Abstract
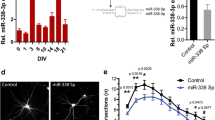
MicroRNA-124 (miR-124), a brain-specific miRNA molecule, has been implicated in stimulating neurite outgrowth and elongation during neuronal differentiation. However, the direct target genes and the mechanisms of miR-124-induced neurite outgrowth are poorly understood. In this study, we demonstrated that miR-124 directly targeted and downregulated the endogenous expression of oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP). A previous study found that the expression of miR-124 increased during brain development. In the present study, we demonstrated that the expression of OSBP decreased during the development of the C57BL/6 mouse cortex, which was negatively correlated with miR-124 expression. OSBP knockdown using specific shRNAs promoted neurite outgrowth and elongation in both Neuro-2a cells and primary cultured mouse cortical neurons. Conversely, OSBP overexpression strongly repressed the neurite elongation-enhancing effect of miR-124 in Neuro-2a cells. Our results suggested that OSBP may be a target and downstream effector of miR-124 for regulating neurite outgrowth and elongation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levanon D, Hsieh CL, Francke U, Dawson PA, Ridgway ND, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1990) cDNA cloning of human oxysterol-binding protein and localization of the gene to human chromosome 11 and mouse chromosome 19. Genomics 7(1):65–74
Taylor FR, Kandutsch AA (1985) Oxysterol binding protein. Chem Phys Lipids 38(1-2):187–194
Taylor FR, Saucier SE, Shown EP, Parish EJ, Kandutsch AA (1984) Correlation between oxysterol binding to a cytosolic binding protein and potency in the repression of hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase. J Biol Chem 259(20):12382–12387
Dawson PA, Van der Westhuyzen DR, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1989) Purification of oxysterol binding protein from hamster liver cytosol. J Biol Chem 264(15):9046–9052
Olkkonen VM, Li S (2013) Oxysterol-binding proteins: sterol and phosphoinositide sensors coordinating transport, signaling and metabolism. Prog Lipid Res 52(4):529–538. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.004
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303(5654):83–86. doi:10.1126/science.1091903
Lee S, Vasudevan S (2013) Post-transcriptional stimulation of gene expression by microRNAs. Adv Exp Med Biol 768:97–126. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_7
Papagiannakopoulos T, Kosik KS (2009) MicroRNA-124: micromanager of neurogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 4(5):375–376. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2009.04.007
Visvanathan J, Lee S, Lee B, Lee JW, Lee SK (2007) The microRNA miR-124 antagonizes the anti-neural REST/SCP1 pathway during embryonic CNS development. Genes Dev 21(7):744–749. doi:10.1101/gad.1519107
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA, Maniatis T (2007) The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 27(3):435–448. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.07.015
Akerblom M, Sachdeva R, Barde I, Verp S, Gentner B, Trono D, Jakobsson J (2012) MicroRNA-124 is a subventricular zone neuronal fate determinant. J of Neurosci Official J Soc Neurosci 32(26):8879–8889. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0558-12.2012
Cheng LC, Pastrana E, Tavazoie M, Doetsch F (2009) miR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Nat Neurosci 12(4):399–408. doi:10.1038/nn.2294
Yu JY, Chung KH, Deo M, Thompson RC, Turner DL (2008) MicroRNA miR-124 regulates neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Exp Cell Res 314(14):2618–2633. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.06.002
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Lin L, Lin F, Li T, Du H, Chen R, Zheng W et al (2013) Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the axonal outgrowth through activation of PI3K/AKT signaling in primary cortical neurons followed oxygen-glucose deprivation injury. PLoS One 8(11):e78514. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078514
Smirnova L, Grafe A, Seiler A, Schumacher S, Nitsch R, Wulczyn FG (2005) Regulation of miRNA expression during neural cell specification. Eur J Neurosci 21(6):1469–1477. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03978.x
Sempere LF, Freemantle S, Pitha-Rowe I, Moss E, Dmitrovsky E, Ambros V (2004) Expression profiling of mammalian microRNAs uncovers a subset of brain-expressed microRNAs with possible roles in murine and human neuronal differentiation. Genome Biol 5(3):R13. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-3-r13
Gu X, Meng S, Liu S, Jia C, Fang Y, Li S, Fu C, Song Q et al (2014) miR-124 represses ROCK1 expression to promote neurite elongation through activation of the PI3K/Akt signal pathway. J Mol Neurosci MN 52(1):156–165. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-0190-6
Franke K, Otto W, Johannes S, Baumgart J, Nitsch R, Schumacher S (2012) miR-124-regulated RhoG reduces neuronal process complexity via ELMO/Dock180/Rac1 and Cdc42 signalling. EMBO J 31(13):2908–2921. doi:10.1038/emboj.2012.130
Beh CT, Cool L, Phillips J, Rine J (2001) Overlapping functions of the yeast oxysterol-binding protein homologues. Genetics 157(3):1117–1140
Beh CT, Rine J (2004) A role for yeast oxysterol-binding protein homologs in endocytosis and in the maintenance of intracellular sterol-lipid distribution. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 14):2983–2996. doi:10.1242/jcs.01157
Fiore RS, Bayer VE, Pelech SL, Posada J, Cooper JA, Baraban JM (1993) p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase in brain: prominent localization in neuronal cell bodies and dendrites. Neuroscience 55(2):463–472
Zhu X, Assoian RK (1995) Integrin-dependent activation of MAP kinase: a link to shape-dependent cell proliferation. Mol Biol Cell 6(3):273–282
Campbell JS, Wenderoth MP, Hauschka SD, Krebs EG (1995) Differential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in response to basic fibroblast growth factor in skeletal muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(3):870–874
Perron JC, Bixby JL (1999) Distinct neurite outgrowth signaling pathways converge on ERK activation. Mol Cell Neurosci 13(5):362–378. doi:10.1006/mcne.1999.0753
Wang PY, Weng J, Anderson RG (2005) OSBP is a cholesterol-regulated scaffolding protein in control of ERK 1/2 activation. Science 307(5714):1472–1476. doi:10.1126/science.1107710
Wu KY, Zippin JH, Huron DR, Kamenetsky M, Hengst U, Buck J, Levin LR, Jaffrey SR (2006) Soluble adenylyl cyclase is required for netrin-1 signaling in nerve growth cones. Nat Neurosci 9(10):1257–1264. doi:10.1038/nn1767
Low VF, Fiorini Z, Fisher L, Jasoni CL (2012) Netrin-1 stimulates developing GnRH neurons to extend neurites to the median eminence in a calcium- dependent manner. PLoS One 7(10):e46999. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046999
Gomes C, Smith SC, Youssef MN, Zheng JJ, Hagg T, Hetman M (2011) RNA polymerase 1-driven transcription as a mediator of BDNF-induced neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem 286(6):4357–4363. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.170134
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81071016), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0647), the Key Project of Guangdong Province (CXZD1018), and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and the Innovative Research Team in University (IRT1142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Xi Gu and Aili Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Li, A., Liu, S. et al. MicroRNA124 Regulated Neurite Elongation by Targeting OSBP. Mol Neurobiol 53, 6388–6396 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9540-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9540-4