Abstract
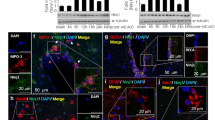
Osteopontin (OPN) is a phosphorylated glycoprotein possessing an arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD)-motif, which binds to several cell surface integrins and mediates a wide range of cellular processes. Inductions of OPN have been reported in the postischemic brain, and the neuroprotective effects of OPN have been demonstrated in animal models of stroke. In the present study, we showed a robust neuroprotective effect of RGD-containing icosamer OPN peptide (OPNpt20) in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia (middle cerebral artery occlusion, MCAO). Intranasally administered OPNpt20 reduced mean infarct volume by 79.7 % compared to the treatment-naïve MCAO control animals and markedly ameliorated neurological deficits. In addition, OPNpt20 significantly suppressed the inductions of iNOS and of inflammatory markers in postischemic brains and in primary microglial cultures, demonstrating anti-inflammatory effects. Administration of a mutant peptide, in which RGD was replaced by arginine-alanine-alanine (RAA), failed to suppress infarct volumes in MCAO animals and co-administration of OPNpt20 with anti-αvβ3 integrin antibody failed to suppress iNOS induction in primary microglia culture, indicating that the RGD motif in OPNpt20 and endogenous αvβ3 integrin play critical roles. Furthermore, pull-down assay revealed a direct binding between OPNpt20 and αvβ3 integrin in primary microglia culture. Together, these results indicate that RGD-containing OPN icosamer has therapeutic potential in the postischemic brain and αvβ3 integrin-mediated anti-inflammatory effect might be an underlying mechanism.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RGD:
-
Arginine-glycine-aspartate
- SLAY:
-
Serine-leucine-alanine-tyrosine
- RAA:
-
Arginine-alanine-alanine
- SLAA:
-
Serine-leucine-alanine-alanine
- OPN:
-
Osteopontin
- OPNpt20:
-
20 amino acid peptide of osteopontin
- OPNpt20-RAA:
-
Mutant 20 amino acid peptide of osteopontin (in which RGD motif is replaced by RAA)
- OPNpt20-SLAA:
-
Mutant 20 amino acid peptide of osteopontin (in which SLAY motif is replaced by SLAA)
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- mNSS:
-
Modified neurological severity score
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- GMS:
-
Gelatin microsphere
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
References
Denhardt DT, Giachelli CM, Rittling SR (2001) Role of osteopontin in cellular signaling and toxicant injury. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:723–749
Platzer G, Schedlbauer A, Chemelli A, Ozdowy P, Coudevylle N, Auer R et al (2011) The metastasis-associated extracellular matrix protein osteopontin forms transient structure in ligand interaction sites. Biochemistry 50:6113–6124
Thayer JM, Giachelli CM, Mirkes PE, Schwartz SM (1995) Expression of osteopontin in the head process late in gastrulation in the rat. J Exp Zool 272:240–244
Steinman L, Martin R, Bernard C, Conlon P, Oksenberg JR (2002) Multiple sclerosis: deeper understanding of its pathogenesis reveals new targets for therapy. Annu Rev Neurosci 25:491–505
Xu G, Nie H, Li N, Zheng W, Zhang D, Feng G et al (2005) Role of osteopontin in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis. J Clin Invest 115:1060–1067
Ohsuzu F (2004) The roles of cytokines, inflammation and immunity in vascular diseases. J Atheroscler Thromb 11:313–321
Xanthou G, Alissafi T, Semitekolou M, Simoes DC, Economidou E, Gaga M et al (2007) Osteopontin has a crucial role in allergic airway disease through regulation of dendritic cell subsets. Nat Med 13:570–578
Wang X, Louden C, Yue TL, Ellison JA, Barone FC, Solleveld HA et al (1998) Delayed expression of osteopontin after focal stroke in the rat. J Neurosci 18:2075–2083
Wung JK, Perry G, Kowalski A, Harris PL, Bishop GM, Trivedi MA et al (2007) Increased expression of the remodeling- and tumorigenic-associated factor osteopontin in pyramidal neurons of the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Curr Alzheimer Res 4:67–72
Iczkiewicz J, Rose S, Jenner P (2007) Osteopontin expression in activated glial cells following mechanical- or toxin-induced nigral dopaminergic cell loss. Exp Neurol 207:95–106
Borges K, Gearing M, Rittling S, Sorensen ES, Kotloski R, Denhardt DT et al (2008) Characterization of osteopontin expression and function after status epilepticus. Epilepsia 49:1675–1685
Ellison JA, Velier JJ, Spera P, Jonak ZL, Wang X, Barone FC et al (1998) Osteopontin and its integrin receptor alpha(v)beta3 are upregulated during formation of the glial scar after focal stroke. Stroke 29:1698–1707
He B, Mirza M, Weber GF (2006) An osteopontin splice variant induces anchorage independence in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 25:2192–2202
Standal T, Borset M, Sundan A (2004) Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone remodeling. Exp Oncol 26:179–184
Yokosaki Y, Matsuura N, Sasaki T, Murakami I, Schneider H, Higashiyama S et al (1999) The integrin alpha(9)beta(1) binds to a novel recognition sequence (SVVYGLR) in the thrombin-cleaved amino-terminal fragment of osteopontin. J Biol Chem 274:36328–36334
Bayless KJ, Meininger GA, Scholtz JM, Davis GE (1998) Osteopontin is a ligand for the alpha4beta1 integrin. J Cell Sci 111:1165–1174
