Abstract
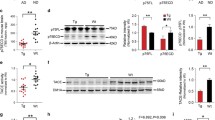
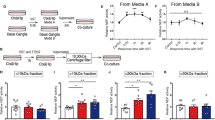
In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the impaired clearance of β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) due to disrupted tight junction and transporter proteins is the prominent cause of disease progression. Somatostatin (SST) blocks the aggregation of Aβ and inflammation whereas reduction of SST levels in the CSF and brain tissue is associated with impaired cognitive function and memory loss. However, the role of SST in preservation of blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity and functionality in Aβ-induced toxicity is not known. In the present study using human CMEC/D3 cells, we demonstrate that SST prevents Aβ-induced BBB permeability by regulating LRP1 and RAGE expression and improving the disrupted tight junction proteins. Furthermore, SST abrogates Aβ-induced JNK phosphorylation and expression of MMP2. Taken together, results presented here suggest that SST might serve as a therapeutic intervention in AD via targeting multiple pathways responsible for neurotoxicity, impaired BBB function, and disease progression.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Aβ:
-
β-amyloid peptide
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- hCMEC/D3:
-
Human cerebral microvascular endothelial cell line
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- FAM:
-
Fluorescein amidite
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin 1β
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinases
- ko :
-
Knock out
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- LRP:
-
Lipoprotein receptor-related protein
- MMP:
-
Matrix metallopeptides
- RAGE:
-
Receptor for advanced glycation end products
- SST:
-
Somatostatin
- SSTR:
-
Somatostatin receptor
- tg :
-
Transgenic
- TJP:
-
Tight junction protein
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- ZO:
-
Zonula occluden
References
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer's disease: Genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81(2):741–766
Yankner BA (1996) Mechanisms of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 16(5):921–932
Grammas P (2011) Neurovascular dysfunction, inflammation and endothelial activation: Implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroinflammation 8:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-8-26
Mhatre M, Nguyen A, Kashani S, Pham T, Adesina A, Grammas P (2004) Thrombin, a mediator of neurotoxicity and memory impairment. Neurobiol Aging 25(6):783–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.07.007
Yin X, Wright J, Wall T, Grammas P (2010) Brain endothelial cells synthesize neurotoxic thrombin in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 176(4):1600–1606. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2010.090406
Kumar U (2005) Expression of somatostatin receptor subtypes (SSTR1-5) in Alzheimer's disease brain: An immunohistochemical analysis. Neuroscience 134(2):525–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.04.001
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37(1):13–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030
Begley DJ, Brightman MW (2003) Structural and functional aspects of the blood-brain barrier. Prog Drug Res Fortschr Arzneim Forsch Prog Rech Pharm 61:39–78
Hawkins BT, Davis TP (2005) The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 57(2):173–185. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.57.2.4
Wolburg H, Noell S, Mack A, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fallier-Becker P (2009) Brain endothelial cells and the glio-vascular complex. Cell Tissue Res 335(1):75–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0658-9
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) Claudin-1 and -2: Novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol 141(7):1539–1550
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: A novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123(6 Pt 2):1777–1788
Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K, Kubota K, Saitou M, Tsukita S (1999) Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3, with the COOH termini of claudins. J Cell Biol 147(6):1351–1363
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M (1999) Structural and signalling molecules come together at tight junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11(5):628–633
Eisenhauer PB, Johnson RJ, Wells JM, Davies TA, Fine RE (2000) Toxicity of various amyloid beta peptide species in cultured human blood-brain barrier endothelial cells: Increased toxicity of dutch-type mutant. J Neurosci Res 60(6):804–810. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4547(20000615)60:6<804::aid-jnr13>3.0.co;2-1
