Abstract
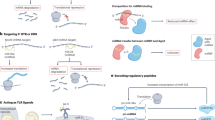
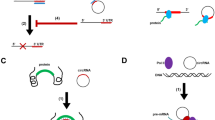
The exciting world of research with RNAs has to its credit some breakthrough findings that led to newer insights on multiple problems including that of human diseases. After the advent of siRNA, microRNA, and lncRNA, exciting novel molecules called circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been recently described. circRNAs are a class of non-coding RNAs, which are produced by scrambling of exons at the time of splicing. They are primarily produced in the brain region and are naturally present inside the cell. The best known ones so far include a particular type of circRNA namely “circular RNA sponge for miR-7” (ciRS-7 and CDR1as) which is the inhibitor of miR-7 microRNA—known to regulate various diseases like, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, and atherosclerosis. Similarly, another circRNA molecule called circmbl modulates the ratio of linear mRNA by competing with linear muscleblind gene through which it is synthesized. Considering the complex association of these molecules with critical microRNAs and gene families, circRNAs might have important roles in the cause and progression of human diseases. In particular, the multi-factorial nature of neurodegenerative diseases does warrant studies employing novel approaches towards identifying underlying root causes of these ailments. The non-coding RNAs, like circRNAs and microRNAs, could well present a common genetic trigger to multiple factors associated with neurodegenerative diseases. A specific fingerprint of a combination of various marker circRNAs could be explored for early diagnostic purpose as well. Herein, we review the possibility of exploring the role of circRNAs in the context of the central nervous system (CNS) and age-associated neurodegenerative diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADAR1:
-
Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA
- AGO:
-
Argonaute
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- CDR1as:
-
Antisense transcript of cerebellar degeneration-related protein 1
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CDR1:
-
Cerebeller degeneration-related protein 1
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- CFH:
-
Complement factor H
- exRNAs:
-
Extracellular RNAs
- fmn :
-
Formin
- HDV:
-
Hepatitis delta virus
- HIPK:
-
Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase
- HD:
-
Huntington’s disease
- tricRNAs:
-
Intronic circRNAs
- EIciRNAs:
-
Intron-exon circRNAs
- IRES:
-
Internal ribosome entry site
- lncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNA
- mRNA:
-
Mature RNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- MBL:
-
Muscleblind
- NDs:
-
Neurodegenerative diseases
- ncRNAs:
-
Non-coding RNAs
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- piRNAs:
-
Piwi-interacing RNAs
- pre-mRNA:
-
Precursor-mature RNA
- RCRs:
-
Reverse complementary repeats
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- snRNAs:
-
Small nuclear RNAs
- snoRNAs:
-
Small nucleolar RNAs
- SRY:
-
Sex determining region Y
- TDP:
-
TAR DNA-binding protein
- tRNA:
-
Transfer RNA
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- ZNF:
-
Zinc finger
References
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK (1976) Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 73(11):3852–3856
Hsu MT, Coca-Prados M (1979) Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature 280(5720):339–340
Wang KS, Choo QL, Weiner AJ, Ou JH, Najarian RC, Thayer RM, Mullenbach GT, Denniston KJ et al (1986) Structure, sequence and expression of the hepatitis delta (delta) viral genome. Nature 323(6088):508–514. doi:10.1038/323508a0
Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, Lacayo N, Brown PO (2012) Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One 7(2):e30733. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030733
Nigro JM, Cho KR, Fearon ER, Kern SE, Ruppert JM, Oliner JD, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1991) Scrambled exons. Cell 64(3):607–613
Caldas C, So CW, MacGregor A, Ford AM, McDonald B, Chan LC, Wiedemann LM (1998) Exon scrambling of MLL transcripts occur commonly and mimic partial genomic duplication of the gene. Gene 208(2):167–176
Bailleul B (1996) During in vivo maturation of eukaryotic nuclear mRNA, splicing yields excised exon circles. Nucleic Acids Res 24(6):1015–1019
Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, Hacker A, Walter M, Koopman P, Goodfellow P, Lovell-Badge R (1993) Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell 73(5):1019–1030
Burd CE, Jeck WR, Liu Y, Sanoff HK, Wang Z, Sharpless NE (2010) Expression of linear and novel circular forms of an INK4/ARF-associated non-coding RNA correlates with atherosclerosis risk. PLoS Genet 6(12):e1001233. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001233
