Abstract
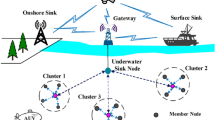
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) consist of small battery-limited devices called sensor nodes. The communication between sensor nodes is a type of peer-to-peer communication, since each node has the same capability and role. One of the recent application areas of these nodes is underwater sensing. Communication in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks (UWSN) is challenging since radio frequencies cannot be used. Instead acoustic waves, which cause extra challenges, are used in UWSN. Since UWSNs are deployed in hostile environment, nodes can be captured by an adversary. In order to secure UWSNs, key distribution problem must be addressed. Moreover, UWSNs are inherently mobile since the nodes may be drifted in the sea. In this paper, we propose a key distribution model which is applied for two group mobility models, namely nomadic mobility model and meandering mobility model. In both schemes hierarchical structure is used and communication is handled via well-known Blom’s key distribution scheme. Our simulation results show that mobility causes some temporary decreases in the connectivity, but our schemes help to heal the connectivity performance in time. Moreover, our schemes show good resiliency performance such that capture of some nodes by an adversary only causes very small amount of links between uncaptured nodes to be compromised.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz IF, Su W, Sankarasubramaniam Y, Cayirci E (2002) Wireless sensor networks: a survey. Comput Netw 38(4):393–422
Akyildiz IF, Pompili D, Melodia T (2004) Challenges for efficient communication in underwater acoustic sensor networks. ACM SIGBED Rev 1(1)
Blom R (1985) An optimal class of symmetric key generation systems. In: Beth T, Cot N, Ingemarsson I (eds) Advances in cryptology: proceedings of EUROCRYPT 84, lecture notes in computer science, vol. 209, Springer-Verlag, 335–338
Camp T, Boleng J, Davies V (2002) A survey of mobility models for AD hoc network research. In: Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing (WCMC): special issue on mobile Ad Hoc networking: research. Trends Appl 2(5):483–502
Caruso A, Paparella F, Vieira LFM, Erol M, Gerla M (2008) The meandering current mobility model and its impact on underwater mobile sensor networks. In: Proceedings of INFOCOM, 221–225.
Chandrasekhar V, Seah WK, Choo YS, Ee HV (2006) Localization in underwater sensor networks: survey and challenges. In: WUWNet’06, Los Angeles, CA, USA, pp 33–40
Chen K, Zhou Y, He J (2009) A localization scheme for underwater wireless sensor networks. In: Int’l J Adv Sci Tech 4:9–16
Cheng Y, Agrawal DP (2007) An improved key distribution mechanism for large-scale hierarchical wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw 5(1):35–48
Cui JH, Kong J, Gerla M, Zhou S (2006) The challenges of building scalable mobile underwater wireless sensor networks for aquatic applications. IEEE Netw (0890–8044), 12–17, May/June 2006
Cui J-H, Xie P, Yan H, Hu T, Shi Z, Fei Y, Zhou S, Zhou Z, Peng Z (2009) Aqua-sim: an ns-2 based simulator for underwater sensor networks. In: Proc. of IEEE OCEANS’09, Biloxi, MS
Detweiller C, Vasilescu I, Rus D (2007) An underwater sensor network with dual communications, sensing, and mobility, presented at Oceans 2007—Europe, Aberdeen, pp 1–6
Dhurandher SK, Khairwal S, Obaidat MS, Misra S (2009) Efficient data acquisition in underwater wireless sensor Ad Hoc networks. Wirel Commun IEEE 16(6):70–78. doi:10.1109/MWC.2009.5361181
Dhurandher S, Obaidat M, Gupta M (2012) An acoustic communication based AQUA-GLOMO simulator for underwater networks. Human-centric Comput Info Sci 2:3
Ponomarchuk Y, Seo D (2010) Intrusion detection based on traffic analysis and fuzzy inference system in wireless sensor networks. J Converg 1(1):35–42
Sarkar P, Saha A (2011) Security enhanced communication in wireless sensor networks using Reed-Muller codes and partially balanced incomplete block designs. J Converg 2(1):23–30
Syed A, Heidemann J (2006) Time synchronization for high latency acoustic networks. In: Proc. of infocom. Barcelona, Spain, April 2006, pp 1–12
Tseng F, Chou L, Chao H (2011) A survey of black hole attacks in wireless mobile Ad Hoc networks. Human-centric Comput Info Sci 1:4
Ünlü A, Levi A (2008) Two-tier, location-aware and highly resilient key predistribution scheme for wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of BCS visions of computer science conference, pp 355–366,September 2008, London, UK
Ünlü A, Levi A (2010) Two-tier, scalable and highly resilient key predistribution scheme for location-aware wireless sensor network deployments. Mob Netw Appl 15(4):517–529
Ünlü A, Armağan Ö, Levi A, Savaş E, Erçetin Ö (2007) Key predistribution schemes for sensor networks for continuous deployment scenario. IFIP/TC6 Networking 2007, Springer, LNCS 4479, pp 239–250, May 2007
Vasilescu I, Kotay K, Rus D, Dunbabin M, Corke P (2005) Data collection, storage, and retrieval with an underwater sensor network. In: SenSys’05, San Diego, California, USA, pp 154–165
Wander A, Gura N, Eberle H, Gupta V, Shantz S (2005) Energy analysis of public-key cryptography for wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE international conference on pervasive computing and communication 2005 (PerCom’05), IEEE Comput Soc, pp 324–328
Acknowledgements
We thank Merve Sahin, Salim Sarimurat and A. Onur Catakoglu for their careful review on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is supported by Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) under grant 110E180
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalkan, K., Levi, A. Key distribution scheme for peer-to-peer communication in mobile underwater wireless sensor networks. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 7, 698–709 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-012-0182-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-012-0182-2