Kalaria RN (2010) Vascular basis for brain degeneration: Faltering controls and risk factors for dementia. Nutr Rev 68(Suppl 2):S74–S87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00352.x
Zlokovic BV (2008) The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57(2):178–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.003
Huttunen HJ, Kuja-Panula J, Sorci G, Agneletti AL, Donato R, Rauvala H (2000) Coregulation of neurite outgrowth and cell survival by amphoterin and S100 proteins through receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) activation. J Biol Chem 275(51):40096–40105. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M006993200
Kanekiyo T, Cirrito JR, Liu CC, Shinohara M, Li J, Schuler DR, Shinohara M, Holtzman DM et al (2013) Neuronal clearance of amyloid-beta by endocytic receptor LRP1. J Neurosci 33(49):19276–19283. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3487-13.2013
Kook SY, Seok Hong H, Moon M, Mook-Jung I (2013) Disruption of blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Tissue Barriers 1(2):e23993. https://doi.org/10.4161/tisb.23993
Chen F, Ohashi N, Li W, Eckman C, Nguyen JH (2009) Disruptions of occludin and claudin-5 in brain endothelial cells in vitro and in brains of mice with acute liver failure. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 50(6):1914–1923. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23203
Gu Z, Cui J, Brown S, Fridman R, Mobashery S, Strongin AY, Lipton SA (2005) A highly specific inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-9 rescues laminin from proteolysis and neurons from apoptosis in transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 25(27):6401–6408. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1563-05.2005
Dhanda S, Sandhir R (2017) Blood-brain barrier permeability is exacerbated in experimental model of hepatic encephalopathy via MMP-9 activation and downregulation of tight junction proteins. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0521-7
Beal MF (1990) Somatostatin in neurodegenerative illnesses. Metab Clin Exp 39(9 Suppl 2):116–119
Binaschi A, Bregola G, Simonato M (2003) On the role of somatostatin in seizure control: Clues from the hippocampus. Rev Neurosci 14(3):285–301
Epelbaum J, Dournaud P, Fodor M, Viollet C (1994) The neurobiology of somatostatin. Crit Rev Neurobiol 8(1–2):25–44
Fox L, Alford M, Achim C, Mallory M, Masliah E (1997) Neurodegeneration of somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons in HIV encephalitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56(4):360–368
Davies P, Katzman R, Terry RD (1980) Reduced somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in cerebral cortex from cases of Alzheimer disease and Alzheimer senile dementa. Nature 288(5788):279–280
Kowall NW, Beal MF (1988) Cortical somatostatin, neuropeptide Y, and NADPH diaphorase neurons: Normal anatomy and alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 23(2):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410230202
Beal MF, Mazurek MF, Tran VT, Chattha G, Bird ED, Martin JB (1985) Reduced numbers of somatostatin receptors in the cerebral cortex in Alzheimer's disease. Science (New York, NY) 229(4710):289–291
Geci C, How J, Alturaihi H, Kumar U (2007) Beta-amyloid increases somatostatin expression in cultured cortical neurons. J Neurochem 101(3):664–673. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04415.x
Saito T, Iwata N, Tsubuki S, Takaki Y, Takano J, Huang SM, Suemoto T, Higuchi M et al (2005) Somatostatin regulates brain amyloid beta peptide Abeta42 through modulation of proteolytic degradation. Nat Med 11(4):434–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1206
Basivireddy J, Somvanshi RK, Romero IA, Weksler BB, Couraud PO, Oger J, Kumar U (2013) Somatostatin preserved blood brain barrier against cytokine induced alterations: Possible role in multiple sclerosis. Biochem Pharmacol 86(4):497–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.06.001
Adori C, Gluck L, Barde S, Yoshitake T, Kovacs GG, Mulder J, Magloczky Z, Havas L et al (2015) Critical role of somatostatin receptor 2 in the vulnerability of the central noradrenergic system: New aspects on Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 129(4):541–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1394-3
Weksler BB, Subileau EA, Perriere N, Charneau P, Holloway K, Leveque M, Tricoire-Leignel H, Nicotra A et al (2005) Blood-brain barrier-specific properties of a human adult brain endothelial cell line. FASEB J 19(13):1872–1874. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-3458fje
Alemi M, Gaiteiro C, Ribeiro CA, Santos LM, Gomes JR, Oliveira SM, Couraud PO, Weksler B et al (2016) Transthyretin participates in beta-amyloid transport from the brain to the liver--involvement of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1? Sci Rep 6:20164. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20164
