Abstract
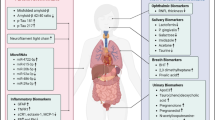
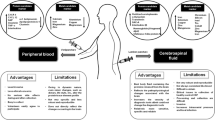
Neurological disorders are found to be influencing the peripheral tissues outside CNS. Recent developments in biomarkers for CNS have emerged with various diagnostic and therapeutic shortcomings. The role of central biomarkers including CSF-based and molecular imaging-based probes are still unclear for early diagnosis of major neurological diseases. Current trends show that early detection of neurodegenerative diseases with non-invasive methods is a major focus of researchers, and the development of biomarkers aiming peripheral tissues is in demand. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases are known for the progressive loss in neural structures or functions, including the neural death. Various dysfunctions of metabolic and biochemical pathways are associated with early occurrence of neuro-disorders in peripheral tissues including skin, blood cells, and eyes. This article reviews the peripheral biomarkers explored for early detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases including blood cells, skin fibroblast, proteomics, saliva, olfactory, stomach and colon, heart and peripheral nervous system, and others.

Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reitz C, Mayeux R (2014) Alzheimer disease: epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochem Pharmacol 88(4):640–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.024
Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM (2007) Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 3(3):186–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2007.04.381
Gatz M, Reynolds CA, Fratiglioni L, Johansson B, Mortimer JA, Berg S, Fiske A, Pedersen NL (2006) Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63(2):168–174. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.63.2.168
Petersen RC, Stevens JC, Ganguli M, Tangalos EG, Cummings JL, DeKosky ST (2001) Practice parameter: early detection of dementia: mild cognitive impairment (an evidence-based review). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Arch Neurology 56(9):1133–1142
Tiraboschi P, Hansen LA, Thal LJ, Corey-Bloom J (2004) The importance of neuritic plaques and tangles to the development and evolution of AD. Neurology 62(11):1984–1989
Brookmeyer R, Gray S, Kawas C (1998) Projections of Alzheimer’s disease in the United States and the public health impact of delaying disease onset. Am J Public Health 88(9):1337–1342
Pascale A, Amadio M, Govoni S, Battaini F (2007) The aging brain, a key target for the future: the protein kinase C involvement. Pharmacol Res 55(6):560–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2007.04.013
Alkon DL, Sun MK, Nelson TJ (2007) PKC signaling deficits: a mechanistic hypothesis for the origins of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28(2):51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2006.12.002
Janoshazi A, Sellal F, Marescaux C, Danion JM, Warter JM, de Barry J (2006) Alteration of protein kinase C conformation in red blood cells: a potential marker for Alzheimer’s disease but not for Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27(2):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.02.009
Hye A, Kerr F, Archer N, Foy C, Poppe M, Brown R, Hamilton G, Powell J et al (2005) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is increased in white cells early in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 373(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.10.031
Vossel KA, Xu JC, Fomenko V, Miyamoto T, Suberbielle E, Knox JA, Ho K, Kim DH et al (2015) Tau reduction prevents Abeta-induced axonal transport deficits by blocking activation of GSK3beta. J Cell Biol 209(3):419–433. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201407065
Deng J, Habib A, Obregon DF, Barger SW, Giunta B, Wang YJ, Hou H, Sawmiller D et al (2015) Soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha inhibits tau phosphorylation through modulation of GSK3beta signaling pathway. J Neurochem 135(3):630–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13351
Catricala S, Torti M, Ricevuti G (2012) Alzheimer disease and platelets: how’s that relevant. Immunity & Ageing 9(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4933-9-20
Tang K, Hynan LS, Baskin F, Rosenberg RN (2006) Platelet amyloid precursor protein processing: a bio-marker for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 240(1-2):53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2005.09.002
Baskin F, Rosenberg RN, Iyer L, Hynan L, Cullum CM (2000) Platelet APP isoform ratios correlate with declining cognition in AD. Neurology 54(10):1907–1909
Chatterjee P, Gupta VB, Fagan AM, Jasielec MS, Xiong C, Sohrabi HR, Dhaliwal S, Taddei K et al (2015) Decreased platelet APP isoform ratios in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease: baseline data from a DIAN cohort subset. Curr Alzheimer Res 12(2):157–164