Hansen TB, Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Villadsen SB, Statham AL, Clark SJ, Kjems J (2011) miRNA-dependent gene silencing involving Ago2-mediated cleavage of a circular antisense RNA. EMBO J 30(21):4414–4422. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.359
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495(7441):384–388. doi:10.1038/nature11993
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD et al (2013) Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495(7441):333–338. doi:10.1038/nature11928
Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, Xiang JF, Yin QF, Xing YH, Zhu S, Yang L et al (2013) Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell 51(6):792–806. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.017
Lasda E, Parker R (2014) Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. RNA 20(12):1829–1842. doi:10.1261/rna.047126.114
Shapiro MB, Senapathy P (1987) RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 15(17):7155–7174
de la Mata M, Lafaille C, Kornblihtt AR (2010) First come, first served revisited: factors affecting the same alternative splicing event have different effects on the relative rates of intron removal. RNA 16(5):904–912. doi:10.1261/rna.1993510
Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu X, Chen LL, Yang L (2014) Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell 159(1):134–147. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.001
Rodriguez-Trelles F, Tarrio R, Ayala FJ (2006) Origins and evolution of spliceosomal introns. Annu Rev Genet 40:47–76. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090625
Kiss T, Filipowicz W (1995) Exonucleolytic processing of small nucleolar RNAs from pre-mRNA introns. Genes Dev 9(11):1411–1424
Petfalski E, Dandekar T, Henry Y, Tollervey D (1998) Processing of the precursors to small nucleolar RNAs and rRNAs requires common components. Mol Cell Biol 18(3):1181–1189
Ladewig E, Okamura K, Flynt AS, Westholm JO, Lai EC (2012) Discovery of hundreds of mirtrons in mouse and human small RNA data. Genome Res 22(9):1634–1645. doi:10.1101/gr.133553.111
Rearick D, Prakash A, McSweeny A, Shepard SS, Fedorova L, Fedorov A (2011) Critical association of ncRNA with introns. Nucleic Acids Res 39(6):2357–2366. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1080
Meng X, Li X, Zhang P, Wang J, Zhou Y, Chen M (2016) Circular RNA: an emerging key player in RNA world. Brief Bioinform. doi:10.1093/bib/bbw045
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang X, Zhong G, Yu B et al (2015) Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22(3):256–264. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2959
Liang D, Wilusz JE (2014) Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev 28(20):2233–2247. doi:10.1101/gad.251926.114
Starke S, Jost I, Rossbach O, Schneider T, Schreiner S, Hung LH, Bindereif A (2015) Exon circularization requires canonical splice signals. Cell Rep 10(1):103–111. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.12.002
Ivanov A, Memczak S, Wyler E, Torti F, Porath HT, Orejuela MR, Piechotta M, Levanon EY et al (2015) Analysis of intron sequences reveals hallmarks of circular RNA biogenesis in animals. Cell Rep 10(2):170–177. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.12.019
Westholm JO, Miura P, Olson S, Shenker S, Joseph B, Sanfilippo P, Celniker SE, Graveley BR et al (2014) Genome-wide analysis of drosophila circular RNAs reveals their structural and sequence properties and age-dependent neural accumulation. Cell Rep 9(5):1966–1980. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.10.062
Wang Y, Wang Z (2015) Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA 21(2):172–179. doi:10.1261/rna.048272.114
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF, Sharpless NE (2013) Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 19(2):141–157. doi:10.1261/rna.035667.112
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO (2013) Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet 9(9):e1003777. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003777
Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H, Bartel DP (2014) Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol 15(7):409. doi:10.1186/s13059-014-0409-z
Wang PL, Bao Y, Yee MC, Barrett SP, Hogan GJ, Olsen MN, Dinneny JR, Brown PO et al (2014) Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PLoS One 9(3):e90859. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090859
Ghosal S, Das S, Sen R, Basak P, Chakrabarti J (2013) Circ2Traits: a comprehensive database for circular RNA potentially associated with disease and traits. Front Genet 4:283. doi:10.3389/fgene.2013.00283
Glazar P, Papavasileiou P, Rajewsky N (2014) circBase: a database for circular RNAs. RNA 20(11):1666–1670. doi:10.1261/rna.043687.113
Liu YC, Li JR, Sun CH, Andrews E, Chao RF, Lin FM, Weng SL, Hsu SD et al (2016) CircNet: a database of circular RNAs derived from transcriptome sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D209–D215. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv940
