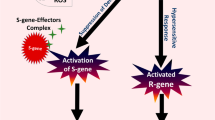
Abstract
The gene-for-gene relationship of host–pathogen interaction explained by H. H. Flor in mid of the 20th century set a milestone in understanding the biochemical and genetic basis of plant diseases and several components involved in plant–pathogen interactions. It highlighted the importance of accomplishing differential sets and understanding the pathogen population structure, it further led to the identification and cloning of several resistance (R) genes in plants. These R genes have been deployed and altered for fighting against diseases in a large number of crops using various conventional approaches and biotechnological tools. Identification of R genes and their corresponding Avr genes in many cases played a significant role in understanding of R-Avr gene interactions. Rapid cloning of R genes and editing of susceptible R genes are the other avenues that have broadened the horizon of utilizing R genes in crop improvement programmes. Further, combining R genes with quantitative disease resistance genes has paved the way to develop durable resistance in cultivars. The recent advances in genetics, genomics, bioinformatics and other OMICS tools are now providing greater prospects for deeper understanding of host–pathogen interaction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adugna A. 2004 Alternate approaches for deploying genes for disease resistance in crop plants. Asian. J. Pl. Sci. 3, 618–623.
Agrios G. N. 1969 Plant pathology, Elsevier Academic Press, UK.
Ali S., Gladieux P., Leconte M., Gautier A., Justesen A. F., Hovmøller M. S. et al. 2014 Origin, migration routes and worldwide population genetic structure of the wheat yellow rust pathogen Puccinia striiformis f sp tritici. PLoS Pathog. 10, e1003903.
Ansan-Melayah D., Balesdent M. H., Delourme R., Pilet M. L., Tanguy X., Renard M. et al. 1998 Genes for race-specific resistance against blackleg disease in Brassica napus L. Plant Breed. 117, 373–378.
Arora S., Steuernagel B., Gaurav K., Chandramohan S., Long Y., Matny O. et al. 2019 Resistance gene cloning from a wild crop relative by sequence capture and association genetics. Nat. Biotechnol. 372, 139–143.
Bai Y., Pavan S., Zheng Z., Zappel N. F., Reinstädler A., Lotti C. et al. 2008 Naturally occurring broad-spectrum powdery mildew resistance in a Central American tomato accession is caused by loss of Mlo function. Mol. Plant. Microbe. Interact. 21, 30–39.
Bariana H. S. 2003 Breeding for disease resistance. In Encyclopedia of applied plant sciences, pp. 244–253. Harcourt, UK.
Bent A. F. and Mackey D. 2007 Elicitors, effectors, and R genes, the new paradigm and a lifetime supply of questions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 45, 399–436.
Bent A. F., Kunkel B. N., Dahlbeck D., Brown K. L., Schmidt R., Giraudat J. et al. 1994 RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana, a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265, 1856–1860.
Bevan J. R., Clarke D. D. and Crute I. R. 1993 Resistance to Erysiphe fischeri in two populations of Senecio vulgaris. Plant. Pathol. 42, 636–646.
Biffen R. H. 1905 Mendel’s laws of inheritance and wheat breeding. J. Agri. Sci. 1, 4–8.
Blanvillain-Baufumé S., Reschke M., Sole M., Auguy F., Doucoure H., Szurek B. et al. 2017 Targeted promoter editing for rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzaea pv. Oryzeae reveals differential activities for SWEET 14-inducing TAL effectors. Plant Biotechnol. J. 15, 306–317.
Browning J. A. and Frey K. J. 1969 Multiline cultivars as a means of disease control. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 7, 355–382.
Ceasar S. A. and Ignacimuthu S. 2012 Genetic engineering of crop plants for fungal resistance: role of antifungal genes. Biotechnol. Lett. 34, 995–1002.
Center P. G. 1994 The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N, similarity to toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 73, 1101–1115.
Cesari S., Thilliez G., Ribot C., Chalvon V., Michel C., Jauneau A. et al. 2013 The rice resistance protein pair RGA4/RGA5recognizes the Magnaporthe oryzae effectors AVR-Pia and AVR1-CO39 by direct binding. Plant Cell 25, 1463–1481.
Chaijuckam P., Baek J. M., Greer C. A., Webster R. K. and Davis R. M. 2010 Population structure of Rhizoctonia oryzae-sativae in California rice fields. Phytopathol. 100, 502–510.