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J et al (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(30):10513–10518. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804549105
Yang TT, Liu CG, Gao SC, Zhang Y, Wang PC (2018) The serum exosome derived microRNA-135a, −193b, and −384 were potential Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Biomed Environ Sci 31(2):87–96. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2018.011
Kumar S, Vijayan M, Reddy PH (2017) MicroRNA-455-3p as a potential peripheral biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 26(19):3808–3822. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx267
Hara N, Kikuchi M, Miyashita A, Hatsuta H, Saito Y, Kasuga K, Murayama S, Ikeuchi T et al (2017) Serum microRNA miR-501-3p as a potential biomarker related to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-017-0414-z
Tan L, Yu JT, Liu QY, Tan MS, Zhang W, Hu N, Wang YL, Sun L et al (2014) Circulating miR-125b as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 336(1-2):52–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2013.10.002
Galimberti D, Villa C, Fenoglio C, Serpente M, Ghezzi L, Cioffi SM, Arighi A, Fumagalli G et al (2014) Circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis 42(4):1261–1267. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-140756
Kiko T, Nakagawa K, Tsuduki T, Furukawa K, Arai H, Miyazawa T (2014) MicroRNAs in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid as potential markers for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis 39(2):253–259. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-130932
Oh ES, Troncoso JC, Fangmark Tucker SM (2008) Maximizing the potential of plasma amyloid-beta as a diagnostic biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromol Med 10(3):195–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-008-8035-0
Mayeux R, Honig LS, Tang MX, Manly J, Stern Y, Schupf N, Mehta PD (2003) Plasma A[beta]40 and A[beta]42 and Alzheimer’s disease: relation to age, mortality, and risk. Neurology 61(9):1185–1190
Sundelof J, Giedraitis V, Irizarry MC, Sundstrom J, Ingelsson E, Ronnemaa E, Arnlov J, Gunnarsson MD et al (2008) Plasma beta amyloid and the risk of Alzheimer disease and dementia in elderly men: a prospective, population-based cohort study. Arch Neurol 65(2):256–263. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2007.57
van Oijen M, Hofman A, Soares HD, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM (2006) Plasma Abeta(1-40) and Abeta(1-42) and the risk of dementia: a prospective case-cohort study. Lancet Neurol 5(8):655–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(06)70501-4
Fukumoto H, Tennis M, Locascio JJ, Hyman BT, Growdon JH, Irizarry MC (2003) Age but not diagnosis is the main predictor of plasma amyloid beta-protein levels. Arch Neurol 60(7):958–964. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.60.7.958
Tamaoka A, Fukushima T, Sawamura N, Ishikawa K, Oguni E, Komatsuzaki Y, Shoji S (1996) Amyloid beta protein in plasma from patients with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 141(1-2):65–68
Irizarry MC (2004) Biomarkers of Alzheimer disease in plasma. NeuroRx 1(2):226–234. https://doi.org/10.1602/neurorx.1.2.226
Ray S, Britschgi M, Herbert C, Takeda-Uchimura Y, Boxer A, Blennow K, Friedman LF, Galasko DR et al (2007) Classification and prediction of clinical Alzheimer’s diagnosis based on plasma signaling proteins. Nat Med 13(11):1359–1362. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1653
Marksteiner J, Kemmler G, Weiss EM, Knaus G, Ullrich C, Mechtcheriakov S, Oberbauer H, Auffinger S et al (2011) Five out of 16 plasma signaling proteins are enhanced in plasma of patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 32(3):539–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.03.011
Soares HD, Chen Y, Sabbagh M, Roher A, Schrijvers E, Breteler M (2009) Identifying early markers of Alzheimer’s disease using quantitative multiplex proteomic immunoassay panels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1180:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05066.x
Hye A, Lynham S, Thambisetty M, Causevic M, Campbell J, Byers HL, Hooper C, Rijsdijk F et al (2006) Proteome-based plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 129(Pt 11):3042–3050. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl279
Liao PC, Yu L, Kuo CC, Lin C, Kuo YM (2007) Proteomics analysis of plasma for potential biomarkers in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Proteomics Clin Appl 1(5):506–512. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.200600684
Yu HL, Chertkow HM, Bergman H, Schipper HM (2003) Aberrant profiles of native and oxidized glycoproteins in Alzheimer plasma. Proteomics 3(11):2240–2248. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200300475
