Abstract
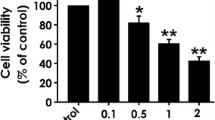
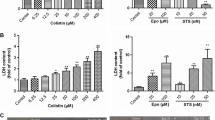
Acrylamide (ACR) is a potent toxin that affects the human nervous system. However, the underlying mechanism of ACR neurotoxicity remains poorly understood. In the present study, we investigated whether ACR induces mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis and the involved signaling pathways in PC12 cells. ACR exposure activated the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in PC12 cells and triggered the up-regulation of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, excessive release of cytochrome c, cleavage of capase-9 and caspase-3, depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane, structural damages to the mitochondria, and compaction of nuclear heterochromatin. ACR-induced oxidative stress was also observed based on distinct increase in cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA), and significant decrease in glutathione (GSH). Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling including extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK), and p38 were phosphorylated by ROS overproduction in PC12 cells in a time-and dose-dependent manner. ACR promoted the translocation of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) from the cytosol to the nucleus, thereby enhancing the expression of downstream γ-glutamyl-cysteine synthetase (γ-GCS). The regulation of Nrf2 activation by MAPK pathways was confirmed by the blockade of MAPK pathways. The suppression of JNK and p38 pathways showed a protective effect on ACR-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Nrf2 knockdown further enhanced MDA production and reduced GSH generation induced by ACR. These results suggest that MAPK and Nrf2 signaling pathways contribute to mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis induced by ACR in PC12 cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACR:
-
Acrylamide
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear transcription factor E2-related factor 2
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen activated protein kinase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal regulated protein kinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehvde
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- γ-GCS:
-
γ-Glutamyl-cysteine synthetase
- MMP:
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
- DMSO:
-
Dimethylsulfoxide
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- MTT:
-
3–4, 5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl-2, 5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide
- JC-1:
-
5–5, 6–6-Tetrachloro-1, 1, 3, 3-tetra-ethylbenzimidazolcarbocya-nine iodide
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DCFH-DA:
-
2, 7-Dichlorofluorescein diacetate
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid;
- BSA:
-
Bull serum albumin
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffer solution
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
References
Soares CM, Alves RC, Casal S, Oliveira MB, Fernandes JO (2010) Development and validation of a matrix solid-phase dispersion method to determine acrylamide in coffee and coffee substitutes. J Food Sci 75:T57–T63
Eberhart BL 2nd, Ewald DK, Sanders RA, Tallmadge DH, Zyzak DV, Strothers MA (2005) Quantitation of acrylamide in food products by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J AOAC Int 88:1205–1211
Erkekoglu P, Baydar T (2014) Acrylamide neurotoxicity. Nutr Neurosci 17:49–57
Abelli L, Ferri GL, Astolfi M, Conte B, Geppetti P, Parlani M, Dahl D, Polak JM, et al. (1991) Acrylamide-induced visceral neuropathy: evidence for the involvement of capsaicin-sensitive nerves of the rat urinary bladder. Neuroscience 41:311–321
Pan X, Guo X, Xiong F, Cheng G, Lu Q, Yan H (2015) Acrylamide increases dopamine levels by affecting dopamine transport and metabolism related genes in the striatal dopaminergic system. Toxicol Lett 236:60–68
Bharath S, Hsu M, Kaur D, Rajagopalan S, Andersen JK (2002) Glutathione, iron and Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Pharmacol 64:1037–1048
Lee JG, Wang YS, Chou CC (2014) Acrylamide-induced apoptosis in rat primary astrocytes and human astrocytoma cell lines. Toxicology in vitro : an international journal published in association with BIBRA 28:562–570
Liu Z, Song G, Zou C, Liu G, Wu W, Yuan T, Liu X (2015) Acrylamide induces mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in BV-2 microglial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 84:42–53
Chen JH, Yang CH, Wang YS, Lee JG, Cheng CH, Chou CC (2013) Acrylamide-induced mitochondria collapse and apoptosis in human astrocytoma cells. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 51:446–452
Zhang L, Gavin T, Barber DS, LoPachin RM (2011) Role of the Nrf2-ARE pathway in acrylamide neurotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 205:1–7
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB (2009) The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 284:13291–13295
Li W, Kong AN (2009) Molecular mechanisms of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Mol Carcinog 48:91–104
Kim EK, Choi EJ (2015) Compromised MAPK signaling in human diseases: an update. Arch Toxicol 89:867–882
Ho PJ, Chou CK, Yeh SF (2012) Role of JNK and p38 MAPK in taiwanin A-induced cell death. Life Sci 91:1358–1365