Chen R. S., Boeger J. M. and McDonald B. A. 1994 Genetic stability in a population of a plant pathogenic fungus over time. Mol. Ecol. 3, 209–218.
Chen L. Q., Hou B. H., Lalonde S., Takanaga H., Hartung M. L., Qu X. et al. 2010 Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 468, 527–532..
Consonni C., Humphry M. E., Hartmann H. A., Livaja M., Durner J., Westphal L. et al. 2006 Conserved requirement for a plant host cell protein in powdery mildew pathogenesis. Nat. Genet. 38, 716–720.
Croll D. and Laine A. L. 2016 What the population genetic structures of host and pathogen tell us about disease evolution? New Phytologist 212, 537–539.
Dadrezaie S. T., Lababidi S., Nazari K., Goltapeh E. M., Afshari F., Alo F. et al. 2013 Molecular genetic diversity in Iranian populations of Puccinia triticina, the causal agent of wheat leaf rust. Am. J. Plant Sci. 4, 1375.
Dixon M. S., Jones D. A., Keddie J. S., Thomas C. M., Harrison K. and Jones J. D. G. 1996 The tomato Cf-2 disease resistance locus comprises two functional genes encoding leucine-rich repeat proteins. Cell 84, 451–459.
Dong O. X. and Ronald P. C. 2019 Genetic engineering for disease resistance in plants, recent progress and future perspectives. Plant. Physiol. 180, 26–38.
Doubly J. A., Flor H. H. and Clagett C. O. 1960 Relation of antigens of Melampsora lini and Linum usitatissimum to resistance and susceptibility. Science 131, 229–229.
Ellingboe A. H. 1982 Host resistance and host–parasite interactions: A Perspective. In Phytopathogenic prokaryotes, pp. 103-117. Academic Press, New York.
Ellis J. G., Lagudah E. S., Spielmeyer W. and Dodds P. N. 2014 The past, present and future of breeding rust resistant wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 5, 641.
Ennos R. A. and McConnell K. C. 1995 Using genetic markers to investigate natural selection in fungal populations. Can. J. Bot. 73, 302–310.
Felix G., Duran J. D., Volko S. and Boller T. 1999 Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most conserved domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant J. 18, 265–276.
Flor H. H. 1942a Inheritance of pathogenicity in a cross between physiologic races 22 and 24 of Melampsora lini. Phytopathol. 32, 5.
Flor H. H. 1942b Inheritance of pathogenicity in Melampsora lini. Phytopathol. 32, 653–669.
Flor H. H. 1946 Genetics of pathogenicity in Melampsora lini. J. Agric. Res. 73, 335–357.
Flor H. H. 1955 Host-parasite interaction in flax-rust-its genetics and other implications. Phytopathology 46, 680–685.
Flor H. H. 1956 The complementary genic systems in flax and flax rust. Adv. Gen. 8, 29–54.
Flor H. H. and Comstock V. E. 1972 Identification of rust-conditioning genes in flax cultivars. Crop Sci. 12, 800–804.
Gabriel D. W., Loschke D. C. and Rolfe B. G. 1988 Gene-for-gene recognition, the ion channel defense model. In Molecular genetics of plant-microbe interactions, pp. 3-14. American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul.
Galvez L. C., Banerjee J., Pinar H. and Mitra A. 2014 Engineered plant virus resistance. Plant. Sci. 228, 11–25.
Gétaz M., Krijger M., Rezzonico F., Smits T. H., van der Wolf J. M. and Pothier J. F. 2018 Genome based population structure analysis of the strawberry plant pathogen Xanthomonas fragariae reveals two distinct groups that evolved independently before its species description. Microb. Genom. 4, e000189.
Giannakopoulou A., Steele J. F. C., Segretin M. E., Bozkurt T. O., Zhou J., Robatzek S. et al. 2015 Tomato I2 immune receptor can be engineered to confer partial resistance to the oomycete Phytophthora infestans in addition to the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 28, 1316–1329.
Gobbin D., Rumbou A., Linde C. C. and Gessler C. 2006 Population genetic structure of Plasmopara viticola after 125 years of colonization in European vineyards. Mol. Plant Pathol. 7, 519–531.