Choi J, Malakowsky CA, Talent JM, Conrad CC, Gracy RW (2002) Identification of oxidized plasma proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293(5):1566–1570. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-291x(02)00420-5
Wu YY, Hsu JL, Wang HC, Wu SJ, Hong CJ, Cheng IH (2015) Alterations of the neuroinflammatory markers IL-6 and TRAIL in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra 5(3):424–434. https://doi.org/10.1159/000439214
Frederikse PH, Garland D, Zigler JS Jr, Piatigorsky J (1996) Oxidative stress increases production of beta-amyloid precursor protein and beta-amyloid (Abeta) in mammalian lenses, and Abeta has toxic effects on lens epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 271(17):10169–10174
Frederikse PH, Ren XO (2002) Lens defects and age-related fiber cell degeneration in a mouse model of increased AbetaPP gene dosage in Down syndrome. Am J Pathol 161(6):1985–1990
Melov S, Wolf N, Strozyk D, Doctrow SR, Bush AI (2005) Mice transgenic for Alzheimer disease beta-amyloid develop lens cataracts that are rescued by antioxidant treatment. Free Radic Biol Med 38(2):258–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.10.023
Goldstein LE, Muffat JA, Cherny RA, Moir RD, Ericsson MH, Huang X, Mavros C, Coccia JA et al (2003) Cytosolic beta-amyloid deposition and supranuclear cataracts in lenses from people with Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 361(9365):1258–1265. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(03)12981-9
Moncaster JA, Pineda R, Moir RD, Lu S, Burton MA, Ghosh JG, Ericsson M, Soscia SJ et al (2010) Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta links lens and brain pathology in Down syndrome. PLoS One 5(5):e10659. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010659
Kerbage C, Sadowsky CH, Jennings D, Cagle GD, Hartung PD (2013) Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by detecting exogenous fluorescent signal of ligand bound to Beta amyloid in the lens of human eye: an exploratory study. Front Neurol 4:62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2013.00062
Michael R, Rosandic J, Montenegro GA, Lobato E, Tresserra F, Barraquer RI, Vrensen GF (2013) Absence of beta-amyloid in cortical cataracts of donors with and without Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Eye Res 106:5–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2012.10.012
Ho CY, Troncoso JC, Knox D, Stark W, Eberhart CG (2014) Beta-amyloid, phospho-tau and alpha-synuclein deposits similar to those in the brain are not identified in the eyes of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease patients. Brain Pathol 24(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12070
Bei L, Shui YB, Bai F, Nelson SK, Van Stavern GP, Beebe DC (2015) A test of lens opacity as an indicator of preclinical Alzheimer disease. Exp Eye Res 140:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2015.03.010
Berisha F, Feke GT, Trempe CL, McMeel JW, Schepens CL (2007) Retinal abnormalities in early Alzheimer’s disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48(5):2285–2289. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.06-1029
Kirbas S, Turkyilmaz K, Anlar O, Tufekci A, Durmus M (2013) Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with Alzheimer disease. J Neuroophthalmol 33(1):58–61. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNO.0b013e318267fd5f
Lu Y, Li Z, Zhang X, Ming B, Jia J, Wang R, Ma D (2010) Retinal nerve fiber layer structure abnormalities in early Alzheimer’s disease: evidence in optical coherence tomography. Neurosci Lett 480(1):69–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.06.006
Chi Y, Wang YH, Yang L (2010) The investigation of retinal nerve fiber loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi 46(2):134–139
Gao L, Liu Y, Li X, Bai Q, Liu P (2015) Abnormal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and macula lutea in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 60(1):162–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2014.10.011
Gunes A, Demirci S, Tok L, Tok O, Demirci S (2015) Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in Alzheimer disease using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Turk J Med Sci 45(5):1094–1097
Perez SE, Lumayag S, Kovacs B, Mufson EJ, Xu S (2009) Beta-amyloid deposition and functional impairment in the retina of the APPswe/PS1DeltaE9 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(2):793–800. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.08-2384
Liu B, Rasool S, Yang Z, Glabe CG, Schreiber SS, Ge J, Tan Z (2009) Amyloid-peptide vaccinations reduce {beta}-amyloid plaques but exacerbate vascular deposition and inflammation in the retina of Alzheimer’s transgenic mice. Am J Pathol 175(5):2099–2110. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2009.090159
