Abstract
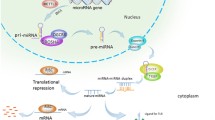
MicroRNAs (miRNAs, miRs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression posttranscriptionally. Although discovered only recently in the early 1990s, this relatively new group of molecules has already been proven to play an essential role in the regulation of many physiological and, most importantly, pathological processes such as cancer. A large number of miRNAs has been found to be involved in the pathogenesis of various human malignancies, and expression of miRNAs has been demonstrated to correlate with clinic and outcome. In tumors of the brain, however, the investigations on the role of miRNAs are still in its infancy, and most publications refer to the most common primary brain tumor, the glioma (mostly glioblastoma). But despite the fact that there is only limited data available so far, these first results are very promising and implicate that miRNAs might open a new perspective for diagnostics and treatment of this disease. With this review article, we aim to provide a short overview of miRNA biogenesis, function and regulation in general. Thereafter, the clinical relevant data about miRNAs in the two most common primary malignant brain tumors in adults (glioblastomas) and children (medulloblastomas) will be summarized, and their potential impact on diagnostics and treatment will be highlighted.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P, Parkin DM (2004) GLOBOCAN 2002: Cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide, Version 2.0. IARC CancerBase No. 5. IARC, Lyon
Tran B, Rosenthal MA (2010) Survival comparison between glioblastoma multiforme and other incurable cancers. J Clin Neurosci 17(4):417–421
Rossi A, Caracciolo V, Russo G, Reiss K, Giordano A (2008) Medulloblastoma: from molecular pathology to therapy. Clin Cancer Res 14(4):971–976
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G (1993) Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75:855–862
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ (2008) MiRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D154–158
Novakova J, Slaby O, Vyzula R, Michalek J (2009) MicroRNA involvement in glioblastoma pathogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386(1):1–5
Purow BW, Schiff D (2010) Glioblastoma genetics: in rapid flux. Discov Med 9(45):125–131
Lawler S, Chiocca EA (2009) Emerging functions of microRNAs in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 92(3):297–306
Nagarajan RP, Costello JF (2009) Epigenetic mechanisms in glioblastoma multiforme. Semin Cancer Biol 19(3):188–197
Pang JC, Kwok WK, Chen Z, Ng HK (2009) Oncogenic role of microRNAs in brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol 117(6):599–611
Turner JD, Williamson R, Almefty KK, Nakaji P, Porter R, Tse V, Kalani MY (2010) The many roles of microRNAs in brain tumor biology. Neurosurg Focus 28(1):E3
Garzon R, Fabbri M, Cimmino A, Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends Mol Med 12(12):580–587
Lynam-Lennon N, Maher SG, Reynolds JV (2009) The roles of microRNA in cancer and apoptosis. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 84(1):55–71
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Hummel R, Hussey DJ, Haier J. (2011) Review: the impact of MiRNAs on resistance to anticancer treatment: the future for MiRNA-based targeted therapy? In Mulligan JA (ed) MicroRNA: Expression, detection and therapeutic strategies, Chapter 5. Nova Science Publishers, New York
Inui M, Martello G, Piccolo S (2010) MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(4):252–263
Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC (2009) Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(2):126–139