Weber GF, Ashkar S, Glimcher MJ, Cantor H (1996) Receptor-ligand interaction between CD44 and osteopontin (Eta-1). Science 271:509–512
Meller R, Stevens SL, Minami M, Cameron JA, King S, Rosenzweig H et al (2005) Neuroprotection by osteopontin in stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:217–225
Doyle KP, Yang T, Lessov NS, Ciesielski TM, Stevens SL, Simon RP et al (2008) Nasal administration of osteopontin peptide mimetics confers neuroprotection in stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1235–1248
Wu B, Ma Q, Suzuki H, Chen C, Liu W, Tang J et al (2011) Recombinant osteopontin attenuates brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Neurocrit Care 14:109–117
Suzuki H, Hasegawa Y, Chen W, Kanamaru KT, Zhang JH (2010) Recombinant osteopontin in cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Ann Neurol 68:650–660
Iczkiewicz J, Broom L, Cooper JD, Wong AM, Rose S, Jenner P (2010) The RGD-containing peptide fragment of osteopontin protects tyrosine hydroxylase positive cells against toxic insult in primary ventral mesencephalic cultures and in the rat substantia nigra. J Neurochem 114(6):1792–1804
Chen W, Ma Q, Suzuki H, Hartman R, Tang J, Zhang JH (2011) Osteopontin reduced hypoxia-ischemia neonatal brain injury by suppression of apoptosis in a rat pup model. Stroke 42(3):764–769
van Velthoven CT, Heijnen CJ, van Bel F, Kavelaars A (2011) Osteopontin enhances endogenous repair after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Stroke 42(8):2294–2301
Jin Y, Kim IY, Kim ID, Lee HK, Park JY, Han PL et al (2014) Biodegradable gelatin microspheres enhance the neuroprotective potency of osteopontin via quick and sustained release in the post-ischemic brain. Acta Biomater 10(7):3126–3135
Kim ID, Shin JH, Kim SW, Choi S, Ahn J, Han PL et al (2012) Intranasal delivery of HMGB1 siRNA confers target gene knockdown and robust neuroprotection in the postischemic brain. Mol Ther 20:829–839
Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M, Willing AE et al (2001) Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke 32:2682–2688
Kim JB, Lim CM, Yu YM, Lee JK (2008) Induction and subcellular localization of high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) in the postischemic rat brain. J Neurosci Res 86:1125–1131
Kim JB, Sig Choi J, Yu YM, Nam K, Piao CS, Kim SW et al (2006) HMGB1, a novel cytokine-like mediator linking acute neuronal death and delayed neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain. J Neurosci 26:6413–6421
Gao C, Guo H, Mi Z, Grusby MJ, Kuo PC (2007) Osteopontin induces ubiquitin-dependent degradation of STAT1 in RAW264.7 murine macrophages. J Immunol 178:1870–1881
Schroeter M, Zickler P, Denhardt DT, Hartung HP, Jander S (2006) Increased thalamic neurodegeneration following ischaemic cortical stroke in osteopontin-deficient mice. Brain 129:1426–1437
Choi JS, Kim HY, Cha JH, Choi JY, Lee MY (2007) Transient microglial and prolonged astroglial upregulation of osteopontin following transient forebrain ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1151:195–202
Scott JA, Weir ML, Wilson SM, Xuan JW, Chambers AF, McCormack DG (1998) Osteopontin inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase activity in rat vascular tissue. Am J Physiol 275:H2258–H2265
Li H, Shen H, Yan G, Zhang Y, Liu M, Fang P et al (2015) Site-specific structural characterization of O-glycosylation and identification of phosphorylation sites of recombinant osteopontin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1854(6):581–591
Kale S, Raja R, Thorat D, Soundararajan G, Patil TV, Kundu GC (2014) Osteopontin signaling upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in tumor-associated macrophages leading to enhanced angiogenesis and melanoma growth via α9β1 integrin. Oncogene 33(18):2295–2306
Yan YP, Lang BT, Vemuganti R, Dempsey RJ (2009) Osteopontin is a mediator of the lateral migration of neuroblasts from the subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int 55:826–832
Ophascharoensuk V, Giachelli CM, Gordon K, Hughes J, Pichler R, Brown P et al (1999) Obstructive uropathy in the mouse: role of osteopontin in interstitial fibrosis and apoptosis. Kidney Int 56:571–580
Shin YJ, Kim HL, Choi JS, Choi JY, Cha JH, Lee MY (2011) Osteopontin: correlation with phagocytosis by brain macrophages in a rat model of stroke. Glia 59:413–423
Shin YJ, Kim HL, Park JM, Cho JM, Kim CY, Choi KJ et al (2012) Overlapping distribution of osteopontin and calcium in the ischemic core of rat brain after transient focal ischemia. J Neurotrauma 29:1530–1538
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by a Medical Research Center Grant 2014R1A5A2009392 (to J.-K.L.) funded by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yin-Chuan Jin and Hahnbie Lee contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
(GIF 200 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, YC., Lee, H., Kim, SW. et al. Intranasal Delivery of RGD Motif-Containing Osteopontin Icosamer Confers Neuroprotection in the Postischemic Brain via αvβ3 Integrin Binding. Mol Neurobiol 53, 5652–5663 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9480-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9480-z