Abstract
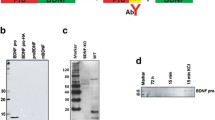
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes synaptic strengthening through the regulation of kinase and phosphatase activity. Conversely, striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) opposes synaptic strengthening through inactivation or internalization of signaling molecules. Here, we investigated whether BDNF regulates STEP levels/activity. BDNF induced a reduction of STEP61 levels in primary cortical neurons, an effect that was prevented by inhibition of tyrosine kinases, phospholipase C gamma, or the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). The levels of pGluN2BTyr1472 and pERK1/2Thr202/Tyr204, two STEP substrates, increased in BDNF-treated cultures, and blockade of the UPS prevented STEP61 degradation and reduced BDNF-induced GluN2B and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Moreover, brief or sustained cell depolarization reduced STEP61 levels in cortical neurons by different mechanisms. BDNF also promoted UPS-mediated STEP61 degradation in cultured striatal and hippocampal neurons. In contrast, nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3 had no effect on STEP61 levels. Our results thus indicate that STEP61 degradation is an important event in BDNF-mediated effects.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee HK (2006) Synaptic plasticity and phosphorylation. Pharmacol Ther 112:810–832
Cowansage KK, Ledoux JE, Monfils MH (2010) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a dynamic gatekeeper of neural plasticity. Curr Mol Pharmacol 3:12–29
Lynch G, Rex CS, Chen LY, Gall CM (2008) The substrates of memory: defects, treatments, and enhancement. Eur J Pharmacol 585:2–13
Park H, Poo MM (2013) Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:7–23
Minichiello L (2009) TrkB signalling pathways in LTP and learning. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:850–860
Segal RA (2003) Selectivity in neurotrophin signaling: theme and variations. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:299–330
Jeanneteau F, Deinhardt K, Miyoshi G, Bennett AM, Chao MV (2010) The MAP kinase phosphatase MKP-1 regulates BDNF-induced axon branching. Nat Neurosci 13:1373–1379
Briz V, Hsu YT, Li Y, Lee E, Bi X, Baudry M (2013) Calpain-2-mediated PTEN degradation contributes to BDNF-induced stimulation of dendritic protein synthesis. J Neurosci 33:4317–4328
Shimizu K, Phan T, Mansuy IM, Storm DR (2007) Proteolytic degradation of SCOP in the hippocampus contributes to activation of MAP kinase and memory. Cell 128:1219–1229
Fitzpatrick CJ, Lombroso PJ (2011) The role of striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) in cognition. Front Neuroanat 5:47
Bult A, Zhao F, Dirkx R Jr, Raghunathan A, Solimena M, Lombroso PJ (1997) STEP: a family of brain-enriched PTPs. Alternative splicing produces transmembrane, cytosolic and truncated isoforms. Eur J Cell Biol 72:337–344
Sharma E, Zhao F, Bult A, Lombroso PJ (1995) Identification of two alternatively spliced transcripts of STEP: a subfamily of brain-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatases. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 32:87–93
Goebel-Goody SM, Davies KD, Alvestad Linger RM, Freund RK, Browning MD (2009) Phospho-regulation of synaptic and extrasynaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in adult hippocampal slices. Neuroscience 158:1446–1459
Oyama T, Goto S, Nishi T, Sato K, Yamada K, Yoshikawa M, Ushio Y (1995) Immunocytochemical localization of the striatal enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase in the rat striatum: a light and electron microscopic study with a complementary DNA-generated polyclonal antibody. Neuroscience 69:869–880
Xu J, Kurup P, Zhang Y, Goebel-Goody SM, Wu PH, Hawasli AH, Baum ML, Bibb JA et al (2009) Extrasynaptic NMDA receptors couple preferentially to excitotoxicity via calpain-mediated cleavage of STEP. J Neurosci 29:9330–9343
Boulanger LM, Lombroso PJ, Raghunathan A, During MJ, Wahle P, Naegele JR (1995) Cellular and molecular characterization of a brain-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Neurosci 15:1532–1544
Lorber B, Berry M, Hendriks W, Den HJ, Pulido R, Logan A (2004) Stimulated regeneration of the crushed adult rat optic nerve correlates with attenuated expression of the protein tyrosine phosphatases RPTPalpha, STEP, and LAR. Mol Cell Neurosci 27:404–416
Kurup P, Zhang Y, Xu J, Venkitaramani DV, Haroutunian V, Greengard P, Nairn AC, Lombroso PJ (2010) Abeta-mediated NMDA receptor endocytosis in Alzheimer's disease involves ubiquitination of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP61. J Neurosci 30:5948–5957