Saito Y, Liang G, Egger G, Friedman JM, Chuang JC, Coetzee GA, Jones PA (2006) Specific activation of microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer cell 9(6):435–443
Saito Y, Friedman JM, Chihara Y, Egger G, Chuang JC, Liang G (2009) Epigenetic therapy upregulates the tumor suppressor microRNA-126 and its host gene EGFL7 in human cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379(3):726–731
Cai Y, Yu X, Hu S, Yu J (2009) A brief review on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf 7(4):147–154
Chuang JC, Jones PA (2007) Epigenetics and microRNAs. Pediatr Res 61(5 Pt 2):24R–29R
Chen Y, Gao W, Luo J, Tian R, Sun H, Zou S (2011) Methyl-CpG binding protein MBD2 is implicated in methylation-mediated suppression of miR-373 in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Rep 25:443–451
Stumpel DJ, Schotte D, Lange-Turenhout EA, Schneider P, Seslija L, de Menezes RX, Marquez VE, Pieters R, den Boer ML, Stam RW (2010) Hypermethylation of specific microRNA genes in MLL-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia: major matters at a micro scale. Leukemia 25(3):429–439
Langevin SM, Stone RA, Bunker CH, Lyons-Weiler MA, Laframboise WA, Kelly L, Seethala RR, Grandis JR, Sobol RW, Taioli E (2010) MicroRNA-137 promoter methylation is associated with poorer overall survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer 117(7):1454–1462
Schotte D, Lange-Turenhout EA, Stumpel DJ, Stam RW, Buijs-Gladdines JG, Meijerink JP, Pieters R, Den Boer ML (2010) Expression of miR-196b is not exclusively MLL-driven but is especially linked to activation of HOXA genes in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 95(10):1675–1682
Matei DE, Nephew KP (2010) Epigenetic therapies for chemoresensitization of epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 116:195–201
Kelly TK, De Carvalho DD, Jones PA (2010) Epigenetic modifications as therapeutic targets. Nat Biotechnol 28:1069–1078
Cheung HH, Lee TL, Rennert OM, Chan WY (2009) DNA methylation of cancer genome. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 87:335–350
Humeniuk R, Mishra PJ, Bertino JR, Banerjee D (2009) Molecular targets for epigenetic therapy of cancer. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 10:161–165
Pawlicki JM, Steitz JA (2010) Nuclear networking fashions pre-messenger RNA and primary microRNA transcripts for function. Trends Cell Biol 20(1):52–61
Cowland JB, Hother C, Grønbaek K (2007) MicroRNAs and cancer. APMIS 115(10):1090–1106
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2005) Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol 3:e85
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS, Johnson JM (2005) Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target RNAs. Nature 433:769–773
Ambros V (2003) MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113(6):673–676, Erratum in: (2003) Cell 114(2):269
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(9):2999–3004
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007) microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 302(1):1–12
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, Calin GA, Liu CG, Croce CM, Harris CC (2006) Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 9(3):189–198
Cho WC (2007) OncomiRs: the discovery and progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer 6:60
Eder M, Scherr M (2005) MicroRNA and lung cancer. N Engl J Med 352:2446–2448
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW, Hannon GJ, Hammond SM (2005) A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435(7043):828–833
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM, Ramos KS, Colburn NH, Li Y (2008) MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene 27(31):4373–4379