Loo DT, Copani A, Pike CJ, Whittemore ER, Walencewicz AJ, Cotman CW (1993) Apoptosis is induced by beta-amyloid in cultured central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90(17):7951–7955
Deane R, Du Yan S, Submamaryan RK, LaRue B, Jovanovic S, Hogg E, Welch D, Manness L et al (2003) RAGE mediates amyloid-beta peptide transport across the blood-brain barrier and accumulation in brain. Nat Med 9(7):907–913. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm890
Deane R, Sagare A, Zlokovic BV (2008) The role of the cell surface LRP and soluble LRP in blood-brain barrier Abeta clearance in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Pharm Des 14(16):1601–1605
Liguz-Lecznar M, Urban-Ciecko J, Kossut M (2016) Somatostatin and somatostatin-containing neurons in shaping neuronal activity and plasticity. Front Neural Circuits 10:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2016.00048
Matsuoka N, Maeda N, Yamaguchi I, Satoh M (1994) Possible involvement of brain somatostatin in the memory formation of rats and the cognitive enhancing action of FR121196 in passive avoidance task. Brain Res 642(1–2):11–19
Abbott NJ (2000) Inflammatory mediators and modulation of blood-brain barrier permeability. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20(2):131–147
Ramasamy R, Yan SF, Schmidt AM (2009) RAGE: Therapeutic target and biomarker of the inflammatory response--the evidence mounts. J Leukoc Biol 86(3):505–512. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0409230
Reed-Geaghan EG, Savage JC, Hise AG, Landreth GE (2009) CD14 and toll-like receptors 2 and 4 are required for fibrillar a{beta}-stimulated microglial activation. J Neurosci 29(38):11982–11992. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3158-09.2009
Smith DG, Cappai R, Barnham KJ (2007) The redox chemistry of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid beta peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768(8):1976–1990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.02.002
Green PG, Basbaum AI, Levine JD (1992) Sensory neuropeptide interactions in the production of plasma extravasation in the rat. Neuroscience 50(3):745–749
Szolcsanyi J, Helyes Z, Oroszi G, Nemeth J, Pinter E (1998) Release of somatostatin and its role in the mediation of the anti-inflammatory effect induced by antidromic stimulation of sensory fibres of rat sciatic nerve. Br J Pharmacol 123(5):936–942. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0701685
Szolcsanyi J, Pinter E, Helyes Z, Oroszi G, Nemeth J (1998) Systemic anti-inflammatory effect induced by counter-irritation through a local release of somatostatin from nociceptors. Br J Pharmacol 125(4):916–922. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0702144
Epelbaum J, Guillou JL, Gastambide F, Hoyer D, Duron E, Viollet C (2009) Somatostatin, Alzheimer's disease and cognition: An old story coming of age? Prog Neurobiol 89(2):153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.07.002
Tornavaca O, Chia M, Dufton N, Almagro LO, Conway DE, Randi AM, Schwartz MA, Matter K et al (2015) ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation. J Cell Biol 208(6):821–838. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201404140
Stamatovic SM, Dimitrijevic OB, Keep RF, Andjelkovic AV (2006) Protein kinase Calpha-RhoA cross-talk in CCL2-induced alterations in brain endothelial permeability. J Biol Chem 281(13):8379–8388. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M513122200
Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Kunkel SL, Andjelkovic AV (2003) Potential role of MCP-1 in endothelial cell tight junction ‘opening’: Signaling via rho and rho kinase. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 22):4615–4628. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00755
Cirrito JR, Deane R, Fagan AM, Spinner ML, Parsadanian M, Finn MB, Jiang H, Prior JL et al (2005) P-glycoprotein deficiency at the blood-brain barrier increases amyloid-beta deposition in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Clin Invest 115(11):3285–3290. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci25247
Qosa H, Abuznait AH, Hill RA, Kaddoumi A (2012) Enhanced brain amyloid-beta clearance by rifampicin and caffeine as a possible protective mechanism against Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 31(1):151–165. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2012-120319
Qosa H, LeVine H 3rd, Keller JN, Kaddoumi A (2014) Mixed oligomers and monomeric amyloid-beta disrupts endothelial cells integrity and reduces monomeric amyloid-beta transport across hCMEC/D3 cell line as an in vitro blood-brain barrier model. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(9):1806–1815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.06.029