Gomez-Casati D. F., Pagani M. A., Busi M. V. and Bhadauria V. 2016 Omics Approaches for the Engineering of Pathogen Resistant Plants. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 19, 89–98.
Gómez-Gómez L. and Boller T. 2000 FLS2: an LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell 5, 1003–1011.
Gu K., Yang B., Tian D., Wu L., Wang D., Sreekala C. et al. 2005 R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 435, 1122–1125.
Halperin S. O., Tou C. J., Wong E. B., Modavi C., Schaffer D. V. and Dueber J. E. 2018 CRISPR-guided DNA polymerases enable diversification of all nucleotides in a tunable window. Nature 560, 248–252.
Huang N., Angeles E. R. and Domingo J. 1997 Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice, marker assisted selection using RFLP and PCR. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95, 313–320.
Hückelhoven R. and Panstruga R. 2011 Cell biology of the plantpowdery mildew interaction. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 14, 738–746.
Humphry M., Reinstaedler A., Ivanov S., Bisseling T. O. and Panstruga R. 2011 Durable broad spectrum powdery mildew resistance in pea er1 plants is conferred by natural loss-of function mutations in PsMLO1. Mol. Plant Pathol. 12, 866–878.
Irzykowska L., Weber Z. and Bocianowski J. 2012 Comparison of Claviceps purpurea populations originated from experimental plots or fields of rye. Open Life Sci. 7, 839–849.
Ishibashi K., Kezuka Y., Kobayashi C., Kato M., Inoue T., Nonaka T. et al. 2014 Structural basis for the recognition-evasion arms race between Tomato mosaic virus and the resistance gene Tm-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, E3486–E3495.
Jana T., Sharma T. R. and Singh N. K. 2005 SSR-based detection of genetic variability in the charcoal root rot pathogen Macrophomina phaseolina. Mycol. Res. 109, 81–86.
Jia H., Orbovic V., Jones J. B. and Wang N. 2016 Modification of the PthA4 effector binding elements in type I CsLOB1 promoter using Cas9/sgRNA to produce transgenic Duncan grapefruit alleviating XccDpthA4: dCsLOB1.3 infection. Plant Biotechnol. J. 14, 1291–1301.
Jiang W., Zhou H., Bi H., Fromm M., Yang B. and Weeks D. P. 2013 Demonstration of CRISPR/Cas9/sgRNA- mediated targeted gene modification in Arabidopsis, tobacco, sorghum and rice. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, e188.
Jiménez-Becerril M. F., Hernández-Delgado S., Solís-Oba M. and González Prieto J. M. 2018 Analysis of mitochondrial genetic diversity of Ustilago maydis in Mexico. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 29, 1–8.
Jiwan D., Roalson E. H., Main D. and Dhingra A. 2013 Antisense expression of peach mildew resistance locus O PpMlo1 gene confers cross-species resistance to powdery mildew in Fragaria x ananassa. Transgenic Res. 22, 1119–1131.
Johal G. S. and Briggs S. P. 1992 Reductase activity encoded by the HM1 disease resistance gene in maize. Science 258, 985–987.
Jones J. D. and Dangl J. L. 2006 The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323–329.
Jones D. A., Thomas C. M., Hammond-Kosack K. E., Balint-Kurti P. J. and Jones J. D. 1994 Isolation of the tomato Cf-9 gene for resistance to Cladosporium fulvum by transposon tagging. Science 266, 789–793.
JungehÜLsing U. and Tudzynski P. 1997 Analysis of genetic diversity in Claviceps purpurea by RAPD markers. Mycol. Res. 101, 1–6.
Jupe F., Witek K., Verweij W., Śliwka J., Pritchard L., Etherington G. J. et al. 2013 Resistance gene enrichment sequencing Ren Seq enables reannotation of the NB-LRR gene family from sequenced plant genomes and rapid mapping of resistance loci in segregating populations. Plant J. 76, 530–544.
Jupe F., Chen X., Verweij W., Witek K., Jones J. D. and Hein I. 2014 Genomic DNA library preparation for resistance gene enrichment and sequencing RenSeq in plants. In Plant-pathogen interactions Humana Press, Totowa, pp. 291–303.
Keen N. T. and Bruegger B. 1977 Phytoalexins and chemicals that elicit their production in plants. In Host plant resistance to pests American Chemical Society, Washington, pp. 1–26.
