Abstract
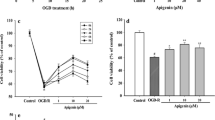
Oxidative stress is closely related to the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke. Protocatechualdehyde (PCA) is a phenolic acid compound that has the putative antioxidant activities. The present study was aimed to investigate the molecular mechanisms involved in the antioxidative effect of PCA against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. The experiment stroke model was produced in Sprague–Dawley rats via middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). To model ischemia-like conditions in vitro, differentiated SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to transient oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD). Treatment with PCA significantly improved neurologic score, reduced infarct volume and necrotic neurons, and also decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) contents at 24 h after reperfusion. Meanwhile, PCA significantly increased the transcription nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expressions in the ischemic cerebral cortex as shown by immunofluorescence staining and Western blot analysis. In vitro experiment showed that PCA protected differentiated SH-SY5Y cells against OGD-induced injury. Likewise, PCA also increased markedly the Nrf2 and HO-1 expressions in a dose-dependent manner. The neuroprotection effect of PCA was abolished by knockdown of Nrf2 and HO-1. Moreover, knockdown of protein kinase Cε (PKCε) also blocked PCA-induced Nfr2 nuclear translocation, HO-1 expression, and neuroprotection. Taken together, these results provide evidences that PCA can protect against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative injury, and the neuroprotective effect involves the PKCε/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feigin VL, Mensah GA, Norrving B, Murray CJ, Roth GA, GBD 2013 Stroke Panel Experts Group (2015) Atlas of the Global Burden of Stroke (1990–2013): The GBD 2013 Study. Neuroepidemiology 45(3):230–236
Candelario-Jalil E (2009) Injury and repair mechanisms in ischemic stroke: considerations for the development of novel neurotherapeutics. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 10(7):644–654
Crack PJ, Taylor JM (2005) Reactive oxygen species and the modulation of stroke. Free Radic Biol Med 38(11):1433–1444
Li X, Ye F, Li L, Chang W, Wu X, Chen J (2015) The role of HO-1 in protection against lead-induced neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 52:1–11
Ding Y, Chen M, Wang M, Li Y, Wen A (2015) Posttreatment with 11-Keto-beta-Boswellic acid ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: Nrf2/HO-1 pathway as a potential mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 52(3):1430–1439
Motterlini R, Green CJ, Foresti R (2002) Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 by redox signals involving nitric oxide. Antioxid Redox Signal 4(4):615–624
Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M (2005) Molecular mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal 7(3–4):385–394
Itoh K, Tong KI, Yamamoto M (2004) Molecular mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive response to electrophiles. Free Radic Biol Med 36(10):1208–1213
Kong AN, Owuor E, Yu R, Hebbar V, Chen C, Hu R, Mandlekar S (2001) Induction of xenobiotic enzymes by the MAP kinase pathway and the antioxidant or electrophile response element (ARE/EpRE). Drug Metab Rev 33(3–4):255–271
Nakaso K, Yano H, Fukuhara Y, Takeshima T, Wada-Isoe K, Nakashima K (2003) PI3K is a key molecule in the Nrf2-mediated regulation of antioxidative proteins by hemin in human neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Lett 546(2–3):181–184
Numazawa S, Ishikawa M, Yoshida A, Tanaka S, Yoshida T (2003) Atypical protein kinase C mediates activation of NF-E2-related factor 2 in response to oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285(2):C334–C342
Peng B, Zhao P, Lu YP, Chen MM, Sun H, Wu XM, Zhu L (2013) Z-ligustilide activates the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Brain Res 1520:168–177
Guo C, Zhu Y, Weng Y, Wang S, Guan Y, Wei G, Yin Y, Xi M et al (2014) Therapeutic time window and underlying therapeutic mechanism of breviscapine injection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 151(1):660–666
Yang C, Zhang X, Fan H, Liu Y (2009) Curcumin upregulates transcription factor Nrf2, HO-1 expression and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res 1282:133–141