Snyder EM, Nong Y, Almeida CG, Paul S, Moran T, Choi EY, Nairn AC, Salter MW et al (2005) Regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by amyloid-beta. Nat Neurosci 8:1051–1058
Munoz JJ, Tarrega C, Blanco-Aparicio C, Pulido R (2003) Differential interaction of the tyrosine phosphatases PTP-SL, STEP and HePTP with the mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and p38alpha is determined by a kinase specificity sequence and influenced by reducing agents. Biochem J 372:193–201
Paul S, Nairn AC, Wang P, Lombroso PJ (2003) NMDA-mediated activation of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP regulates the duration of ERK signaling. Nat Neurosci 6:34–42
Zhang Y, Venkitaramani DV, Gladding CM, Zhang Y, Kurup P, Molnar E, Collingridge GL, Lombroso PJ (2008) The tyrosine phosphatase STEP mediates AMPA receptor endocytosis after metabotropic glutamate receptor stimulation. J Neurosci 28:10561–10566
Nguyen TH, Liu J, Lombroso PJ (2002) Striatal enriched phosphatase 61 dephosphorylates Fyn at phosphotyrosine 420. J Biol Chem 277:24274–24279
Poddar R, Deb I, Mukherjee S, Paul S (2010) NR2B-NMDA receptor mediated modulation of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP regulates glutamate induced neuronal cell death. J Neurochem 115:1350–1362
Xu J, Kurup P, Bartos JA, Patriarchi T, Hell JW, Lombroso PJ (2012) Striatal-enriched protein-tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) regulates Pyk2 kinase activity. J Biol Chem 287:20942–20956
Paul S, Snyder GL, Yokakura H, Picciotto MR, Nairn AC, Lombroso PJ (2000) The dopamine/D1 receptor mediates the phosphorylation and inactivation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase STEP via a PKA-dependent pathway. J Neurosci 20:5630–5638
Valjent E, Pascoli V, Svenningsson P, Paul S, Enslen H, Corvol JC, Stipanovich A, Caboche J et al (2005) Regulation of a protein phosphatase cascade allows convergent dopamine and glutamate signals to activate ERK in the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:491–496
Braithwaite SP, Xu J, Leung J, Urfer R, Nikolich K, Oksenberg D, Lombroso PJ, Shamloo M (2008) Expression and function of striatal enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase is profoundly altered in cerebral ischemia. Eur J Neurosci 27:2444–2452
Gurd JW, Bissoon N, Nguyen TH, Lombroso PJ, Rider CC, Beesley PW, Vannucci SJ (1999) Hypoxia-ischemia in perinatal rat brain induces the formation of a low molecular weight isoform of striatal enriched tyrosine phosphatase (STEP). J Neurochem 73:1990–1994
Nguyen TH, Paul S, Xu Y, Gurd JW, Lombroso PJ (1999) Calcium-dependent cleavage of striatal enriched tyrosine phosphatase (STEP). J Neurochem 73:1995–2001
Mukherjee S, Poddar R, Deb I, Paul S (2011) Dephosphorylation of specific sites in the KIS domain leads to ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP. Biochem J
Carty NC, Xu J, Kurup P, Brouillette J, Goebel-Goody SM, Austin DR, Yuan P, Chen G et al (2012) The tyrosine phosphatase STEP: implications in schizophrenia and the molecular mechanism underlying antipsychotic medications. Transl Psychiatry 2, e137
Goebel-Goody SM, Wilson-Wallis ED, Royston S, Tagliatela SM, Naegele JR, Lombroso PJ (2012) Genetic manipulation of STEP reverses behavioral abnormalities in a fragile X syndrome mouse model. Genes Brain Behav 11:586–600
Saavedra A, Giralt A, Rue L, Xifro X, Xu J, Ortega Z, Lucas JJ, Lombroso PJ et al (2011) Striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase expression and activity in Huntington's disease: a STEP in the resistance to excitotoxicity. J Neurosci 31:8150–8162
Zhang Y, Kurup P, Xu J, Carty N, Fernandez SM, Nygaard HB, Pittenger C, Greengard P et al (2010) Genetic reduction of striatal-enriched tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) reverses cognitive and cellular deficits in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:19014–19019
Gallo G, Ernst AF, McLoon SC, Letourneau PC (2002) Transient PKA activity is required for initiation but not maintenance of BDNF-mediated protection from nitric oxide-induced growth-cone collapse. J Neurosci 22:5016–5023
Gao Y, Nikulina E, Mellado W, Filbin MT (2003) Neurotrophins elevate cAMP to reach a threshold required to overcome inhibition by MAG through extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent inhibition of phosphodiesterase. J Neurosci 23:11770–11777
Cheng X, Ma Y, Moore M, Hemmings BA, Taylor SS (1998) Phosphorylation and activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:9849–9854
Zadran S, Jourdi H, Rostamiani K, Qin Q, Bi X, Baudry M (2010) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and epidermal growth factor activate neuronal m-calpain via mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation. J Neurosci 30:1086–1095