Zheng LL, Li JH, Wu J, Sun WJ, Liu S, Wang ZL, Zhou H, Yang JH et al (2016) deepBase v2.0: identification, expression, evolution and function of small RNAs, LncRNAs and circular RNAs from deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D196–D202. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1273
Dudekula DB, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, De S, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2016) CircInteractome: a web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biol 13(1):34–42. doi:10.1080/15476286.2015.1128065
Suzuki H, Zuo Y, Wang J, Zhang MQ, Malhotra A, Mayeda A (2006) Characterization of RNase R-digested cellular RNA source that consists of lariat and circular RNAs from pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res 34(8):e63. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl151
Schindler CW, Krolewski JJ, Rush MG (1982) Selective trapping of circular double-stranded DNA molecules in solidifying agarose. Plasmid 7(3):263–270
Yang L, Duff MO, Graveley BR, Carmichael GG, Chen LL (2011) Genomewide characterization of non-polyadenylated RNAs. Genome Biol 12(2):R16. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-2-r16
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431(7006):350–355. doi:10.1038/nature02871
Baek D, Villen J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP (2008) The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 455(7209):64–71. doi:10.1038/nature07242
Chao CW, Chan DC, Kuo A, Leder P (1998) The mouse formin (Fmn) gene: abundant circular RNA transcripts and gene-targeted deletion analysis. Mol Med 4(9):614–628
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S et al (2014) circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 56(1):55–66. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.019
Barrett SP, Salzman J (2016) Circular RNAs: analysis, expression and potential functions. Development 143(11):1838–1847. doi:10.1242/dev.128074
Wu TT, Su YH, Block TM, Taylor JM (1998) Atypical splicing of the latency-associated transcripts of herpes simplex type 1. Virology 243(1):140–149. doi:10.1006/viro.1998.9036
Chen W, Schuman E (2016) Circular RNAs in brain and other tissues: a functional enigma. Trends Neurosci 39(9):597–604. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2016.06.006
Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, Li Y, Abounader R, Hawkinson M, Lee J, Fine H et al (2008) microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 68(10):3566–3572. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6639
Thum T, Galuppo P, Wolf C, Fiedler J, Kneitz S, van Laake LW, Doevendans PA, Mummery CL et al (2007) MicroRNAs in the human heart: a clue to fetal gene reprogramming in heart failure. Circulation 116(3):258–267. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.687947
Junn E, Lee KW, Jeong BS, Chan TW, Im JY, Mouradian MM (2009) Repression of alpha-synuclein expression and toxicity by microRNA-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(31):13052–13057. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906277106
Wang Y, Liu J, Liu C, Naji A, Stoffers DA (2013) MicroRNA-7 regulates the mTOR pathway and proliferation in adult pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 62(3):887–895. doi:10.2337/db12-0451
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK, Kumar R (2008) MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase 1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res 68(20):8195–8200. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2103
Webster RJ, Giles KM, Price KJ, Zhang PM, Mattick JS, Leedman PJ (2009) Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in human cancer cells by microRNA-7. J Biol Chem 284(9):5731–5741. doi:10.1074/jbc.M804280200
Saydam O, Senol O, Wurdinger T, Mizrak A, Ozdener GB, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Yi M, Stephens RM et al (2011) miRNA-7 attenuation in Schwannoma tumors stimulates growth by upregulating three oncogenic signaling pathways. Cancer Res 71(3):852–861. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1219
Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, Chen J, Tian L (2012) MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 55(6):1852–1862. doi:10.1002/hep.25576
Zhang N, Li X, Wu CW, Dong Y, Cai M, Mok MT, Wang H, Chen J et al (2013) microRNA-7 is a novel inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene 32(42):5078–5088. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.526
Hansen TB, Kjems J, Damgaard CK (2013) Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res 73(18):5609–5612. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1568
Doxakis E (2010) Post-transcriptional regulation of alpha-synuclein expression by mir-7 and mir-153. J Biol Chem 285(17):12726–12734. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.086827
Asikainen S, Rudgalvyte M, Heikkinen L, Louhiranta K, Lakso M, Wong G, Nass R (2010) Global microRNA expression profiling of Caenorhabditis elegans Parkinson’s disease models. J Mol Neurosci 41(1):210–218. doi:10.1007/s12031-009-9325-1
