Abstract
Background
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a critical promoter of blood vessel growth during embryonic development and neovascularisation in tumours. VEGF serves as a logical target for antiangiogenic cancer therapy because of its fundamental role in tumour angiogenesis. This study is to investigate the inhibitory effects of FP3, a novel VEGF blocker, on angiogenesis in vitro and tumour growth in vivo.
Methods
The inhibitory effects of FP3 on angiogenesis in vitro were evaluated by using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and rat aortic ring. The inhibitory effects of FP3 on tumour growth and angiogenesis in vivo were evaluated in a human non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line A549 tumour xenograft model with the methods of tumour growth regression assay and immunohistochemical staining, respectively.
Results
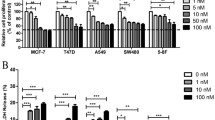
In experiments with HUVECs, FP3 inhibited cell proliferation and migration. In rat aortic ring assay, FP3 suppressed VEGF-induced vessel sprouting. In tumour growth regression assay, FP3 significantly blocked the growth of A549 tumour in the subcutaneous tumour xenograft model and dramatically decreased the vessel density of tumour.
Conclusions
FP3 has excellent inhibitory effects on tumour angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo, therefore it could be used as an effective antiangiogenic agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257
Rafii S, Lyden D, Benezra R et al (2002) Vascular and haematopoietic stem cells: novel targets for anti-angiogenesis therapy? Nat Rev Cancer 2:826–835
Shibuya M (2001) Structure and function of VEGF/VEGF-receptor system involved in angiogenesis. Cell Struct Funct 26:25–35
Giaccone G (2007) The potential of antiangiogenic therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:1961–1970
Teng LS, Jin KT, He KF et al (2010) Advances in combination of antiangiogenic agents targeting VEGF-binding and conventional chemotherapy and radiation for cancer treatment. J Chin Med Assoc 73:281–288
Teng LS, Jin KT, He KF et al (2010) Clinical applications of VEGF-trap (aflibercept) in cancer treatment. J Chin Med Assoc 73:449–456
Zhang M, Zhang J, Yan M et al (2008) Recombinant anti-vascular endothelial growth factor fusion protein efficiently suppresses choroidal neovascularization in monkeys. Mol Vis 14:37–49
Zhang M, Yu D, Yang C et al (2009) The pharmacology study of a new recombinant human VEGF receptor-fc fusion protein on experimental choroidal neovascularization. Pharm Res 26:204–210
Kim JH, Kim JH, Yu YS et al (2008) Antiangiogenic effect of deguelin on choroidal neovascularization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324:643–647
Mountain DJ, Singh M, Singh K (2008) Downregulation of VEGF-D expression by interleukin-1beta in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells is mediated by MAPKs and PKCalpha/beta1. J Cell Physiol 215:337–343
Nicosia RF, Ottinetti A (1990) Modulation of microvascular growth and morphogenesis by reconstituted basement membrane gel in three-dimensional cultures of rat aorta: a comparative study of angiogenesis in matrigel, collagen, fibrin, and plasma clot. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 26:119–128
Staton CA, Stribbling SM, Tazzyman S et al (2004) Current methods for assaying angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Int J Exp Pathol 85:233–248
Kim ES, Serur A, Huang J et al (2002) Potent VEGF blockade causes regression of coopted vessels in a model of neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:11399–11404
Dickson PV, Hamner JB, Sims TL et al (2007) Bevacizumab-induced transient remodeling of the vasculature in neuroblastoma xenografts results in improved delivery and efficacy of systemically administered chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 13:3942–3950
Kamat AA, Merritt WM, Coffey D et al (2007) Clinical and biological significance of vascular endothelial growth factor in endometrial cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:7487–7495
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W et al (2004) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2335–2342
Reck M, von Pawel J, Zatloukal P et al (2009) Phase III trial of cisplatin plus gemcitabine with either placebo or bevacizumab as first-line therapy for nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: AVAil. J Clin Oncol 27:1227–1234
Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM et al (2003) A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N Engl J Med 349:427–434
Yang JC (2004) Bevacizumab for patients with metastatic renal cancer: an update. Clin Cancer Res 10:6367S–6370S
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
McMahon G (2000) VEGF receptor signaling in tumor angiogenesis. Oncologist 5:3–10
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25:581–611
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:1011–1027
Bergers G, Benjamin LE (2003) Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 3:401–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, K., He, K., Teng, F. et al. FP3: a novel VEGF blocker with antiangiogenic effects in vitro and antitumour effects in vivo . Clin Transl Oncol 13, 878–884 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-011-0749-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-011-0749-z