Gao JW, Yamane T, Maita H, Ishikawa S, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Pu XP, Ariga H (2011) DJ-1-Mediated protective effect of protocatechuic aldehyde against oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells. J Pharmacol Sci 115(1):36–44
Zhang L, Ji Y, Kang Z, Lv C, Jiang W (2015) Protocatechuic aldehyde ameliorates experimental pulmonary fibrosis by modulating HMGB1/RAGE pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 283(1):50–56
Zhou Z, Liu Y, Miao AD, Wang SQ (2005) Protocatechuic aldehyde suppresses TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 513(1–2):1–8
Xing YL, Zhou Z, Agula ZZY, Ma YJ, Zhao YL, Xiao XH, Wang SQ (2012) Protocatechuic aldehyde inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell apoptosis via regulation of caspase-3. Phytother Res 26(9):1334–1341
Wei G, Guan Y, Yin Y, Duan J, Zhou D, Zhu Y, Quan W, Xi M et al (2013) Anti-inflammatory effect of protocatechuic aldehyde on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Inflammation 36(3):592–602
Zhao X, Zhai S, An MS, Wang YH, Yang YF, Ge HQ, Liu JH, Pu XP (2013) Neuroprotective effects of protocatechuic aldehyde against neurotoxin-induced cellular and animal models of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 8(10):e78220
Xiong L, Zheng Y, Wu M, Hou L, Zhu Z, Zhang X, Lu Z (2003) Preconditioning with isoflurane produces dose-dependent neuroprotection via activation of adenosine triphosphate-regulated potassium channels after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Anesth Analg 96(1):233–237
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20(1):84–91
Belayev L, Khoutorova L, Deisher TA, Belayev A, Busto R, Zhang Y, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD (2003) Neuroprotective effect of SolCD39, a novel platelet aggregation inhibitor, on transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 34(3):758–763
Moro MA, Almeida A, Bolanos JP, Lizasoain I (2005) Mitochondrial respiratory chain and free radical generation in stroke. Free Radic Biol Med 39(10):1291–1304
Cindric M, Cipak A, Zapletal E, Jaganjac M, Milkovic L, Waeg G, Stolc S, Zarkovic N et al (2013) Stobadine attenuates impairment of an intestinal barrier model caused by 4-hydroxynonenal. Toxicol In Vitro 27(1):426–432
Valavanidis A, Vlachogianni T, Fiotakis C (2009) 8-hydroxy-2′ -deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): a critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 27(2):120–139
Chen H, Yoshioka H, Kim GS, Jung JE, Okami N, Sakata H, Maier CM, Narasimhan P et al (2011) Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: mechanisms of cell death and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(8):1505–1517
Moon CY, Ku CR, Cho YH, Lee EJ (2012) Protocatechuic aldehyde inhibits migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and intravascular thrombosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 423(1):116–121
Li C, Jiang W, Zhu H, Hou J (2012) Antifibrotic effects of protocatechuic aldehyde on experimental liver fibrosis. Pharm Biol 50(4):413–419
Xu Y, Jiang WL, Zhang SP, Zhu HB, Hou J (2012) Protocatechuic aldehyde protects against experimental sepsis in vitro and in vivo. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 110(4):384–389
Chang ZQ, Gebru E, Lee SP, Rhee MH, Kim JC, Cheng H, Park SC (2011) In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of protocatechualdehyde isolated from Phellinus gilvus. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 57(1):118–122
Behl C, Moosmann B (2002) Oxidative nerve cell death in Alzheimer’s disease and stroke: antioxidants as neuroprotective compounds. Biol Chem 383(3–4):521–536
Pinheiro FF, Fontenele MA, de Sousa NJ, Fonteles AA, da Silva AT, de Araujo RP, Santos DCM, de Souza CM et al (2014) Caffeic acid protects mice from memory deficits induced by focal cerebral ischemia. Behav Pharmacol 25(7):637–647
Kim YM, Pae HO, Park JE, Lee YC, Woo JM, Kim NH, Choi YK, Lee BS et al (2011) Heme oxygenase in the regulation of vascular biology: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(1):137–167
Ishii T, Itoh K, Takahashi S, Sato H, Yanagawa T, Katoh Y, Bannai S, Yamamoto M (2000) Transcription factor Nrf2 coordinately regulates a group of oxidative stress-inducible genes in macrophages. J Biol Chem 275(21):16023–16029
Shah ZA, Li RC, Thimmulappa RK, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Biswal S, Dore S (2007) Role of reactive oxygen species in modulation of Nrf2 following ischemic reperfusion injury. Neuroscience 147(1):53–59
