Abstract
Background and purpose
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has traditionally been considered radioresistant with a limited role for conventional fractionation as a local approach. Nevertheless, since the appearance of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), radiotherapy (RT) has been increasingly employed in the management of metastatic RCC (mRCC). The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of SBRT for synchronous and metachronous oligo metastatic RCC patients in terms of local control, delay of systemic treatment, overall survival and toxicity.
Patients and methods
A Monocentric single institution retrospective data collection was performed. Inclusion criteria were: (1) oligo-recurrent or oligo-progressive disease (less than 5 metastases) in mRCC patients after radical/partial nephrectomy or during systemic therapy, (2) metastasectomy or other metastasis-directed, rather than SBRT not feasible, (3) any contraindication to receive systemic therapy (such as comorbidities), (4) all the histologies were included, (5) available signed informed consent form for treatment. Tumor response and toxicity were evaluated using the response evaluation criteria in solid tumors and the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.03, respectively. Progression-free survival in-field and out-field (in-field and out-field PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated via the Kaplan–Meier method. The drug treatment-free interval was calculated from the start of SBRT to the beginning of any systemic therapy.
Results
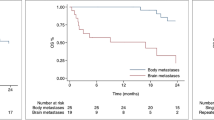
From 2010 to December 2018, 61 patients with extracranial and intracranial metastatic RCC underwent SBRT on 83 lesions. Intracranial and extracranial lesions were included. Forty-five (74%) patients were treated for a solitary metastatic lesion. Median RT dose was 25 Gy (range 10–52) in 5–10 fractions. With a median follow-up of 2.3 years (range 0–7.15), 1-year in-field PFS was 70%, 2-year in-field PFS was 55%. One year out-field PFS was 39% and 1-year OS was 78%. Concomitant systemic therapy was employed for only 11 (18%) patients, for the others 50 (82%) the drug treatment-free rate was 70% and 50% at 1 and 2 years, respectively. No > G1 acute and late toxicities were reported.
Conclusion
The pattern of failure was pre-dominantly out-of-field, even if the population was negatively selected and the used RT dose could be considered palliative. Therefore, SBRT appears to be a well-tolerated, feasible and safe approach in oligo metastatic RCC patients with an excellent in-field PFS. SBRT might play a role in the management of selected RCC patients allowing for a delay systemic therapy begin (one out of two patients were free from new systemic therapy at 2 years after SBRT). Further research on SBRT dose escalation is warranted.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BED:
-
Biologically effective dose
- BM:
-
Brain metastasis
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CR:
-
Complete response
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTV:
-
Clinical target volume
- CTCAE:
-
Common terminology criteria for adverse events
- EQD2:
-
EQuivalent dose in 2 Gy fractions
- ESMO:
-
European Society for Medical Oncology
- GTV:
-
Gross tumor volume
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- IEO:
-
European Institute of Oncology IRCCS
- LCR:
-
Local control rate
- mRCC:
-
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- OAR:
-
Organ at risk
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PD:
-
Progression of disease
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- PR:
-
Partial response
- PTV:
-
Planning target volume
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- RECIST:
-
Response evaluation criteria in solid tumors
- RT:
-
Radiotherapy
- SBRT:
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy
- SD:
-
Stable disease
- SFI:
-
Systemic treatment-free interval
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30.
Rabinovitch RA, Zelefsky MJ, Gaynor JJ, et al. Patterns of failure following surgical resection of renal cell carcinoma: implications for adjuvant local and systemic therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:206–12.
Kim SP, Weight CJ, Leibovich BC, et al. Outcomes and clinicopathologic variables associated with late recurrence after nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2011;78:1101–6.
Moreira M, Pobel C, Epaillard N, et al. Resistance to cancer immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020;3:454–71. https://doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2020.16.
Gomez DR, Tang C, Zhang J, et al. Local consolidative therapy vs maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(18):1558–65. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.00201.
Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard of care palliative treatment in patients with oligometastatic cancers (SBRT-COMET): a randomised, phase 2, open-label trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10185):2051–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32487-5.
Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:8–10.