Minones-Moyano E, Porta S, Escaramis G, Rabionet R, Iraola S, Kagerbauer B, Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Ferrer I et al (2011) MicroRNA profiling of Parkinson’s disease brains identifies early downregulation of miR-34b/c which modulate mitochondrial function. Hum Mol Genet 20(15):3067–3078. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr210
Hebert SS, Horre K, Nicolai L, Papadopoulou AS, Mandemakers W, Silahtaroglu AN, Kauppinen S, Delacourte A et al (2008) Loss of microRNA cluster miR-29a/b-1 in sporadic Alzheimer's disease correlates with increased BACE1/beta-secretase expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(17):6415–6420. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710263105
Maes OC, An J, Sarojini H, Wang E (2008) Murine microRNAs implicated in liver functions and aging process. Mech Ageing Dev 129(9):534–541. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2008.05.004
Cogswell JP, Ward J, Taylor IA, Waters M, Shi Y, Cannon B, Kelnar K, Kemppainen J et al (2008) Identification of miRNA changes in Alzheimer’s disease brain and CSF yields putative biomarkers and insights into disease pathways. J Alzheimers Dis 14(1):27–41
Maes OC, Chertkow HM, Wang E, Schipper HM (2009) MicroRNA: implications for Alzheimer disease and other human CNS disorders. Curr Genomics 10(3):154–168. doi:10.2174/138920209788185252
Lukiw WJ (2013) Circular RNA (circRNA) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Front Genet 4:307. doi:10.3389/fgene.2013.00307
Lukiw WJ, Surjyadipta B, Dua P, Alexandrov PN (2012) Common micro RNAs (miRNAs) target complement factor H (CFH) regulation in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and in age-related macular degeneration (AMD). International journal of biochemistry and molecular biology 3(1):105–116
Dimmeler S, Nicotera P (2013) MicroRNAs in age-related diseases. EMBO Mol Med 5(2):180–190. doi:10.1002/emmm.201201986
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glazar P, Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M et al (2015) Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell 58(5):870–885. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.027
You X, Vlatkovic I, Babic A, Will T, Epstein I, Tushev G, Akbalik G, Wang M et al (2015) Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci 18(4):603–610. doi:10.1038/nn.3975
Armakola M, Higgins MJ, Figley MD, Barmada SJ, Scarborough EA, Diaz Z, Fang X, Shorter J et al (2012) Inhibition of RNA lariat debranching enzyme suppresses TDP-43 toxicity in ALS disease models. Nat Genet 44(12):1302–1309. doi:10.1038/ng.2434
Sakamoto K, Huang BW, Iwasaki K, Hailemariam K, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Tsuji Y (2010) Regulation of genotoxic stress response by homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 through phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element-binding protein at serine 271. Mol Biol Cell 21(16):2966–2974. doi:10.1091/mbc.E10-01-0015
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang R, Sun W, Dou K et al (2015) Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett 365(2):141–148. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.003
Chen Y, Li C, Tan C, Liu X (2016) Circular RNAs: a new frontier in the study of human diseases. J Med Genet 53(6):359–365. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-103758
Wu P, Zuo X, Deng H, Liu X, Liu L, Ji A (2013) Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Bull 97:69–80. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.06.001
Lu D, Xu AD (2016) Mini review: circular RNAs as potential clinical biomarkers for disorders in the central nervous system. Front Genet 7:53. doi:10.3389/fgene.2016.00053
Zhang Y, Xue W, Li X, Zhang J, Chen S, Zhang JL, Yang L, Chen LL (2016) The biogenesis of nascent circular RNAs. Cell Rep 15(3):611–624. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.058
Grasso M, Piscopo P, Crestini A, Confaloni A, Denti MA (2015) Circulating microRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases. EXS 106:151–169. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-0955-9_7
Fenoglio C, Ridolfi E, Galimberti D, Scarpini E (2012) MicroRNAs as active players in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci 13(10):13227–13239. doi:10.3390/ijms131013227
Acknowledgments
We thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research for funding our research; vide Network Project BSC0118 (EpiHeD). CSIR-CDRI Communication number is 9357.
Authors’ Contributions
All the authors (KL, S, HR, BT, and NA) contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, L., Shamsuzzama, Haque, R. et al. Circular RNAs: the Emerging Class of Non-coding RNAs and Their Potential Role in Human Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol Neurobiol 54, 7224–7234 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0213-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0213-8