Keswani C., Bisen K., Singh S. P., Sarma B. K. and Singh H. B. 2016 A proteomic approach to understand the tripartite interactions between plant-Trichoderma-pathogen: investigating the potential for efficient biological control. In Plant, soil and microbes, pp. 79-93. Springer.
Kim S. H., Qi D., Ashfield T., Helm M. and Innes R. W. 2016 Using decoys to expand the recognition specificity of a plant disease resistance protein. Science 351, 684–687.
Kooman-Gersmann M., Honee G., Bonnema G. and De Wit P. 1996 A high-affinity binding site for the AVR9 peptide elicitor of Cladosporium fulvum is present on plasma membranes of tomato and other solanaceous plants. Plant Cell 8, 929–938.
Kourelis J. and van der Hoorn R. A. 2018 Defended to the nines, 25 years of resistance gene cloning identifies nine mechanisms for R protein function. Plant Cell 30, 285–299.
Krasileva K. V., Dahlbeck D. and Staskawicz B. J. 2010 Activation of an Arabidopsis resistance protein is specified by the in planta association of its leucine-rich repeat domain with the cognate oomycete effector. Plant Cell 22, 2444–2458.
Kroj T., Chanclud E., Michel-Romiti C., Grand X. and Morel J. B. 2016 Integration of decoy domains derived from protein targets of pathogen effectors into plant immune receptors is widespread. New Phytol. 210, 618–626.
Kumari M., Rai A. K., Devanna B. N., Singh P. K., Kapoor R., Rajashekara H. et al. 2017 Co-transformation mediated stacking of blast resistance genes Pi54 and Pi54rh in rice provides broad spectrum resistance against Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant. Cell. Rep. 36, 1747–1755.
Lewis J. D., Wu R., Guttman D. S. and Desveaux D. 2010 Allelespecific virulence attenuation of the Pseudomonas syringae HopZ1a type III effector via the Arabidopsis ZAR1 resistance protein. PLoS Genet. 6, e1000894..
Li T., Liu B., Spalding M. H., Weeks D. P. and Yang B. 2012 High-efficiency TALEN-based gene editing produces disease-resistant rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 390–392.
Li H., Zhou G. Y., Liu J. A. and Xu J. 2016 Population genetic analyses of the fungal pathogen Colletotrichum fructicola on tea-oil trees in China. PloS One 11, e0156841.
Liu Q., Yuan M., Zhou Y., Li X., Xiao J. and Wang S. 2011 A paralog of the MtN3/saliva family recessively confers race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 34, 1958–1969.
Loegering W. Q. and Ellingboe A. H. 1987 H. H. Flor, Pioneer in phytopathology. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 25, 59–66.
Lorang J. M., Sweat T. A. and Wolpert T. J. 2007 Plant disease susceptibility conferred by a “resistance” gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 14861–14866.
Luderer R. 2001 No evidence for binding between resistance gene product Cf-9 of tomato and avirulence gene product AVR9 of Cladosporium fulvum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 14, 867–876.
Luo Y., Ma T., Zhang A., Ong K. H., Li Z., Yang J. and Yin Z. 2016 Marker-assisted breeding of the rice restorer line Wanhui 6725 for disease resistance, submergence tolerance and aromatic fragrance. Rice 9, 1–13.
Maciel J. L., Ceresini P. C., Castroagudin V. L., Zala M., Kema G. H. and McDonald B. A. 2014 Population structure and pathotype diversity of the wheat blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae 25 years after its emergence in Brazil. Phytopathology 104, 95–107.
Martin G. B. 1996 Molecular cloning of plant disease resistance genes. In Plant-microbe interactions Springer, Boston, pp. 1–32.
Martin G. B., Brommonschenkel S. H., Chunwongse J., Frary A., Ganal M. W., Spivey R. et al. 1993 Map-based cloning of a protein kinase gene conferring disease resistance in tomato. Science 262, 1432–1436.
McDonald B. A. 1997 The population genetics of fungi, tools and techniques. Phytopathol. 874, 448–453.
McDonald B. A. and Linde C. 2002 Pathogen population genetics, evolutionary potential and durable resistance. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 40, 349–379.