Motzer RJ, Mazumdar M, Bacik J, et al. Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2530–40.
Alt AL, Boorjian SA, Lohse CM, et al. Survival after complete surgical resection of multiple metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2011;117:2873–82.
Van der Poel HG, Roukema JA, Horenblas S, et al. Metastasectomy in renal cell carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Eur Urol. 1999;35:197–203.
Naito S, Kinoshita H, Kondo T, et al. Prognostic factors of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma with removed metastases: a multicenter study of 556 patients. Urology. 2013;82:846–51.
Zaid HB, Parker WP, Safdar NS, et al. Outcomes following complete surgical metastasectomy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Urol. 2017;197:44–9.
Rühle A, Andratschke N, Siva S, Guckenberger M. Is there a role for stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma? Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2019;26(18):104–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctro.2019.04.012.
Walsh L, Stanfield JL, Cho LC, et al. Efficacy of ablative high-doseper-fraction radiation for implanted human renal cell cancer in a nude mouse model. Eur Urol. 2006;50:795–800 (discussion 800).
Ning S, Trisler K, Wessels BW, et al. Radiobiologic studies of radioimmunotherapy and external beam radiotherapy in vitro and in vivo in human renal cell carcinoma xenografts. Cancer. 1997;80(12 Suppl):2519–28.
Deschavanne PJ, Fertil B. A review of human cell radiosensitivity in vitro. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;34:251–66.
Franzese C, Franceschini D, Di Brina L, et al. Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in the management of oligometastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2019;201:70–5.
Meyer E, Pasquier D, Bernadou G, et al. Stereotactic radiation therapy in the strategy of treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a study of the Getug Group. Eur J Cancer. 2018;98:38–47.
Ranck MC, Golden DW, Corbin KS, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for the treatment of oligometastatic renal cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;36:589–95.
Stinauer MA, Kavanagh BD, Schefter TE, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for melanoma and renal cell carcinoma: impact of single fraction equivalent dose on local control. Radiat Oncol. 2011;6:34.
Stenman M, Sinclair G, Paavola P, Wersall P, Harmenberg U, Lindskog M. Overall survival after stereotactic radiotherapy or surgical metastasectomy in oligometastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated at two Swedish centres 2005–2014. Radiother Oncol. 2018;127:501–6.
Teh B, Bloch C, Galli-Guevara M, et al. The treatment of primary and metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with image guided stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). Biomed Imaging Interv J. 2007;3:e6.
Wersall PJ, Blomgren H, Lax I, et al. Extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy for primary and metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Radiother Oncol: J Eur Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 2005;77:88–95.
Zelefsky MJ, Greco C, Motzer R, et al. Tumor control outcomes after hypofractionated and single-dose stereotactic image guided intensity modulated radiotherapy for extracranial metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:1744–8.
Svedman C, Sandstrom P, Pisa P, et al. A prospective phase II trial of using extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy in primary and metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2006;45:870–5.
Kothari G, Foroudi F, Gill S, et al. Outcomes of stereotactic radiotherapy for cranial and extracranial metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Acta Oncol. 2015;54:148–57.
Timmerman RD. An overview of hypofractionation and introduction to this issue of seminars in radiation oncology. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2008;18:215–22.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:228.
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse EventsCTCAE. Available on 07th/01/2021 at https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm.
Kroeze SGC, Fritz C, Schaule J, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy or targeted therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15284.
Zhang Y, Schoenhals J, Christie A, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy (SAbR) used to defer systemic therapy in oligometastatic renal cell cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;105(2):367–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.07.023.
Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:706–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz056.
Kato S, Demura S, Murakami H, Tsuchiya H. Surgical metastasectomy for renal cell carcinoma: which patients are the real candidates for surgery? Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(Suppl 8):S273. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.11.139.PMID:32015992;PMCID:PMC6976505.
Daliani DD, Tannir NM, Papandreou CN, et al. Prospective assessment of systemic therapy followed by surgical removal of metastases in selected patients with renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2015;104:456.
