boys) were included in the study. PTX3 levels were compared between the groups with or without MS. In addition, PTX3 was analysed separately by subgroups according to the presence of specific MS components.
Results
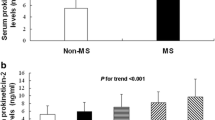
Plasma PTX3 concentrations were significantly higher in obese children and adolescents with metabolic syndrome than in those without MS (2.1 ± 1.2 ng/ml and 1.4 ± 0.9 ng/ml respectively; P = 0.02). Patients with low HDL levels (<40 mg/dl) had higher plasma PTX3 concentrations than those with normal HDL levels (P = 0.05). Similarly, those who had high triglyceride levels (≥150 mg/dl) had higher PTX3 levels (P = 0.01). PTX3 levels were negatively correlated with HDL cholesterol (r = −0.32, P = 0.003) among all patients.
Conclusions
PTX3 levels are higher in obese children and adolescents with metabolic syndrome than in those without MS. Thus, PTX3 levels might be a useful biomarker for children and adolescents with metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular risks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rolland-Cachera MF. Childhood obesity: current definitions and recommendations for their use. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011;6:325–31.
Itagi V, Patil R. Obesity in children and adolescents and its relationship with hypertension. Turk J Med Sci. 2011;41:259–66.
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS. Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2003;12:1785–8.
Ogawa T, Kawano Y, Imamura T, Kawakita K, Sagara M, Matsuo T, et al. Reciprocal contribution of pentraxin 3 and C-reactive protein to obesity and metabolic syndrome. Obesity. 2010;18:1871–4.
Abderrahim-Ferkoune A, Bezy O, Chiellini C, Maffei M, Grimaldi P, Bonino F, et al. Characterization of the long pentraxin PTX3 as a TNF alpha-induced secreted protein of adipose cells. J Lipid Res. 2003;44:994–1000.
Alberti L, Gilardini L, Zulian A, Micheletto G, Peri G, Doni A, et al. Expression of long pentraxin PTX3 in human adipose tissue and its relation with cardiovascular risk factors. Atherosclerosis. 2009;202:455–60.
Garlanda C, Bottazzi B, Bastone A, Mantovani A. Pentraxins at the crossroads between innate immunity, inflammation, matrix deposition, and female fertility. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:337–66.
Chu SH, Park JH, Lee MK, Jekal Y, Ahn KY, Chung JY, et al. The association between pentraxin 3 and insulin resistance in obese children at baseline and after physical activity intervention. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;413:1430–7.
Shim BJ, Jeon HK, Lee SJ, Kim SS, Park MY, Lee DH, et al. The relationship between serum pentraxin 3 and central obesity in st-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients. Korean Circ J. 2010;40:308–13.
Ozturk A, Mazicioglu MM, Hatipoglu N, Budak N, Keskin G, Yazlak Z, et al. Reference body mass index curves for Turkish children 6–18 y of age. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2008;21:827–36.
Hatipoglu N, Ozturk A, Mazicioglu MM, Kurtoglu S, Seyhan S, Lokoglu F. Waist circumference percentiles for 7–17-y-old Turkish children and adolescents. Eur J Pediatr. 2008;167:383–9.
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, Arslanian S, et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents—an IDF concensus report. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8:299–306.
Inokuchi M, Matsuo N, Anzo M, Takayama JI, Hasegawa T. Age- dependent percentile for waist circumference for Japanese children based on the 1992–1994 cross-sectional national survey data. Eur J Pediatr. 2007;166:655–61.
Zanetti M, Bosutti A, Ferreira C, Vinci P, Biolo G, Fonda M, et al. Circulating pentraxin 3 levels are higher in metabolic syndrome with subclinical atherosclerosis: evidence for association with atherogenic lipid profile. Clin Exp Med. 2009;9:243–8.
Miyaki A, Maeda S, Yoshizawa M, Misono M, Sasai H, Shimojo N, et al. Is pentraxin 3 involved in obesity-induced decrease arterial distensibility? J Atheroscler Thromb. 2010;17:278–84.
Boehme M, Kaehne F, Kuehne A, Bernhardt W, Schröder M, Pommer W, et al. Pentraxin 3 is elevated in haemodialysis patients and is associated with cardiovascular disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:2224–9.
Suzuki S, Takeishi Y, Niizeki T, Koyama Y, Kitahara T, Sasaki T, et al. Pentraxin 3, a new marker for vascular inflammation, predicts adverse clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure. Am Heart J. 2008;155:75–81.
Karakas MF, Buyukkaya E, Kurt M, Motor S, Akcay AB, Karakas E, et al. Serum pentraxin-3 levels are associated with the severity of metabolic syndrome. Med Princ Pract. 2013;22:274–9.
Mantovani A, Garlanda C, Bottazzi B, Peri G, Doni A, Martinez de la Torre Y, et al. The long pentraxin PTX3 in vascular pathology. Vascul Pharmacol. 2006;45:326–30.
Napoleone E, Di Santo A, Bastone A, Peri G, Mantovani A, de Gaetano G, et al. Long pentraxin PTX3 upregulates tissue factor expression in human endothelial cells: a novel link between vascular inflammation and clotting activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:782–7.
Witasp A, Carrero JJ, Michaëlsson K, Ahlström H, Kullberg J, Adamsson V, et al. Inflammatory biomarker pentraxin 3 (PTX3) in relation to obesity, body fat depots, and weight loss. Obesity. Published Online First. 2014. doi: 10.1002/oby.20695.
Klouche M, Peri G, Knabbe C, Eckstein HH, Schmid FX, Schmitz G, et al. Modified atherogenic lipoproteins induce expression of pentraxin-3 by human vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 2004;175:221–8.
Boden WE. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol as an independent risk factor in cardiovascular disease: assessing the data from framingham to the veterans affairs high-density lipoprotein intervention trial. Am J Cardiol. 2000;86:S19–22.
Osorio-Conles O, Guitart M, Chacón MR, Maymo-Masip E, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Montori-grau M, et al. Plasma PTX3 protein levels inversely correlate with insulin secretion and obesity, where as visceral adipose tissue PTX3 gene expression is increased in obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;301:1254–61.
Aydogdu A, Tasci I, Tapan S, Basaran Y, Aydogan U, Meric C. High plasma level of long Pentraxin 3 is associated with insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2012;28:722–5.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Dr. Sebahattin Muhtaroglu for performing analyses in the biochemistry laboratory of Erciyes University, Medical Faculty.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
Health Goverment of Turkey provided financial help to conduct the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kardas, F., Akın, L., Kurtoglu, S. et al. Plasma Pentraxin 3 as a Biomarker of Metabolic Syndrome. Indian J Pediatr 82, 35–38 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-014-1542-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-014-1542-0