McDowell J. M. and Woffenden B. J. 2003 Plant disease resistance genes, recent insights and potential applications. Trends Biotechnol. 21, 178–183.
Mi J., Yang D., Chen Y., Jiang J., Mou H., Huang J. et al. 2018 Accelerated molecular breeding of a novel P/TGMS line with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight in two-line hybrid rice. Rice 11, 11.
Miedaner T. and Korzun V. 2012 Marker-assisted selection for disease resistance in wheat and barley breeding. Phytopathology 1026, 560–566.
Mindrinos M., Katagiri F., Yu G. L. and Ausubel F. M. 1994 The A. thaliana disease resistance gene RPS2 encodes a protein containing a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeats. Cell 78, 1089–1099.
Moges A. D., Admassu B., Belew D., Yesuf M., Njuguna J., Kyalo M. and Ghimire S. R. 2016 Development of microsatellite markers and analysis of genetic diversity and population structure of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides from Ethiopia. PloS One 11(3), e0151257.
Mohan K. M., Madhav M. S., Prasad M. S., Devi S. J., Kumar G. R. and Viraktamath B. C. 2012 Analysis of population structure of Magnaporthe grisea using genome specific microsatellite markers. Curr. Trends. Biotechnol. Pharm. 6, 173–182.
Mundt C. C. 2002 Use of multiline cultivars and cultivar mixtures for disease management. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 40, 381–410.
Oliva R., Ji C., Atienza-Grande G., Huguet-Tapia J., Prez-Quintero A. and Li T. 2019 Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 1344–1350.
Onaga G., Wydra K., Koopmann B., Séré Y. and von Tiedemann A. 2015 Population structure, pathogenicity and mating type distribution of Magnaporthe oryzae isolates from East Afr. Phytopathol. 105, 1137–1145.
Owati A., Agindotan B. and Burrows M. 2019 First microsatellite markers developed and applied for the genetic diversity study and population structure of Didymella pisi associated with ascochyta blight of dry pea in Montana. Fungal Biol. 123, 384–392.
Panwar V., McCallum B. and Bakkeren G. 2013a Endogenous silencing of Puccinia triticina pathogenicity genes through in planta-expressed sequences leads to the suppression of rust diseases on wheat. Plant J. 73, 521–948.
Panwar V., McCallum B. and Bakkeren G. 2013b Host-induced gene silencing of wheat leaf rust fungus Puccinia triticina pathogenicity genes mediated by the Barley stripe mosaic virus. Plant Mol. Biol. 81, 595–608.
Pavan S., Schiavulli A., Appiano M., Marcotrigiano A. R., Cillo F., Visser R. G. F. et al. 2011 Pea powdery mildew er1 resistance is associated to loss-of-function mutations at a MLO homologous locus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 123, 1425–1431.
Piffanelli P., Zhou F., Casais C., Orme J., Jarosch B., Schaffrath U. et al. 2002 The barley MLO modulator of defense and cell death is responsive to biotic and abiotic stress stimuli. Plant Physiol. 129, 1076–1085.
Pink D. A. and Hand P. 2003 Plant resistance and strategies for breeding resistant varieties. Plant Protect. Sci. 38, 9–14.
Pink D. and Puddephat I. 1999 Deployment of disease resistance genes by plant transformation a ‘mix and match’ approach. Trends Plant. Sci. 4, 71–75.
Pombo M. A., Zheng Y., Fernandez-Pozo N., Dunham D. M., Fei Z. and Martin G. B. 2014 Transcriptomic analysis reveals tomato genes whose expression is induced specifically during effector-triggered immunity and identifies the Epk1 protein kinase which is required for the host response to three bacterial effector proteins. Genome Biol. 15, 492.
Pradhan S. K., Nayak D. K., Mohanty S., Behera L., Barik S. R., Pandit E. et al. 2015 Pyramiding of three bacterial blight resistance genes for broad-spectrum resistance in deepwater rice variety Jalmagna. Rice 8, 19.
Prasad P., Savadi S., Bhardwaj S. C. and Gupta P. K. 2020 The progress of leaf rust research in wheat. Fungal Biol. 124, 537–550.
Pruitt R. N. 2015 The rice immune receptor XA21 recognizes a tyrosine-sulfated protein from a Gram-negative bacterium. Sci. Adv. 1, e1500245.
