Abstract
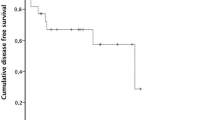
The aim of this article is to identify the cellular mitotic activity using Ki-67 monoclonal antibody for predicting relapses of nasal polyposis after surgery. A prospective study was conducted at Kartal Training and Research Hospital Otolaryngology Department between January 2006 and September 2008. Nasal polyps were obtained from all patients and pathological materials were analyzed for the Ki-67 staining using immunohistochemistry. Patients were followed after surgery for 12 months for relapse. There was no statistically significant difference between recurrent and nonrecurrent polyps. Polyp recurrence has a multifactorial origin. Ki-67 index alone does not provide sufficient information about polyp recurrence before the operation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coste A, Rateau JG, Roudot-Thoraval F, Chapelin C, Gilain L, Poron F, Peynegre R, Bernaudin JF, Escudier E (1996) Increased epithelial cell proliferation in nasal polyps. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122(4):432–436
Huisman MA, De Heer E, Grote JJ (2003) Cholesteatoma epithelium is characterized by increased expression of Ki-67, p53 and p21, with minimal apoptosis. Acta Otolaryngol 123(3):377–382
Koda M, Sulkowski S, Kanczuga-Koda L, Surmacz E, Sulkowska M (2004) Expression of ERalpha, ERbeta and Ki-67 in primary tumors and lymph node metastases in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 11(4):753–759
Liu M, Lawson G, Delos M, Jamart J, Ide C, Coche E, Weynand B, Desuter G, Hamoir M, Remacle M, Marbaix E (2003) Predictive value of the fraction of cancer cells immunolabeled for proliferating cell nuclear antigen or Ki-67 in biopsies of head and neck carcinomas to identify lymph node metastasis: comparison with clinical and radiologic examinations. Head Neck 25(4):280–288
Bussi M, Carlevato MT, Majore L, Battaglio S, Napoli P, Cortesina G (1995) The problem of recurrence of rhino-sinusal polyposis: pilot trial with locally administered azelastine HCL in the prevention of relapses. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 15(2):101–106
Morinaka S, Nakamura H (2000) Inflammatory cells in nasal mucosa and nasal polyps. Auris Nasus Larynx 27(1):59–64
Petruson B, Hansson HA, Petruson K (1988) Insulin-like growth factor I is a possible pathogenic mechanism in nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol 106(12):156–160
Xu Y, Wu Z, Tao Z, Hua Q, Jin K (2003) Possible role of transforming growth factor alpha on the cholesteatoma growth regulation. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi 17(1):32–34
Hsu MC, Shun CT, Liu CM (2002) Increased epithelial cell proliferation in nasal polyps. J Formos Med Assoc 101(3):227–229
Coste A, Rateau JG, Bernaudin JF, Peynegre R, Escudier E (1996) Nasal polyposis pathogenesis: a flow cytometric and immunohistochemical study of epithelial cell proliferation. Acta Otolaryngol 116(5):755–761
Bruno E, Mohamed El, Alessandrini M, Russo S, Schiaroli S, De Lorenzo A, Di Girolamo A (2002) Long-term follow-up of cellular proliferation as a predictive index for the relapse of nasal polyposis. Am J Rhinol 16(5):237–241
Welkoborsky HJ, Portmann K, Hoffmann F, Jacob R, Mann WJ, Amedee RG (2000) Proliferative activity and cytometric characteristics in polyps of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Am J Rhinol 14(2):87–91
Kösem M, Bulut G, Kaya Z (2010) Analysis of Ki-67 immunoreactivity in recurring and nonrecurring nasal polyps. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 39(4):464–467
Cortesina G, Cardarelli L, Riontino E, Majore L, Ragona R, Bussi M (1999) Multi-center study of recurrent nasal sinus polyposis: prognostic factors and possibility of prophylaxis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 19(6):315–324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tezer, I., Celebi Erdivanli, O., Sanli, A. et al. Could Cellular Proliferation Be a Predictive Index for the Relapse of Nasal Polyposis and Down-Regulated by Nasal Steroid Treatment?. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65 (Suppl 2), 329–332 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-012-0485-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-012-0485-x