Wakabayashi N, Itoh K, Wakabayashi J, Motohashi H, Noda S, Takahashi S, Imakado S, Kotsuji T et al (2003) Keap1-null mutation leads to postnatal lethality due to constitutive Nrf2 activation. Nat Genet 35(3):238–245
Ramos-Gomez M, Kwak MK, Dolan PM, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Talalay P, Kensler TW (2001) Sensitivity to carcinogenesis is increased and chemoprotective efficacy of enzyme inducers is lost in nrf2 transcription factor-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(6):3410–3415
Takagi T, Kitashoji A, Iwawaki T, Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M, Yoshimura S, Iwama T, Hara H (2014) Temporal activation of Nrf2 in the penumbra and Nrf2 activator-mediated neuroprotection in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Free Radic Biol Med 72:124–133
Thimmulappa RK, Mai KH, Srisuma S, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Biswal S (2002) Identification of Nrf2-regulated genes induced by the chemopreventive agent sulforaphane by oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Res 62(18):5196–5203
Owuor ED, Kong AN (2002) Antioxidants and oxidants regulated signal transduction pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 64(5–6):765–770
Jiang G, Hu Y, Liu L, Cai J, Peng C, Li Q (2014) Gastrodin protects against MPP(+)-induced oxidative stress by up regulates heme oxygenase-1 expression through p38 MAPK/Nrf2 pathway in human dopaminergic cells. Neurochem Int 75:79–88
Jin M, Kumar A, Kumar S (2012) Ethanol-mediated regulation of cytochrome P450 2A6 expression in monocytes: role of oxidative stress-mediated PKC/MEK/Nrf2 pathway. PLoS One 7(4):e35505
Buelna-Chontal M, Guevara-Chavez JG, Silva-Palacios A, Medina-Campos ON, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Zazueta C (2014) Nrf2-regulated antioxidant response is activated by protein kinase C in postconditioned rat hearts. Free Radic Biol Med 74:145–156
Espada S, Rojo AI, Salinas M, Cuadrado A (2009) The muscarinic M1 receptor activates Nrf2 through a signaling cascade that involves protein kinase C and inhibition of GSK-3beta: connecting neurotransmission with neuroprotection. J Neurochem 110(3):1107–1119
Mylroie H, Dumont O, Bauer A, Thornton CC, Mackey J, Calay D, Hamdulay SS, Choo JR et al (2015) PKCepsilon-CREB-Nrf2 signalling induces HO-1 in the vascular endothelium and enhances resistance to inflammation and apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res 106(3):509–519
Bar-Am O, Amit T, Youdim MB (2007) Aminoindan and hydroxyaminoindan, metabolites of rasagiline and ladostigil, respectively, exert neuroprotective properties in vitro. J Neurochem 103(2):500–508
Dave KR, DeFazio RA, Raval AP, Torraco A, Saul I, Barrientos A, Perez-Pinzon MA (2008) Ischemic preconditioning targets the respiration of synaptic mitochondria via protein kinase C epsilon. J Neurosci 28(16):4172–4182
Quesada A, Ogi J, Schultz J, Handforth A (2011) C-terminal mechano-growth factor induces heme oxygenase-1-mediated neuroprotection of SH-SY5Y cells via the protein kinase C/Nrf2 pathway. J Neurosci Res 89(3):394–405
Di-Capua N, Sperling O, Zoref-Shani E (2003) Protein kinase C-epsilon is involved in the adenosine-activated signal transduction pathway conferring protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in primary rat neuronal cultures. J Neurochem 84(2):409–412
Lange-Asschenfeldt C, Raval AP, Dave KR, Mochly-Rosen D, Sick TJ, Perez-Pinzon MA (2004) Epsilon protein kinase C mediated ischemic tolerance requires activation of the extracellular regulated kinase pathway in the organotypic hippocampal slice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24(6):636–645
Acknowledgments
This present study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81403134). We thank our colleagues from the Department of Neurology for their constructive advices on our experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No competing interests.
Ethics Approval
Experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation of the Fourth Military Medical University (Xi’an, China).
Additional information
Chao Guo, Shiquan Wang, Jialin Duan and Na Jia contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Wang, S., Duan, J. et al. Protocatechualdehyde Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Oxidative Injury Via Protein Kinase Cε/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 54, 833–845 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9690-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9690-z