Frost S, Kanagasingam Y, Sohrabi H, Vignarajan J, Bourgeat P, Salvado O, Villemagne V, Rowe CC et al (2013) Retinal vascular biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Psychiatry 3:e233. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2012.150
Blanks JC, Hinton DR, Sadun AA, Miller CA (1989) Retinal ganglion cell degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 501(2):364–372
Blanks JC, Schmidt SY, Torigoe Y, Porrello KV, Hinton DR, Blanks RH (1996) Retinal pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. II. Regional neuron loss and glial changes in GCL. Neurobiol Aging 17(3):385–395
Sadun AA, Bassi CJ (1990) Optic nerve damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Ophthalmology 97(1):9–17
Williams PA, Thirgood RA, Oliphant H, Frizzati A, Littlewood E, Votruba M, Good MA, Williams J et al (2013) Retinal ganglion cell dendritic degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 34(7):1799–1806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.01.006
Lu Y, Tang N, Wang R (2012) Retinal ganglion cell loss on APP/PS1 transgenic mice with Alzheimer’s disease. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi 48(9):836–841
Zhao WQ, Ravindranath L, Mohamed AS, Zohar O, Chen GH, Lyketsos CG, Etcheberrigaray R, Alkon DL (2002) MAP kinase signaling cascade dysfunction specific to Alzheimer’s disease in fibroblasts. Neurobiol Dis 11(1):166–183
Veeranna, Kaji T, Boland B, Odrljin T, Mohan P, Basavarajappa BS, Peterhoff C, Cataldo A et al (2004) Calpain mediates calcium-induced activation of the Erk1,2 MAPK pathway and cytoskeletal phosphorylation in neurons: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 165(3):795–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63342-1
Khan TK, Alkon DL (2006) An internally controlled peripheral biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: Erk1 and Erk2 responses to the inflammatory signal bradykinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(35):13203–13207. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605411103
Khan TK, Alkon DL (2010) Early diagnostic accuracy and pathophysiologic relevance of an autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer’s disease peripheral biomarker. Neurobiol Aging 31(6):889–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.07.010
Peterson C, Gibson GE, Blass JP (1985) Altered calcium uptake in cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 312(16):1063–1065. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm198504183121618
Peterson C, Ratan RR, Shelanski ML, Goldman JE (1986) Cytosolic free calcium and cell spreading decrease in fibroblasts from aged and Alzheimer donors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83(20):7999–8001
Peterson C, Ratan RR, Shelanski ML, Goldman JE (1988) Altered response of fibroblasts from aged and Alzheimer donors to drugs that elevate cytosolic free calcium. Neurobiol Aging 9(3):261–266
Peterson C, Goldman JE (1986) Alterations in calcium content and biochemical processes in cultured skin fibroblasts from aged and Alzheimer donors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83(8):2758–2762
Kumar U, Dunlop DM, Richardson JS (1994) Mitochondria from Alzheimer’s fibroblasts show decreased uptake of calcium and increased sensitivity to free radicals. Life Sci 54(24):1855–1860
Borden LA, Maxfield FR, Goldman JE, Shelanski ML (1992) Resting [Ca2+]i and [Ca2+]i transients are similar in fibroblasts from normal and Alzheimer’s donors. Neurobiol Aging 13(1):33–38
Etcheberrigaray R, Ito E, Kim CS, Alkon DL (1994) Soluble beta-amyloid induction of Alzheimer’s phenotype for human fibroblast K+ channels. Science 264(5156):276–279
Hirashima N, Etcheberrigaray R, Bergamaschi S, Racchi M, Battaini F, Binetti G, Govoni S, Alkon DL (1996) Calcium responses in human fibroblasts: a diagnostic molecular profile for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 17(4):549–555
Ito E, Oka K, Etcheberrigaray R, Nelson TJ, McPhie DL, Tofel-Grehl B, Gibson GE, Alkon DL (1994) Internal Ca2+ mobilization is altered in fibroblasts from patients with Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(2):534–538
Etcheberrigaray R, Hirashima N, Nee L, Prince J, Govoni S, Racchi M, Tanzi RE, Alkon DL (1998) Calcium responses in fibroblasts from asymptomatic members of Alzheimer’s disease families. Neurobiol Dis 5(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.1998.0176
Sharma S, Moon CS, Khogali A, Haidous A, Chabenne A, Ojo C, Jelebinkov M, Kurdi Y et al (2013) Biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease (recent update). Neurochem Int 63(3):201–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.06.005
Louis ED, Bennett DA (2007) Mild Parkinsonian signs: an overview of an emerging concept. Mov Disord 22(12):1681–1688. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21433