Jia JM, Chen Q, Zhou Y, Miao S, Zheng J, Zhang C, Xiong ZQ (2008) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-tropomyosin-related kinase B signaling contributes to activity-dependent changes in synaptic proteins. J Biol Chem 283:21242–21250
Lin SY, Wu K, Levine ES, Mount HT, Suen PC, Black IB (1998) BDNF acutely increases tyrosine phosphorylation of the NMDA receptor subunit 2B in cortical and hippocampal postsynaptic densities. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 55:20–27
Xu F, Plummer MR, Len GW, Nakazawa T, Yamamoto T, Black IB, Wu K (2006) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor rapidly increases NMDA receptor channel activity through Fyn-mediated phosphorylation. Brain Res 1121:22–34
Wu CL, Yin JH, Hwang CS, Chen SD, Yang DY, Yang DI (2012) c-Jun-dependent sulfiredoxin induction mediates BDNF protection against mitochondrial inhibition in rat cortical neurons. Neurobiol Dis 46:450–462
Zhang Z, Fan J, Ren Y, Zhou W, Yin G (2013) The release of glutamate from cortical neurons regulated by BDNF via the TrkB/Src/PLC-gamma1 pathway. J Cell Biochem 114:144–151
Zhou X, Xiao H, Wang H (2011) Developmental changes of TrkB signaling in response to exogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor in primary cortical neurons. J Neurochem 119:1205–1216
Pulido R, Zuniga A, Ullrich A (1998) PTP-SL and STEP protein tyrosine phosphatases regulate the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1 and ERK2 by association through a kinase interaction motif. EMBO J 17:7337–7350
Okamura A, Goto S, Nishi T, Yamada K, Yoshikawa M, Ushio Y (1997) Postnatal ontogeny of striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) in rat striatum. Exp Neurol 145:228–234
Knusel B, Rabin S, Widmer HR, Hefti F, Kaplan DR (1992) Neurotrophin-induced trk receptor phosphorylation and cholinergic neuron response in primary cultures of embryonic rat brain neurons. Neuroreport 3:885–888
Widmer HR, Knusel B, Hefti F (1992) Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis by brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 in rat cerebral cortical neurons developing in culture. J Neurochem 59:2113–2124
Widmer HR, Kaplan DR, Rabin SJ, Beck KD, Hefti F, Knusel B (1993) Rapid phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma 1 by brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 in cultures of embryonic rat cortical neurons. J Neurochem 60:2111–2123
Kume T, Nishikawa H, Tomioka H, Katsuki H, Akaike A, Kaneko S, Maeda T, Kihara T et al (2000) p75-mediated neuroprotection by NGF against glutamate cytotoxicity in cortical cultures. Brain Res 852:279–289
Androutsellis-Theotokis A, McCormack WJ, Bradford HF, Stern GM, Pliego-Rivero FB (1996) The depolarisation-induced release of [125I]BDNF from brain tissue. Brain Res 743:40–48
Goodman LJ, Valverde J, Lim F, Geschwind MD, Federoff HJ, Geller AI, Hefti F (1996) Regulated release and polarized localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 7:222–238
Lim ST, Esfahani K, Avdoshina V, Mocchetti I (2011) Exogenous gangliosides increase the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuropharmacology 60:1160–1167
Mowla SJ, Pareek S, Farhadi HF, Petrecca K, Fawcett JP, Seidah NG, Morris SJ, Sossin WS et al (1999) Differential sorting of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 19:2069–2080
Cazorla M, Premont J, Mann A, Girard N, Kellendonk C, Rognan D (2011) Identification of a low-molecular weight TrkB antagonist with anxiolytic and antidepressant activity in mice. J Clin Invest 121:1846–1857
Cheng PL, Lu H, Shelly M, Gao H, Poo MM (2011) Phosphorylation of E3 ligase Smurf1 switches its substrate preference in support of axon development. Neuron 69:231–243
Lin MY, Lin YM, Kao TC, Chuang HH, Chen RH (2011) PDZ-RhoGEF ubiquitination by Cullin3-KLHL20 controls neurotrophin-induced neurite outgrowth. J Cell Biol 193:985–994
Sen N, Snyder SH (2011) Neurotrophin-mediated degradation of histone methyltransferase by S-nitrosylation cascade regulates neuronal differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:20178–20183
Jeanneteau F, Garabedian MJ, Chao MV (2008) Activation of Trk neurotrophin receptors by glucocorticoids provides a neuroprotective effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:4862–4867
He YY, Zhang XY, Yung WH, Zhu JN, Wang JJ (2013) Role of BDNF in central motor structures and motor diseases. Mol Neurobiol 48:783–793
Kurup PK, Xu J, Videira RA, Ononenyi C, Baltazar G, Lombroso PJ, Nairn AC (2015) STEP61 is a substrate of the E3 ligase parkin and is upregulated in Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:1202–1207
Finkbeiner S (2000) Calcium regulation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:394–401