Newhouse K, Hsuan SL, Chang SH, Cai B, Wang Y, Xia Z (2004) Rotenone-induced apoptosis is mediated by p38 and JNK MAP kinases in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 79:137–146
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431
Cheng CH, Yang WT, Gwo JC (2002) The ultrastructure of the mature spermatozoon of the bivalve Gafrarium Tumidum (Bivalvia, Heterodonta, Veneridae, Circinae). J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 34:51–54
Calleman CJ, Wu Y, He F, Tian G, Bergmark E, Zhang S, Deng H, Wang Y, et al. (1994) Relationships between biomarkers of exposure and neurological effects in a group of workers exposed to acrylamide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 126:361–371
Tardiff RG, Gargas ML, Kirman CR, Carson ML, Sweeney LM (2010) Estimation of safe dietary intake levels of acrylamide for humans. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 48:658–667
Martin TF, Grishanin RN (2003) PC12 cells as a model for studies of regulated secretion in neuronal and endocrine cells. Methods Cell Biol 71:267–286
Mehri S, Abnous K, Mousavi SH, Shariaty VM, Hosseinzadeh H (2012) Neuroprotective effect of crocin on acrylamide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:227–235
Yousef MI, El-Demerdash FM (2006) Acrylamide-induced oxidative stress and biochemical perturbations in rats. Toxicology 219:133–141
Pan X, Zhu L, Lu H, Wang D, Lu Q, Yan H (2015) Melatonin attenuates oxidative damage induced by acrylamide in vitro and in vivo. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 703709:2015
Halliwell B (2006) Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem 97:1634–1658
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis : an international journal on programmed cell death 12:913–922
Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2002) Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival. J Cell Physiol 192:1–15
Rodriguez-Ramiro I, Ramos S, Bravo L, Goya L, Martin MA (2011) Procyanidin B2 and a cocoa polyphenolic extract inhibit acrylamide-induced apoptosis in human Caco-2 cells by preventing oxidative stress and activation of JNK pathway. J Nutr Biochem 22:1186–1194
Friedman M (2003) Chemistry, biochemistry, and safety of acrylamide. A review Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 51:4504–4526
Woo SH, Park IC, Park MJ, Lee HC, Lee SJ, Chun YJ, Lee SH, Hong SI, et al. (2002) Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis through a reactive oxygen species-dependent pathway and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in HeLa cells. Int J Oncol 21:57–63
Sumizawa T, Igisu H (2007) Apoptosis induced by acrylamide in SH-SY5Y cells. Arch Toxicol 81:279–282
Zou X, Gao J, Zheng Y, Wang X, Chen C, Cao K, Xu J, Li Y, et al. (2014) Zeaxanthin induces Nrf2-mediated phase II enzymes in protection of cell death. Cell Death Dis 5:e1218
Ryter SW, Kim HP, Hoetzel A, Park JW, Nakahira K, Wang X, Choi AM (2007) Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:49–89
Baird L, Dinkova-Kostova AT (2011) The cytoprotective role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Arch Toxicol 85:241–272
Botta D, White CC, Vliet-Gregg P, Mohar I, Shi S, McGrath MB, McConnachie LA, Kavanagh TJ (2008) Modulating GSH synthesis using glutamate cysteine ligase transgenic and gene-targeted mice. Drug Metab Rev 40:465–477
Gan FF, Ling H, Ang X, Reddy SA, Lee SS, Yang H, Tan SH, Hayes JD, et al. (2013) A novel shogaol analog suppresses cancer cell invasion and inflammation, and displays cytoprotective effects through modulation of NF-kappaB and Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272:852–862
Lee DS, Kim KS, Ko W, Li B, Jeong GS, Jang JH, Oh H, Kim YC (2014) The cytoprotective effect of sulfuretin against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced hepatotoxicity through Nrf2/ARE and JNK/ERK MAPK-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression. Int J Mol Sci 15:8863–8877
Roy Chowdhury S, Sengupta S, Biswas S, Sinha TK, Sen R, Basak RK, Adhikari B, Bhattacharyya A (2014) Bacterial fucose-rich polysaccharide stabilizes MAPK-mediated Nrf2/Keap1 signaling by directly scavenging reactive oxygen species during hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of human lung fibroblast cells. PLoS One 9:e113663
Lee MS, Lee B, Park KE, Utsuki T, Shin T, Oh CW, Kim HR (2015) Dieckol enhances the expression of antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes by the activation of Nrf2-MAPK signalling pathway in HepG2 cells. Food Chem 174:538–546
Filomeni G, Piccirillo S, Rotilio G, Ciriolo MR (2012) p38(MAPK) and ERK1/2 dictate cell death/survival response to different pro-oxidant stimuli via p53 and Nrf2 in neuroblastoma cells SH-SY5Y. Biochem Pharmacol 83:1349–1357
Vari R, D’Archivio M, Filesi C, Carotenuto S, Scazzocchio B, Santangelo C, Giovannini C, Masella R (2011) Protocatechuic acid induces antioxidant/detoxifying enzyme expression through JNK-mediated Nrf2 activation in murine macrophages. J Nutr Biochem 22:409–417
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the contribution of all the members participating in this study. The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81373042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, X., Yan, D., Wang, D. et al. Mitochondrion-Mediated Apoptosis Induced by Acrylamide is Regulated by a Balance Between Nrf2 Antioxidant and MAPK Signaling Pathways in PC12 Cells. Mol Neurobiol 54, 4781–4794 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0021-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0021-1