Ravensdale M., Bernoux M., Ve T., Kobe B., Thrall P. H., Ellis J. G. and Dodds P. N. 2012 Intramolecular interaction influences binding of the Flax L5 and L6 resistance proteins to their AvrL567 ligands. PLoS Pathog. 8, e1003004.
Rêgo T. J., Elena G., Correia K. C., Tovar-Pedraza J. M., Câmara M. P., Armengol J. et al. 2019 Genetic diversity and population structure of Lasiodiplodia theobromae from different hosts in northeastern Brazil and Mexico. Plant Pathol. 68, 930–938.
Römer P., Hahn S., Jordan T., Strauss T., Bonas U. and Lahaye T. 2007 Plant pathogen recognition mediated by promoter activation of the pepper Bs3 resistance gene. Science 318, 645–648.
Rotblat B., Enshell-Seijffers D., Gershoni J. M., Schuster S. and Avni A. 2002 Identification of an essential component of the elicitation active site of the EIX protein elicitor. Plant J. 32, 1049–1055.
Sadanand S. 2018 EvolvR-ing to targeted mutagenesis. Nat. Biotechnol. 36, 819.
Salmeron J. M., Oldroyd G. E. D., Rommens C. M. T., Scofield S. R., Kim H.-S., Lavelle D. T. et al. 1996 Tomato Prf is a member of the leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes and lies embedded within the Pto kinase gene cluster. Cell 86, 123–133.
Sanchez A. C., Brar D. S. and Huang N. 2000 Sequence tagged site marker assisted selection for three bacterial blight resistance genes in rice. Crop Sci. 40, 792–797.
Sarris P. F., Cevik V., Dagdas G., Jones J. D. G. and Krasileva K. V. 2016 Comparative analysis of plant immune receptor architectures uncovers host proteins likely targeted by pathogens. BMC Biol. 14, 8.
Seto D., Koulena N., Lo T., Menna A., Guttman D. S. and Desveaux D. 2017 Expanded type III effector recognition by the ZAR1 NLR protein using ZED1-related kinases. Nat. Plant 3, 17027.
Sharma T. R., Rai A. K., Gupta S. K., Vijayan J., Devanna B. N. and Ray S. 2012 Rice blast management through host-plant resistance: retrospect and prospects. Agric. Res. 1, 37–52.
Sharma Poudel R., Al-Hashel A. F., Gross T., Gross P. and Brueggeman R. 2018 Pyramiding rpg4 and Rpg1-mediated Stem rust resistance in barley requires the Rrr1 gene for both to function. Front. Plant. Sci. 9, 1789.
Shen Q.-H., Zhou F., Bieri S., Haizel T., Shirasu K. and SchulzeLefert P. 2003 Recognition specificity and RAR1/SGT1 dependence in barley Mla disease resistance genes to the powdery mildew fungus. Plant Cell 15, 732–744.
Singh S., Sidhu J. S. and Huang N. 2001 Pyramiding three bacterial blight resistance genes xa5, xa13 and Xa21 using marker assisted selection into indica cultivar PR106. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102, 1011–1015.
Steuernagel B., Witek K., Jones J. D. and Wulff B. B. 2017. MutRenSeq, a method for rapid cloning of plant disease resistance genes. In Wheat rust diseases, pp. 215-229. Humana Press, New York.
Strauss T. 2012 RNA-seq pinpoints a Xanthomonas TALeffector activated resistance gene in a large-crop genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 19480–19485.
Streubel J., Pesce C., Hutin M., Koebnik R., Boch J. and Szurek B. 2013 Five phylogenetically close rice SWEET genes confer TAL effector-mediated susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New. Phytol. 200, 808–819.
Sundar A. R., Ashwin N. M., Barnabas E. L., Malathi P. and Viswanathan R. 2015 Disease resistance in sugarcane–An overview. Scientia. Agraria. Paranaensis 14, 200–212.
Tan M. A., Hutten R. C., Visser R. G. and van Eck H. J. 2010 The effect of pyramiding Phytophthora infestans resistance genes R Pi-mcd1 and R Pi-ber in potato. Theo. Appl. Genet. 121, 117–125.
Tian D., Wang J., Zeng X., Gu K., Qiu C., Yang X. et al. 2014 The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 26, 497–515.