Gao X, Chen J (2009) Conditional knockout of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus increases death of adult-born immature neurons following traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 26:1325–1335
Gavalda N, Perez-Navarro E, Gratacos E, Comella JX, Alberch J (2004) Differential involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and p42/p44 mitogen activated protein kinase pathways in brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced trophic effects on cultured striatal neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 25:460–468
Gorski JA, Zeiler SR, Tamowski S, Jones KR (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for the maintenance of cortical dendrites. J Neurosci 23:6856–6865
Ivkovic S, Ehrlich ME (1999) Expression of the striatal DARPP-32/ARPP-21 phenotype in GABAergic neurons requires neurotrophins in vivo and in vitro. J Neurosci 19:5409–5419
Marty S, Berninger B, Carroll P, Thoenen H (1996) GABAergic stimulation regulates the phenotype of hippocampal interneurons through the regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuron 16:565–570
Baldelli P, Forni PE, Carbone E (2000) BDNF, NT-3 and NGF induce distinct new Ca2+ channel synthesis in developing hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 12:4017–4032
Culmsee C, Gerling N, Lehmann M, Nikolova-Karakashian M, Prehn JH, Mattson MP, Krieglstein J (2002) Nerve growth factor survival signaling in cultured hippocampal neurons is mediated through TrkA and requires the common neurotrophin receptor P75. Neuroscience 115:1089–1108
Ip NY, Li Y, Yancopoulos GD, Lindsay RM (1993) Cultured hippocampal neurons show responses to BDNF, NT-3, and NT-4, but not NGF. J Neurosci 13:3394–3405
Yamada M, Numakawa T, Koshimizu H, Tanabe K, Wada K, Koizumi S, Hatanaka H (2002) Distinct usages of phospholipase C gamma and Shc in intracellular signaling stimulated by neurotrophins. Brain Res 955:183–190
Barki-Harrington L, Elkobi A, Tzabary T, Rosenblum K (2009) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the 2B subunit of the NMDA receptor is necessary for taste memory formation. J Neurosci 29:9219–9226
Mizuno M, Yamada K, He J, Nakajima A, Nabeshima T (2003) Involvement of BDNF receptor TrkB in spatial memory formation. Learn Mem 10:108–115
Burnouf S, Martire A, Derisbourg M, Laurent C, Belarbi K, Leboucher A, Fernandez-Gomez FJ, Troquier L et al (2013) NMDA receptor dysfunction contributes to impaired brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced facilitation of hippocampal synaptic transmission in a Tau transgenic model. Aging Cell 12:11–23
Crozier RA, Black IB, Plummer MR (1999) Blockade of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors prevents BDNF enhancement of glutamatergic transmission in hippocampal neurons. Learn Mem 6:257–266
Adams JP, Sweatt JD (2002) Molecular psychology: roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42:135–163
Davis S, Laroche S (2006) Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular regulated kinase signalling and memory stabilization: a review. Genes Brain Behav 5(Suppl 2):61–72
Giovannini MG (2006) The role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in memory encoding. Rev Neurosci 17:619–634
Venkitaramani DV, Moura PJ, Picciotto MR, Lombroso PJ (2011) Striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) knockout mice have enhanced hippocampal memory. Eur J Neurosci 33:2288–2298
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Ana López and Maria Teresa Muñoz for their technical support and Dr. Cristina Malagelada and to laboratory members for helpful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by projects PI10/01072, PI13/01250, and RD12/0019/0002, integrated in the “Plan Nacional de I + D + I y cofinanciado por el ISCIII-Subdirección General de Evaluación y el Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER),” Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain (grants SAF2012-39142 to S.G. and SAF2011-29507 to J.A.), Generalitat de Catalunya, Spain (grant 2009SGR-00326 to J.A.), and the National Institutes of Health (grants MH091037 and MH52711 to P.J.L.). A.S. was supported by Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad, Spain (Juan de la Cierva subprogram, grant JCI-2010-08207) and S.T. by Generalitat de Catalunya, Spain (grant AGAUR ST067914).
Conflict of Interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mar Puigdellívol and Shiraz Tyebji contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saavedra, A., Puigdellívol, M., Tyebji, S. et al. BDNF Induces Striatal-Enriched Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 61 Degradation Through the Proteasome. Mol Neurobiol 53, 4261–4273 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9335-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9335-7