Beach TG, Adler CH, Lue L, Sue LI, Bachalakuri J, Henry-Watson J, Sasse J, Boyer S et al (2009) Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol 117(6):613–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0538-8
Grundemann J, Schlaudraff F, Haeckel O, Liss B (2008) Elevated alpha-synuclein mRNA levels in individual UV-laser-microdissected dopaminergic substantia nigra neurons in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Nucleic Acids Res 36(7):e38. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn084
Wu KP, Kim S, Fela DA, Baum J (2008) Characterization of conformational and dynamic properties of natively unfolded human and mouse alpha-synuclein ensembles by NMR: implication for aggregation. J Mol Biol 378(5):1104–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.017
Bonini NM, Giasson BI (2005) Snaring the function of alpha-synuclein. Cell 123(3):359–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.017
Maiti NC, Apetri MM, Zagorski MG, Carey PR, Anderson VE (2004) Raman spectroscopic characterization of secondary structure in natively unfolded proteins: alpha-synuclein. J Am Chem Soc 126(8):2399–2408. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0356176
Mollenhauer B, Trautmann E, Taylor P, Manninger P, Sixel-Doring F, Ebentheuer J, Trenkwalder C, Schlossmacher MG (2013) Total CSF alpha-synuclein is lower in de novo Parkinson patients than in healthy subjects. Neurosci Lett 532:44–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2012.11.004
Kang JH, Irwin DJ, Chen-Plotkin AS, Siderowf A, Caspell C, Coffey CS, Waligorska T, Taylor P et al (2013) Association of cerebrospinal fluid beta-amyloid 1-42, T-tau, P-tau181, and alpha-synuclein levels with clinical features of drug-naive patients with early Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol 70(10):1277–1287. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.3861
Ono K, Yamada M (2014) Alpha-Synuclein in blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with alpha-synucleinopathy. Rinsho Byori 62(3):241–245
Tinsley RB, Kotschet K, Modesto D, Ng H, Wang Y, Nagley P, Shaw G, Horne MK (2010) Sensitive and specific detection of alpha-synuclein in human plasma. J Neurosci Res 88(12):2693–2700. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22417
Foulds PG, Mitchell JD, Parker A, Turner R, Green G, Diggle P, Hasegawa M, Taylor M et al (2011) Phosphorylated alpha-synuclein can be detected in blood plasma and is potentially a useful biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Faseb J 25(12):4127–4137. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.10-179192
El-Agnaf OM, Salem SA, Paleologou KE, Curran MD, Gibson MJ, Court JA, Schlossmacher MG, Allsop D (2006) Detection of oligomeric forms of alpha-synuclein protein in human plasma as a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Faseb J 20(3):419–425. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-1449com
Chau KY, Ching HL, Schapira AH, Cooper JM (2009) Relationship between alpha synuclein phosphorylation, proteasomal inhibition and cell death: relevance to Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. J Neurochem 110(3):1005–1013
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K et al (2002) α-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol 4(2):160
Muntane G, Ferrer I, Martinez-Vicente M (2012) α-Synuclein phosphorylation and truncation are normal events in the adult human brain. Neuroscience 200:106–119
Michell AW, Luheshi LM, Barker RA (2005) Skin and platelet alpha-synuclein as peripheral biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 381(3):294–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2005.02.030
Donadio V, Incensi A, Leta V, Giannoccaro MP, Scaglione C, Martinelli P, Capellari S, Avoni P et al (2014) Skin nerve alpha-synuclein deposits: a biomarker for idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurology 82(15):1362–1369. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000000316
Al-Nimer MS, Mshatat SF, Abdulla HI (2014) Saliva alpha-synuclein and a high extinction coefficient protein: a novel approach in assessment biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. N Am J Med Sci 6(12):633–637. https://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.147980
Del Tredici K, Hawkes CH, Ghebremedhin E, Braak H (2010) Lewy pathology in the submandibular gland of individuals with incidental Lewy body disease and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 119(6):703–713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0665-2
Adler CH, Dugger BN, Hinni ML, Lott DG, Driver-Dunckley E, Hidalgo J, Henry-Watson J, Serrano G et al (2014) Submandibular gland needle biopsy for the diagnosis of Parkinson disease. Neurology 82(10):858–864. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000204