Truniger V. and Aranda M.A. 2009 Recessive resistance to plant viruses. In Advances in virus research: natural and engineered resistance to plant viruses (ed. G. Loebenstein and J. P. Carr Part), pp. 119–231. Academic Press.
Van Der Biezen E. A. and Jones J. D. 1998 Plant disease-resistance proteins and the gene-for-gene concept. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 23, 454–456.
van der Hoorn R. A. and Kamoun S. 2008 From guard to decoy: a new model for perception of plant pathogen effectors. Plant Cell 20, 2009–2017.
Van der Plank J. E. 1968 Disease resistance in plants, pp. 5–7. Academic Press, New York,
Van Schie C. C. and Takken F. L. 2014 Susceptibility genes 101, how to be a good host. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 52, 551–581.
Varallyay E., Giczey G. and Burgyan J. 2012 Virus-induced gene silencing of Mlo genes induces powdery mildew resistance in Triticum aestivum. Arch. Virol. 157, 1345–1350.
Vlot A. C., Dempsey D. A. and Klessig D. F. 2009 Salicylic acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 47, 177–206.
Voytas D. F. and Gao C. 2014 Precision genome engineering and agriculture, opportunities and regulatory challenges. PLoS Biol. 126, e1001877.
Waltz E. 2018 With a free pass., CRISPR-edited plants reach market in record time. Nat. Biotechnol. 36, 6–7.
Wang Y., Cheng X., Shan Q., Zhang Y., Liu J. and Gao C. 2014 Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powdery mildew. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 947.
Wang G., Roux B., Feng F., Guy E., Li L., Li N. et al. 2015a The decoy substrate of a pathogen effector and a pseudokinase specify pathogen-induced modified-self recognition and immunity in plants. Cell Host Microbe 18, 285–295.
Wang C., Zhang X., Fan Y., Gao Y., Zhu Q., Zheng C. et al. 2015b XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol. Plant 8, 290–298.
Wheeler H. 1975 Plant pathogenesis, Springer, New York.
Wolfe M. S. and McDermott J. M. 1994 Population genetics of plant pathogen interactions, the example of the Erysiphe graminis-Hordeum vulgare pathosystem. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 32, 89–113.
Wolt J. D., Wang K. and Yang B. 2016 The regulatory status of genome-edited crops. Plant Biotechnol. J. 142, 510–518.
Wu Y., Xiao N., Chen Y., Yu L., Pan C., Li Y. et al. 2019 Comprehensive evaluation of resistance effects of pyramiding lines with different broad-spectrum resistance genes against Magnaporthe oryzae in rice Oryza sativa L. Rice 12, 11.
Xiao W., Yang Q., Huang M., Guo T., Liu Y., Wang J. et al. 2019 Improvement of rice blast resistance by developing monogenic lines, two-gene pyramids and three-gene pyramid through MAS. Rice 12, 78.
Yin L., Zhang Y., Hao Y. and Lu J. 2014 Genetic diversity and population structure of Plasmopara viticola in China. Eur. J. Plant. Pathol. 140, 365–376.
Zhang K., Halitschke R., Yin C., Liu C. J. and Gan S. S. 2013 Salicylic acid 3-hydroxylase regulates Arabidopsis leaf longevity by mediating salicylic acid catabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 14807–14812.
Zhang X., Peng G., Parks P., Hu B., Li Q., Jiang L. et al. 2017 Identifying seedling and adult plant resistance of Chinese Brassica napus germplasm to Leptosphaeria maculans. Plant Pathol. 665, 752–762.
Zheng Z., Nonomura T., Appiano M., Pavan S., Matsuda Y., Toyoda H. et al. 2013 Loss of function in Mlo orthologs reduces susceptibility of pepper and tomato to powdery mildew disease caused by Leveillula taurica. PloS One 8, e70723.
Zhong X., Zhou Q., Cui N., Cai D. and Tang G. 2019 BvcZR3 and BvHs1pro-1 genes pyramiding enhanced beet cyst nematode Heterodera schachtii Schm resistance in oilseed rape Brassica napus L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 1740.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Manoj Prasad
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, B., Bhatia, D. & Mavi, G.S. Eighty years of gene-for-gene relationship and its applications in identification and utilization of R genes. J Genet 100, 50 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-021-01300-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-021-01300-7