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK (2009) MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(3–4):369–378
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, Iuliano R, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F, Roldo C, Garzon R, Sevignani C, Rassenti L, Alder H, Volinia S, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM (2006) A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 353(17):1793–1801, Erratum in: (2006) N Engl J Med 355(5):533
Liu W, Gong YH, Chao TF, Peng XZ, Yuan JG, Ma ZY, Jia G, Zhao JZ (2009) Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs by microarray: a possible role for microRNAs gene in medulloblastomas. Chin Med J (Engl) 122(20):2405–2411
Hummel R, Maurer J, Haier J (2011) Clinical role of MiRNAs in different brain tumors. In Hayat MA (ed) Brain tumors (Part 1), vol. 3 Springer [Ahead of print]
Ciafrè SA, Galardi S, Mangiola A, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Sabatino G, Negrini M, Maira G, Croce CM, Farace MG (2005) Extensive modulation of a set of microRNAs in primary glioblastoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334(4):1351–1358
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS (2005) MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65(14):6029–6033
Sasayama T, Nishihara M, Kondoh T, Hosoda K, Kohmura E (2009) MicroRNA-10b is overexpressed in malignant glioma and associated with tumor invasive factors, uPAR and RhoC. Int J Cancer 125(6):1407–1413
Xia H, Qi Y, Ng SS, Chen X, Li D, Chen S, Ge R, Jiang S, Li G, Chen Y, He ML, Kung HF, Lai L, Lin MC (2009) microRNA-146b inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by targeting MMPs. Brain Res 1269:158–165
Cortez MA, Nicoloso MS, Shimizu M, Rossi S, Gopisetty G, Molina JR, Carlotti C Jr, Tirapelli D, Neder L, Brassesco MS, Scrideli CA, Tone LG, Georgescu MM, Zhang W, Puduvalli V, Calin GA (2010) miR-29b and miR-125a regulate podoplanin and suppress invasion in glioblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 49(11):981–990
Silber J, Lim DA, Petritsch C, Persson AI, Maunakea AK, Yu M, Vandenberg SR, Ginzinger DG, James CD, Costello JF, Bergers G, Weiss WA, Alvarez-Buylla A, Hodgson JG (2008) miR-124 and miR-137 inhibit proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme cells and induce differentiation of brain tumor stem cells. BMC Med 6:14
Rao SA, Santosh V, Somasundaram K (2010) Genome-wide expression profiling identifies deregulated miRNAs in malignant astrocytoma. Mod Pathol 23(10):1404–1417
Conti A, Aguennouz M, La Torre D, Tomasello C, Cardali S, Angileri FF, Maio F, Cama A, Germanò A, Vita G, Tomasello F (2009) miR-21 and 221 upregulation and miR-181b downregulation in human grade II–IV astrocytic tumors. J Neurooncol 93(3):325–332
Ernst A, Campos B, Meier J, Devens F, Liesenberg F, Wolter M, Reifenberger G, Herold-Mende C, Lichter P, Radlwimmer B (2010) De-repression of CTGF via the miR-17-92 cluster upon differentiation of human glioblastoma spheroid cultures. Oncogene 29(23):3411–3422
Zhang Y, Chao T, Li R, Liu W, Chen Y, Yan X, Gong Y, Yin B, Liu W, Qiang B, Zhao J, Yuan J, Peng X (2008) MicroRNA-128 inhibits glioma cells proliferation by targeting transcription factor E2F3a. J Mol Med 87(1):43–51
Shi L, Cheng Z, Zhang J, Li R, Zhao P, Fu Z, You Y (2008) hsa-mir-181a and hsa-mir-181b function as tumor suppressors in human glioma cells. Brain Res 1236:185–193
Malzkorn B, Wolter M, Liesenberg F, Grzendowski M, Stühler K, Meyer HE, Reifenberger G (2010) Identification and functional characterization of microRNAs involved in the malignant progression of gliomas. Brain Pathol 20(3):539–550
Dou T, Wu Q, Chen X, Ribas J, Ni X, Tang C, Huang F, Zhou L, Lu D (2010) A polymorphism of microRNA196a genome region was associated with decreased risk of glioma in Chinese population. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol [Epub ahead of print]