Cersosimo MG, Perandones C, Micheli FE, Raina GB, Beron AM, Nasswetter G, Radrizzani M, Benarroch EE (2011) Alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in minor salivary gland biopsies of Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov Disord 26(1):188–190. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23344
Duda JE, Shah U, Arnold SE, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1999) The expression of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-synucleins in olfactory mucosa from patients with and without neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Neurol 160(2):515–522. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1999.7228
Beach TG, White CL III, Hladik CL, Sabbagh MN, Connor DJ, Shill HA, Sue LI, Sasse J et al (2009) Olfactory bulb alpha-synucleinopathy has high specificity and sensitivity for Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol 117(2):169–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0450-7
Witt M, Bormann K, Gudziol V, Pehlke K, Barth K, Minovi A, Hahner A, Reichmann H et al (2009) Biopsies of olfactory epithelium in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24(6):906–914. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22464
Lebouvier T, Chaumette T, Damier P, Coron E, Touchefeu Y, Vrignaud S, Naveilhan P, Galmiche JP et al (2008) Pathological lesions in colonic biopsies during Parkinson’s disease. Gut 57(12):1741–1743. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.162503
Lebouvier T, Neunlist M, Bruley des Varannes S, Coron E, Drouard A, N’Guyen JM, Chaumette T, Tasselli M et al (2010) Colonic biopsies to assess the neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease and its relationship with symptoms. PLoS One 5(9):e12728. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012728
Pouclet H, Lebouvier T, Coron E, Bruley des Varannes S, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2012) A comparison between colonic submucosa and mucosa to detect Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 24(4):e202–e205. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01887.x
Pouclet H, Lebouvier T, Coron E, Bruley des Varannes S, Rouaud T, Roy M, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2012) A comparison between rectal and colonic biopsies to detect Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 45(1):305–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.08.014
Shannon KM, Keshavarzian A, Mutlu E, Dodiya HB, Daian D, Jaglin JA, Kordower JH (2012) Alpha-synuclein in colonic submucosa in early untreated Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27(6):709–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23838
Sanchez-Ferro A, Rabano A, Catalan MJ, Rodriguez-Valcarcel FC, Diez SF, Herreros-Rodriguez J, Garcia-Cobos E, Alvarez-Santullano MM et al (2014) In vivo gastric detection of alpha-synuclein inclusions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25988
Iwanaga K, Wakabayashi K, Yoshimoto M, Tomita I, Satoh H, Takashima H, Satoh A, Seto M et al (1999) Lewy body-type degeneration in cardiac plexus in Parkinson’s and incidental Lewy body diseases. Neurology 52(6):1269–1271
Orimo S, Uchihara T, Nakamura A, Mori F, Kakita A, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2008) Axonal alpha-synuclein aggregates herald centripetal degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131(Pt 3):642–650. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm302
Fujishiro H, Frigerio R, Burnett M, Klos KJ, Josephs KA, Delledonne A, Parisi JE, Ahlskog JE et al (2008) Cardiac sympathetic denervation correlates with clinical and pathologic stages of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23(8):1085–1092. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21989
Braak H, de Vos RA, Bohl J, Del Tredici K (2006) Gastric alpha-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci Lett 396(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2005.11.012
Mu L, Sobotka S, Chen J, Su H, Sanders I, Nyirenda T, Adler CH, Shill HA et al (2013) Parkinson disease affects peripheral sensory nerves in the pharynx. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 72(7):614–623. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182965886
Maita C, Tsuji S, Yabe I, Hamada S, Ogata A, Maita H, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Sasaki H et al (2008) Secretion of DJ-1 into the serum of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 431(1):86–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2007.11.027
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F et al (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299(5604):256–259. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1077209
Hong Z, Shi M, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, Jankovic J, Zabetian CP et al (2010) DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 133(Pt 3):713–726. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq008