Loh J, Davis ID, Martin JM, Siva S. Extracranial oligometastatic renal cell carcinoma: current management and future directions. Future Oncol. 2014;10:76174. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.14.40.
Rühle A, Andratschke N, Siva S, et al. Is there a role for stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma? Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2019;18:104–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctro.2019.04.012.
Motzer RJ, Jonash E, Agarwal N, et al. Kidney cancer, Version 2.2017 NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Comp Canc Netw. 2017;15:804.
Altoos B, Amini A, Yacoub M, et al. Local control rates of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (rcc) to thoracic, abdominal, and soft tissue lesions using stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT). Radiat Oncol. 2015;10:218.
Ghia AJ, Chang EL, Bishop AJ, et al. Single fraction versus multifraction spinal stereotactic radiosurgery for spinal metastases from renal cell carcinoma: secondary analysis of phase I/II trials. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(5):829–36.
Briganti A, Montorsi F, Bianchi M, et al. Distribution of metastatic sites in renal cell carcinoma: a population-based analysis. Ann Oncol. 2011;23:973–80.
Sheehan JP, Sun MH, Kondziolka D, et al. Radiosurgery in patients with renal cell carcinoma metastasis to the brain: long-term outcomes and prognostic factors influencing survival and local tumor control. J Neurosurg. 2003;98(2):342–9. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.98.2.0342.
Dudek AZ, Raza A, Chi M, et al. Brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2013;11:155–60.
Cochran DC, Chan MD, Aklilu M, et al. The effect of targeted agents on outcomes in patients with brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma treated with gamma knife surgery: clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2012;116:978–83.
Verma J, Jonasch E, Allen PK, et al. The impact of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on the multimodality treatment of brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;36:620–4.
Seastone DJ, Elson P, Garcia JS, et al. Clinical outcome of stereotactic radiosurgery for central nervous system metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2014;12:111–6.
46.Clinicaltrials.gov [Web site]. Combining Radiosurgery and Nivolumab in the Treatment of Brain Metastases. Available at: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02978404, Accessed 10th Jul 2020.
Triggiani L, Alongi F, Buglione M, et al. Efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy in oligorecurrent and in oligoprogressive prostate cancer: new evidence from a multicentric study. Br J Cancer. 2017;116:1520.
Jereczek-Fossa BA, Fanetti G, Fodor C, et al. Salvage stereotactic body radiotherapy for isolated lymph node recurrent prostate cancer: Single institution series of 94 consecutive patients and 124 lymph nodes. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15:e623–32.
Berkovic P, De Meerleer G, Delrue L, et al. Salvage stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with limited prostate cancer metastases: deferring androgen deprivation therapy. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2013;11:27–32.
Hong JC, Salama JK. The expanding role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in oligometastatic solid tumors: what do we know and where are we going? Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;52:22–32.
Zaorsky NG, Lehrer EJ, Kothari G, Louie AV, Siva S. Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for oligometastatic renal cell carcinoma (SABR ORCA): a meta-analysis of 28 studies. Eur Urol Oncol. 2019;2(5):515–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euo.2019.05.007.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Italian Ministry of Health with Ricerca Corrente and 5×1000 funds. MZ was supported by a research grant from Accuray Inc. entitled “Data collection and analysis of Tomotherapy and CyberKnife breast clinical studies, breast physics studies and prostate study”. MA and FLF were partially supported by a research grant from the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) entitled "Radioablation ± hormonotherapy for prostate cancer oligorecurrences (RADIOSA trial): potential of imaging and biology" registered at ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03940235, approved by the Ethics Committee of IRCCS Istituto Europeo di Oncologia and Centro Cardiologico Monzino (IEO-997).The sponsors did not play any role in the study design, collection, analysis and interpretation of data, nor in the writing of the manuscript, nor in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
In this research, no animals were involved. All patients signed a written informed consent for radiation therapy and written informed consent for the use of the anonymized data for research or educational purpose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marvaso, G., Corrao, G., Oneta, O. et al. Oligo metastatic renal cell carcinoma: stereotactic body radiation therapy, if, when and how?. Clin Transl Oncol 23, 1717–1726 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02574-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02574-0