Kim H, Huang W, Jiang X, Pennicooke B, Park PJ, Johnson MD (2010) Integrative genome analysis reveals an oncomir/oncogene cluster regulating glioblastoma survivorship. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(5):2183–2188
Guan Y, Mizoguchi M, Yoshimoto K, Hata N, Shono T, Suzuki SO, Araki Y, Kuga D, Nakamizo A, Amano T, Ma X, Hayashi K, Sasaki T (2010) MiRNA-196 is upregulated in glioblastoma but not in anaplastic astrocytoma and has prognostic significance. Clin Cancer Res 16(16):4289–4297
Hummel R, Hussey DJ, Haier J (2010) MicroRNAs: predictors and modifiers of chemo- and radiotherapy in different tumour types. Eur J Cancer 46(2):298–311
Feng X, Zhang B, Wang J, Xu X, Lin N, Liu H (2010) Adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA against basic fibroblast growth factor mRNA enhances the sensitivity of glioblastoma cells to chemotherapy. Med Oncol [Epub ahead of print]
Li Y, Li W, Yang Y, Lu Y, He C, Hu G, Liu H, Chen J, He J, Yu H (2009) MicroRNA-21 targets LRRFIP1 and contributes to VM-26 resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Brain Res 1286:13–18
Ren Y, Zhou X, Mei M, Yuan XB, Han L, Wang GX, Jia ZF, Xu P, Pu PY, Kang CS (2010) MicroRNA-21 inhibitor sensitizes human glioblastoma cells U251 (PTEN-mutant) and LN229 (PTEN-wild type) to taxol. BMC Cancer 10:27
Ren Y, Kang CS, Yuan XB, Zhou X, Xu P, Han L, Wang GX, Jia Z, Zhong Y, Yu S, Sheng J, Pu PY (2010) Co-delivery of as-miR-21 and 5-FU by poly(amidoamine) dendrimer attenuates human glioma cell growth in vitro. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 21(3):303–314
Shi L, Chen J, Yang J, Pan T, Zhang S, Wang Z (2010) MiR-21 protected human glioblastoma U87MG cells from chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide induced apoptosis by decreasing Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity. Brain Res 1352:255–264
Gal H, Pandi G, Kanner AA, Ram Z, Lithwick-Yanai G, Amariglio N, Rechavi G, Givol D (2008) MIR-451 and Imatinib mesylate inhibit tumor growth of Glioblastoma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376(1):86–90
Ujifuku K, Mitsutake N, Takakura S, Matsuse M, Saenko V, Suzuki K, Hayashi K, Matsuo T, Kamada K, Nagata I, Yamashita S (2010) miR-195, miR-455-3p and miR-10a(*) are implicated in acquired temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Lett 296(2):241–248
Ferretti E, De Smaele E, Miele E, Laneve P, Po A, Pelloni M, Paganelli A, Di Marcotullio L, Caffarelli E, Screpanti I, Bozzoni I, Gulino A (2008) Concerted microRNA control of Hedgehog signalling in cerebellar neuronal progenitor and tumour cells. EMBO J 27(19):2616–2627
Ferretti E, De Smaele E, Po A, Di Marcotullio L, Tosi E, Espinola MS, Di Rocco C, Riccardi R, Giangaspero F, Farcomeni A, Nofroni I, Laneve P, Gioia U, Caffarelli E, Bozzoni I, Screpanti I, Gulino A (2009) MicroRNA profiling in human medulloblastoma. Int J Cancer 124(3):568–577
Uziel T, Karginov FV, Xie S, Parker JS, Wang YD, Gajjar A, He L, Ellison D, Gilbertson RJ, Hannon G, Roussel MF (2009) The miR-17 92 cluster collaborates with the Sonic Hedgehog pathway in medulloblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(8):2812–2817
Northcott PA, Fernandez LA, Hagan JP, Ellison DW, Grajkowska W, Gillespie Y, Grundy R, Van Meter T, Rutka JT, Croce CM, Kenney AM, Taylor MD (2009) The miR-17/92 polycistron is up-regulated in sonic hedgehog-driven medulloblastomas and induced by N-myc in sonic hedgehog-treated cerebellar neural precursors. Cancer Res 69(8):3249–3255
Liu W, Gong YH, Chao TF, Peng XZ, Yuan JG, Ma ZY, Jia G, Zhao JZ (2009) Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs by microarray: a possible role for microRNAs gene in medulloblastomas. Chin Med J (Engl) 122(20):2405–2411
