Abstract
Purpose
The aim was to investigate whether the quantitation of the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA levels can predict HBV reactivation and advanced liver disease after spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) seroconversion.
Methods
A total of 121 patients who experienced spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion were included in this longitudinal study. Serial HBsAg and HBV DNA levels were measured before and after HBeAg seroconversion.
Results
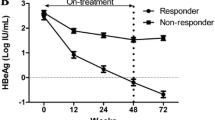
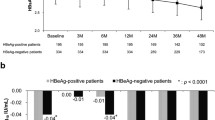
Of the 121 patients, 32 experienced HBV reactivation and six achieved an HBsAg loss after HBeAg seroconversion during the follow-up period. The decline in the HBsAg level was considerably more pronounced in patients without HBV reactivation when compared to those with HBV reactivation (p = 0.016). Multivariate analysis revealed that the age of >40 years at HBeAg seroconversion, male sex, and HBsAg decline, and HBV DNA levels at month 12 after HBeAg seroconversion were independent factors for the development of HBeAg-negative hepatitis. All the six patients who achieved HBsAg loss had HBsAg level of <1,000 IU/mL at month 12 after HBeAg seroconversion (p < 0.001). The risk of HBeAg-negative hepatitis, cirrhosis, and HCC was substantially increased in patients who had a combination of both, i.e., no decline in the HBsAg level and HBV DNA level of >104 copies/mL at month 12 after HBeAg seroconversion.
Conclusions
Combining HBsAg reduction and HBV DNA levels at month 12 after HBeAg seroconversion was a useful marker to predict clinical outcomes in spontaneous HBeAg seroconverters. HBsAg level of <1,000 IU/mL at month 12 after HBeAg seroconversion could predict the HBsAg loss after HBeAg seroconversion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liaw YF, Chu CM, Su IJ, et al. Clinical and histological events preceding hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic type B hepatitis. Gastroneterology 1983;84:216–219
Chu CM, Karayiannis P, Fowler MJ, et al. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Taiwan: study of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum. Hepatology 1985;5:431–434
Chu CM, Hung SJ, Lin J, Tai DI, Liaw YF. Natural history of hepatitis B e antigen to antibody seroconversion in patients with normal serum aminotransferase levels. Am J Med 2004;116:829–834
Hsu YS, Chien RN, Yeh CT, et al. Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2002;35:1522–1527
Hadziyannis SJ, Vassilopoulos D. Hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2001;34:617–624
Brunetto MR, Giarin MM, Oliveri F, et al. Wild-type and e antigen-minus hepatitis B virus in course of chronic hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991;88:4186–4190
Naoumov NV, Schneider R, Grötzinger T, et al. Precore mutant hepatitis B virus infection and liver disease. Gastroenterology 1992;102:538–543
Chu CM, Liaw YF. Predictive factors for reactivation of hepatitis B following hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2007;133:1458–1465
Chu CM, Liaw YF. Genotype C hepatitis B virus infection is associated with a higher risk of reactivation of hepatitis B and progression to cirrhosis than genotype B: a longitudinal study of hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients with normal aminotransferase levels at baseline. J Hepatol 2005;43:411–417
Chu CJ, Hussain M, Lok AS. Hepatitis B virus genotype B is associated with earlier HBeAg seroconversion compared with hepatitis B virus genotype C. Gastroenterology 2002;122:1756–1762
Chen YC, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Age-specific prognosis following spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010;51:435–444
Chen CH, Lee CM, Wang JH, et al. Correlation of quantitative assay of hepatitis B surface antigen and HBV DNA levels in asymptomatic hepatitis B virus carriers. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;16:1213–1218
Werle-Lapostolle B, Bowden S, Locarnini S, et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1750–1758
Thompson AJ, Nguyen T, Iser D, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers: disease phase influences correlation with viral load and intrahepatic hepatitis B virus markers. Hepatology 2010;51:1933–1944
Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Su TH, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels predict surface antigen loss in hepatitis B e antigen seroconverters. Gastroenterology 2011;141:517–525
Lin DY, Sheen IS, Chiu CT, et al. Ultrasonographic changes of early liver cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis B: a longitudinal study. J Clin Ultrasound 1993;21:303–308
Hung CH, Lu SN, Wang JH, et al. Correlation between ultrasonographic and pathologic diagnoses of hepatitis B and C virus-related cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol 2003;38:153–157.
Tai DI, Lin SM, Sheen IS, et al. Long-term outcome of hepatitis B e antigen-negative hepatitis B surface antigen carriers in relation to changes of alanine aminotransferase levels over time. Hepatology 2009;49:1859–1867
Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2005;42:1208–1236
Liaw YF, Leung N, Kao JH, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2008 update. Hepatol Int 2008;2:263–283
Su TH, Hsu CS, Chen CL, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen concentration correlates with HBV DNA level in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Antivir Ther 2010;15:1133–1139
Chen CH, Hung CH, Lee CM, et al. Pre-S deletion and complex mutations of hepatitis B virus related to advanced liver disease in HBeAg-negative patients. Gastroenterology 2007;133:1466–1474
Chen CH, Lee CM, Lu SN, et al. Clinical significance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotypes and precore and core promoter mutations affecting HBV e antigen expression in Taiwan. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:6000–6006
Chen CH, Lee CM, Lu SN, et al. Comparison of sequence changes of precore and core promoter regions in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with and without HBeAg clearance in lamivudine therapy. J Hepatol 2006;44:76–82
Chen CH, Lee CM, Hung CH, et al. Clinical significance and evolution of core promoter and precore mutations in HBeAg-positive patients with HBV genotype B and C: a longitudinal study. Liver Intern 2007;27:806–815
Mizokami M, Nakano T, Orito E, et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype assignment using restriction fragment length polymorphism patterns. FEBS Lett 1999;450:66–71
Kumar M, Chauhan R, Gupta N, et al. Spontaneous increases in alanine aminotransferase levels in asymptomatic chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients. Gastroenterology 2009;136:1272–1280
Jaroszewicz J, Calle Serrano B, Wursthorn K, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infection: a European perspective. J Hepatol 2010;52:514–522
Brunetto MR, Oliveri F, Colombatto P, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen serum levels help to distinguish active from inactive hepatitis B virus genotype D carriers. Gastroenterology 2010;139:483–490
Sonneveld MJ, Rijckborst V, Boucher CA, Hansen BE, Janssen HL. Prediction of sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2b for hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using on-treatment hepatitis B surface antigen decline. Hepatology 2010;52:1217–1251
Chan HL, Wong VW, Wong GL, et al. A longitudinal study on the natural history of serum hepatitis B surface antigen changes in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010;52:1232–1241
Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Chen CL, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus-DNA levels correlate with long-term adverse outcomes in spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconverters. J Infect Dis 2012;205:54–63
Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, et al. Risk evaluation of viral load elevation and associated liver disease/cancer-in HBV. Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology 2006;130:678–686
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 2006;295:65–73
Chen YC, Sheen IS, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Prognosis following spontaneous HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients with or without concurrent infection. Gastroenterology 2002;123:1084–1089
Yuen MF, Wong DK, Sablon E, et al. HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B in the Chinese: virological, histological, and clinical aspects. Hepatology 2004;39:1694–1701
Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, et al. REVEAL-HBV Study Group. Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: a community-based follow-up study. Gastroenterology 2010;139:474–482
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by a grant (No. CMRPG890031) from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, SC., Lu, SN., Lee, CM. et al. Combining the HBsAg decline and HBV DNA levels predicts clinical outcomes in patients with spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion. Hepatol Int 7, 489–499 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-012-9382-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-012-9382-3