Etique N, Verzeaux L, Dedieu S, Emonard H (2013) LRP-1: A checkpoint for the extracellular matrix proteolysis. Biomed Res Int 2013:152163–152167. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/152163
Barmina OY, Walling HW, Fiacco GJ, Freije JM, Lopez-Otin C, Jeffrey JJ, Partridge NC (1999) Collagenase-3 binds to a specific receptor and requires the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein for internalization. J Biol Chem 274(42):30087–30093
Van den Steen PE, Van Aelst I, Hvidberg V, Piccard H, Fiten P, Jacobsen C, Moestrup SK, Fry S et al (2006) The hemopexin and O-glycosylated domains tune gelatinase B/MMP-9 bioavailability via inhibition and binding to cargo receptors. J Biol Chem 281(27):18626–18637. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M512308200
Yang Z, Strickland DK, Bornstein P (2001) Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase 2 levels are regulated by the low density lipoprotein-related scavenger receptor and thrombospondin 2. J Biol Chem 276(11):8403–8408. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008925200
Chen KL, Wang SS, Yang YY, Yuan RY, Chen RM, Hu CJ (2009) The epigenetic effects of amyloid-beta(1-40) on global DNA and neprilysin genes in murine cerebral endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 378(1):57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.10.173
Gao W, Eisenhauer PB, Conn K, Lynch JA, Wells JM, Ullman MD, McKee A, Thatte HS et al (2004) Insulin degrading enzyme is expressed in the human cerebrovascular endothelium and in cultured human cerebrovascular endothelial cells. Neurosci Lett 371(1):6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.07.034
Iwata N, Tsubuki S, Takaki Y, Watanabe K, Sekiguchi M, Hosoki E, Kawashima-Morishima M, Lee HJ et al (2000) Identification of the major Abeta1-42-degrading catabolic pathway in brain parenchyma: Suppression leads to biochemical and pathological deposition. Nat Med 6(2):143–150. https://doi.org/10.1038/72237
Lynch JA, George AM, Eisenhauer PB, Conn K, Gao W, Carreras I, Wells JM, McKee A et al (2006) Insulin degrading enzyme is localized predominantly at the cell surface of polarized and unpolarized human cerebrovascular endothelial cell cultures. J Neurosci Res 83(7):1262–1270. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.20809
Hernandez-Guillamon M, Martinez-Saez E, Delgado P, Domingues-Montanari S, Boada C, Penalba A, Boada M, Pagola J et al (2012) MMP-2/MMP-9 plasma level and brain expression in cerebral amyloid angiopathy-associated hemorrhagic stroke. Brain Pathol (Zurich, Switzerland) 22(2):133–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00512.x
Yin KJ, Cirrito JR, Yan P, Hu X, Xiao Q, Pan X, Bateman R, Song H et al (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases expressed by astrocytes mediate extracellular amyloid-beta peptide catabolism. J Neurosci 26(43):10939–10948. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2085-06.2006
Hartz AM, Bauer B, Soldner EL, Wolf A, Boy S, Backhaus R, Mihaljevic I, Bogdahn U et al (2012) Amyloid-beta contributes to blood-brain barrier leakage in transgenic human amyloid precursor protein mice and in humans with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Stroke 43(2):514–523. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.111.627562
Fromigue O, Hamidouche Z, Marie PJ (2008) Blockade of the RhoA-JNK-c-Jun-MMP2 cascade by atorvastatin reduces osteosarcoma cell invasion. J Biol Chem 283(45):30549–30556. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M801436200
Qosa H, Abuasal BS, Romero IA, Weksler B, Couraud PO, Keller JN, Kaddoumi A (2014) Differences in amyloid-beta clearance across mouse and human blood-brain barrier models: Kinetic analysis and mechanistic modeling. Neuropharmacology 79:668–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.023
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by grants from Canadian Institute of Health Research (MOP 74465) and NSERC (402594-11, 16-05171) Canada to UK. SP is the recipient of CIHR Doctoral Fellowship. FACS study was aided by UBCFlow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This manuscript was written by SP and UK. Immunofluorescence colocalization, biochemical studies were done by SP and Western blot in part was done by RKS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paik, S., Somvanshi, R.K. & Kumar, U. Somatostatin Maintains Permeability and Integrity of Blood-Brain Barrier in β-Amyloid Induced Toxicity. Mol Neurobiol 56, 292–306 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1045-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1045-5