Venkataraman S, Alimova I, Fan R, Harris P, Foreman N, Vibhakar R (2010) MicroRNA 128a increases intracellular ROS level by targeting Bmi-1 and inhibits medulloblastoma cancer cell growth by promoting senescence. PLoS One 5(6):e10748
Pierson J, Hostager B, Fan R, Vibhakar R (2008) Regulation of cyclin dependent kinase 6 by microRNA 124 in medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 90(1):1–7
Li KK, Pang JC, Ching AK, Wong CK, Kong X, Wang Y, Zhou L, Chen Z, Ng HK (2009) miR-124 is frequently down-regulated in medulloblastoma and is a negative regulator of SLC16A1. Hum Pathol 40(9):1234–1243
Wu J, Qian J, Li C, Kwok L, Cheng F, Liu P, Perdomo C, Kotton D, Vaziri C, Anderlind C, Spira A, Cardoso WV, Lü J (2010) miR-129 regulates cell proliferation by downregulating Cdk6 expression. Cell Cycle 9(9):1809–1818
Lu Y, Ryan SL, Elliott DJ, Bignell GR, Futreal PA, Ellison DW, Bailey S, Clifford SC (2009) Amplification and overexpression of Hsa-miR-30b, Hsa-miR-30d and KHDRBS3 at 8q24.22–q24.23 in medulloblastoma. PLoS One 4(7):e6159
Garzia L, Andolfo I, Cusanelli E, Marino N, Petrosino G, De Martino D, Esposito V, Galeone A, Navas L, Esposito S, Gargiulo S, Fattet S, Donofrio V, Cinalli G, Brunetti A, Vecchio LD, Northcott PA, Delattre O, Taylor MD, Iolascon A, Zollo M (2009) MicroRNA-199b-5p impairs cancer stem cells through negative regulation of HES1 in medulloblastoma. PLoS One 4(3):e4998
Li Y, Guessous F, Zhang Y, Dipierro C, Kefas B, Johnson E, Marcinkiewicz L, Jiang J, Yang Y, Schmittgen TD, Lopes B, Schiff D, Purow B, Abounader R (2009) MicroRNA-34a inhibits glioblastoma growth by targeting multiple oncogenes. Cancer Res 69(19):7569–7576
Guessous F, Zhang Y, Kofman A, Catania A, Li Y, Schiff D, Purow B, Abounader R (2010) microRNA-34a is tumor suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle 9(6) [Epub ahead of print]
Pierson J, Hostager B, Fan R, Vibhakar R (2008) Regulation of cyclin dependent kinase 6 by microRNA 124 in medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 90(1):1–7
Li KK, Pang JC, Ching AK, Wong CK, Kong X, Wang Y, Zhou L, Chen Z, Ng HK (2009) miR-124 is frequently down-regulated in medulloblastoma and is a negative regulator of SLC16A1. Hum Pathol 40(9):1234–1243
Cahill DP, Levine KK, Betensky RA, Codd PJ, Romany CA, Reavie LB, Batchelor TT, Futreal PA, Stratton MR, Curry WT, Iafrate AJ, Louis DN (2007) Loss of the mismatch repair protein MSH6 in human glioblastomas is associated with tumor progression during temozolomide treatment. Clin Cancer Res 13(7):2038–2045
Zhang J, Stevens MF, Laughton CA, Madhusudan S, Bradshaw TD (2010) Acquired resistance to temozolomide in glioma cell lines: molecular mechanisms and potential translational applications. Oncology 78(2):103–114
Felsberg J, Thon N, Eigenbrod S, Hentschel B, Sabel MC, Westphal M, Schackert G, Kreth FW, Pietsch T, Löffler M, Weller M, Reifenberger G, Tonn JC, for the German Glioma Network (2011) Promoter methylation and expression of MGMT and the DNA mismatch repair genes MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2 in paired primary and recurrent glioblastomas. Int J Cancer 129(3):659–670. doi:10.1002/ijc.26083
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2008) Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 455(7216):1061–1068
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Research Fellowship of the German Research Foundation (DFG) to R.H. (Hu 1763/1-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hummel, R., Maurer, J. & Haier, J. MicroRNAs in Brain Tumors. Mol Neurobiol 44, 223–234 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8197-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8197-x