Shi M, Zabetian CP, Hancock AM, Ginghina C, Hong Z, Yearout D, Chung KA, Quinn JF et al (2010) Significance and confounders of peripheral DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 480(1):78–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.06.009
Lin X, Cook TJ, Zabetian CP, Leverenz JB, Peskind ER, Hu SC, Cain KC, Pan C et al (2012) DJ-1 isoforms in whole blood as potential biomarkers of Parkinson disease. Sci Rep 2:954. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00954
Church WH, Ward VL (1994) Uric acid is reduced in the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease: effect on dopamine oxidation. Brain Res Bull 33(4):419–425
Davis JW, Grandinetti A, Waslien CI, Ross GW, White LR, Morens DM (1996) Observations on serum uric acid levels and the risk of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Am J Epidemiol 144(5):480–484
Weisskopf MG, O’Reilly E, Chen H, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A (2007) Plasma urate and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Epidemiol 166(5):561–567. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwm127
de Lau LM, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Breteler MM (2005) Serum uric acid levels and the risk of Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 58(5):797–800. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20663
De Vera M, Rahman MM, Rankin J, Kopec J, Gao X, Choi H (2008) Gout and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: a cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 59(11):1549–1554. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24193
Gao X, Chen H, Choi HK, Curhan G, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A (2008) Diet, urate, and Parkinson’s disease risk in men. Am J Epidemiol 167(7):831–838. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwm385
O’Reilly EJ, Gao X, Weisskopf MG, Chen H, Schwarzschild MA, Spiegelman D, Ascherio A (2010) Plasma urate and Parkinson’s disease in women. Am J Epidemiol 172(6):666–670. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwq195
Constantinescu R, Zetterberg H (2011) Urate as a marker of development and progression in Parkinson’s disease. Drugs Today (Barc) 47(5):369–380. https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2011.47.5.1591834
Cipriani S, Chen X, Schwarzschild MA (2010) Urate: a novel biomarker of Parkinson’s disease risk, diagnosis and prognosis. Biomark Med 4(5):701–712. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm.10.94
Chen-Plotkin AS, Hu WT, Siderowf A, Weintraub D, Goldmann Gross R, Hurtig HI, Xie SX, Arnold SE et al (2011) Plasma epidermal growth factor levels predict cognitive decline in Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 69(4):655–663. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22271
Pellecchia MT, Santangelo G, Picillo M, Pivonello R, Longo K, Pivonello C, Vitale C, Amboni M et al (2013) Serum epidermal growth factor predicts cognitive functions in early, drug-naive Parkinson’s disease patients. J Neurol 260(2):438–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6648-6
Qiang JK, Wong YC, Siderowf A, Hurtig HI, Xie SX, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Yearout D et al (2013) Plasma apolipoprotein A1 as a biomarker for Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 74(1):119–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23872
Zhang X, Yin X, Yu H, Liu X, Yang F, Yao J, Jin H, Yang P (2012) Quantitative proteomic analysis of serum proteins in patients with Parkinson’s disease using an isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantification labeling, two-dimensional liquid chromatography, and tandem mass spectrometry. Analyst 137(2):490–495. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1an15551b
Wang ES, Sun Y, Guo JG, Gao X, Hu JW, Zhou L, Hu J, Jiang CC (2010) Tetranectin and apolipoprotein A-I in cerebrospinal fluid as potential biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 122(5):350–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2009.01318.x
Yin GN, Lee HW, Cho JY, Suk K (2009) Neuronal pentraxin receptor in cerebrospinal fluid as a potential biomarker for neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res 1265:158–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.01.058
Gao X, Simon KC, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A (2012) Prospective study of statin use and risk of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 69(3):380–384. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2011.1060
Lee YC, Lin CH, Wu RM, Lin MS, Lin JW, Chang CH, Lai MS (2013) Discontinuation of statin therapy associates with Parkinson disease: a population-based study. Neurology 81(5):410–416. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31829d873c
Cao XY, Lu JM, Zhao ZQ, Li MC, Lu T, An XS, Xue LJ (2017) MicroRNA biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease in serum exosome-like microvesicles. Neurosci Lett 644:94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.02.045
Ma W, Li Y, Wang C, Xu F, Wang M, Liu Y (2016) Serum miR-221 serves as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Cell Biochem Funct 34(7):511–515. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3224
Dong H, Wang C, Lu S, Yu C, Huang L, Feng W, Xu H, Chen X et al (2016) A panel of four decreased serum microRNAs as a novel biomarker for early Parkinson’s disease. Biomarkers 21(2):129–137. https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750x.2015.1118544
Margis R, Margis R, Rieder CR (2011) Identification of blood microRNAs associated to Parkinson’s disease. J Biotechnol 152(3):96–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.01.023
Cardo LF, Coto E, de Mena L, Ribacoba R, Moris G, Menendez M, Alvarez V (2013) Profile of microRNAs in the plasma of Parkinson’s disease patients and healthy controls. J Neurol 260(5):1420–1422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6900-8
Greenberg BM, Frohman E (2010) Optical coherence tomography as a potential readout in clinical trials. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 3(3):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756285610368890
Satue M, Rodrigo MJ, Obis J, Vilades E, Gracia H, Otin S, Fuertes MI, Alarcia R, Crespo JA, Polo V, Larrosa JM, Pablo LE, Garcia-Martin E (2017) Evaluation of progressive visual dysfunction and retinal degeneration in patients with parkinson's disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 58(2):1151–1157. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.16-20460. http://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2604719
Inzelberg R, Ramirez JA, Nisipeanu P, Ophir A (2004) Retinal nerve fiber layer thinning in Parkinson disease. Vision Res 44(24):2793–2797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.visres.2004.06.009
Hajee ME, March WF, Lazzaro DR, Wolintz AH, Shrier EM, Glazman S, Bodis-Wollner IG (2009) Inner retinal layer thinning in Parkinson disease. Arch Ophthalmol 127(6):737–741. https://doi.org/10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.106
Altintas O, Iseri P, Ozkan B, Caglar Y (2008) Correlation between retinal morphological and functional findings and clinical severity in Parkinson’s disease. Doc Ophthalmol 116(2):137–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-007-9091-8
Yavas GF, Yilmaz O, Kusbeci T, Ozturk F (2007) The effect of levodopa and dopamine agonists on optic nerve head in Parkinson disease. Eur J Ophthalmol 17(5):812–816
Wojtkowski M, Srinivasan V, Fujimoto JG, Ko T, Schuman JS, Kowalczyk A, Duker JS (2005) Three-dimensional retinal imaging with high-speed ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 112(10):1734–1746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.05.023
Tian T, Zhu XH, Liu YH (2011) Potential role of retina as a biomarker for progression of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Ophthalmol 4(4):433–438. https://doi.org/10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2011.04.21
Jimenez B, Ascaso FJ, Cristobal JA, Lopez del Val J (2014) Development of a prediction formula of Parkinson disease severity by optical coherence tomography. Mov Disord 29(1):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25747
Lee JY, Ahn J, Kim TW, Jeon BS (2014) Optical coherence tomography in Parkinson’s disease: is the retina a biomarker? J Parkinsons Dis 4(2):197–204. https://doi.org/10.3233/jpd-130306
Archibald NK, Clarke MP, Mosimann UP, Burn DJ (2011) Retinal thickness in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17(6):431–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.03.004
Hye A, Riddoch-Contreras J, Baird AL, Ashton NJ, Bazenet C, Leung R, Westman E, Simmons A et al (2014) Plasma proteins predict conversion to dementia from prodromal disease. Alzheimers Dement 10(6):799–807.e792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2014.05.1749
Blanks JC, Torigoe Y, Hinton DR, Blanks RH (1996) Retinal pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. I. Ganglion cell loss in foveal/parafoveal retina. Neurobiol Aging 17(3):377–384
Menéndez-González M (2014) The many questions on the use of biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases in clinical practice. Front Aging Neurosci 6:45
Funding
The authors (BG and PP) acknowledges The Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University MOE Start-Up Grant and MOE Tier-1 grants (2014-T1-001-229-1T1-04/14 and L0421160-1T1-06/15), Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
Not applicable
Informed Consent
Not applicable
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Htike, T.T., Mishra, S., Kumar, S. et al. Peripheral Biomarkers for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Mol Neurobiol 56, 2256–2277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1151-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1151-4