Abstract
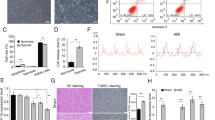
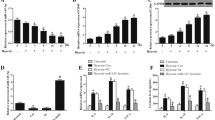
Myocardial infarction (MI) is one of the most common global diseases. Recently, microRNA 199a-5p (miR-199a-5p) has been recognized as a vital regulator in several human diseases. Nevertheless, the function of miR-199a-5p and the associated downstream molecular mechanisms in myocardial injury remain undescribed. Here, we assessed the relative expression of miR-199a-5p in an oxidative stress injury model of human myocardial cells. The effects of miR-199a-5p on myocardial cell viability were determined by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase UTP nick end labeling (TUNEL), flow cytometry, and western blot assays. Online bioinformatic analysis was used to predict the aim of miR-199a-5p in cardiomyocyte injury, which was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assays. miR-199a-5p increased the growth rate of cardiomyocytes after treatment with a hypoxic environment. miR-199a-5p acted as an inhibitor directly targeted hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF1α) expression, which was higher in the cardiomyocyte injury model than that in healthy myocardial cells. Upregulated HIF1α expression abolished miR-199a-5p-induced cell proliferation in the cardiomyocyte hypoxia model. Our results suggest that miR-199a-5p is a potential prognostic biomarker in myocardial damage.





Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Cahill, T. J., Choudhury, R. P., & Riley, P. R. (2017). Heart regeneration and repair after myocardial infarction: Translational opportunities for novel therapeutics. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 16, 699–717.
Reed, G. W., Rossi, J. E., & Cannon, C. P. (2017). Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet, 389, 197–210.
Boon, R. A., & Dimmeler, S. (2015). MicroRNAs in myocardial infarction. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 12, 135–142.
Toldo, S., & Abbate, A. (2018). The NLRP3 inflammasome in acute myocardial infarction. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 15, 203–214.
Lévy, M., Maurey, C., Celermajer, D. S., Vouhé, P. R., Danel, C., Bonnet, D., & Israël-Biet, D. (2007). Impaired apoptosis of pulmonary endothelial cells is associated with intimal proliferation and irreversibility of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 49, 803–810.
Bejerano, T., Etzion, S., Elyagon, S., Etzion, Y., & Cohen, S. (2018). Nanoparticle Delivery of miRNA-21 Mimic to Cardiac Macrophages Improves Myocardial Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction. Nano Letters, 18, 5885–5891.
Qipshidze, K. N., Piell, K. M., Wang, E., & Cole, M. P. (2018). MicroRNAs as predictive biomarkers for myocardial injury in aged mice following myocardial infarction. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 233, 5214–5221.
Goretti, E., Wagner, D. R., & Devaux, Y. (2014). miRNAs as biomarkers of myocardial infarction: A step forward towards personalized medicine? Trends in Molecular Medicine, 20, 716–725.
Yang, Y., Cheng, H. W., Qiu, Y., Dupee, D., Noonan, M., Lin, Y. D., Fisch, S., Unno, K., Sereti, K. I., & Liao, R. (2015). MicroRNA-34a plays a key role in cardiac repair and regeneration following myocardial infarction. Circulation Research, 117, 450–459.
Wang, K., Zhou, L. Y., Wang, J. X., Wang, Y., Sun, T., Zhao, B., Yang, Y. J., An, T., Long, B., Li, N., Liu, C. Y., Gong, Y., Gao, J. N., Dong, Y. H., Zhang, J., & Li, P. F. (2015). E2F1-dependent miR-421 regulates mitochondrial fragmentation and myocardial infarction by targeting Pink1. Nature Communications, 6, 7619.
Halushka, P. V., Goodwin, A. J., & Halushka, M. K. (2019). Opportunities for microRNAs in the crowded field of cardiovascular biomarkers. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease, 14, 211–238.
Gao, F., Kataoka, M., Liu, N., Liang, T., Huang, Z. P., Gu, F., Ding, J., Liu, J., Zhang, F., Ma, Q., Wang, Y., Zhang, M., Hu, X., Kyselovic, J., Hu, X., Pu, W. T., Wang, J., Chen, J., & Wang, D. Z. (2019). Therapeutic role of miR-19a/19b in cardiac regeneration and protection from myocardial infarction. Nature Communications, 10, 1802.
Wang, K., Liu, C. Y., Zhou, L. Y., Wang, J. X., Wang, M., Zhao, B., Zhao, W. K., Xu, S. J., Fan, L. H., Zhang, X. J., Feng, C., Wang, C. Q., Zhao, Y. F., & Li, P. F. (2015). APF lncRNA regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting miR-188-3p. Nature Communications, 6, 6779.
Garg, A., Foinquinos, A., Jung, M., Janssen-Peters, H., Biss, S., Bauersachs, J., Gupta, S. K., & Thum, T. (2020). MiRNA-181a is a novel regulator of aldosterone-mineralocorticoid receptor-mediated cardiac remodelling. European Journal of Heart Failure, 22, 1366–1377.
He, F., Liu, H., Guo, J., Yang, D., Yu, Y., Yu, J., Yan, X., Hu, J., & Du, Z. (2018). Inhibition of MicroRNA-124 Reduces Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis Following Myocardial Infarction via Targeting STAT3. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 51, 186–200.
Garikipati, V., Verma, S. K., Jolardarashi, D., Cheng, Z., Ibetti, J., Cimini, M., Tang, Y., Khan, M., Yue, Y., Benedict, C., Nickoloff, E., Truongcao, M. M., Gao, E., Krishnamurthy, P., Goukassian, D. A., Koch, W. J., & Kishore, R. (2017). Therapeutic inhibition of miR-375 attenuates post-myocardial infarction inflammatory response and left ventricular dysfunction via PDK-1-AKT signalling axis. Cardiovascular Research, 113, 938–949.
Liu, K., Ma, L., Zhou, F., Yang, Y., Hu, H. B., Wang, L., & Zhong, L. (2019). Identification of microRNAs related to myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234, 11380–11390.
Cuevas-Durán, R. E., Medrano-Rodríguez, J. C., Sánchez-Aguilar, M., Soria-Castro, E., Rubio-Ruíz, M. E., Del, V. L., Sánchez-Mendoza, A., Torres-Narvaéz, J. C., Pastelín-Hernández, G., & Ibarra-Lara, L. (2017). Extracts of Crataegus oxyacantha and Rosmarinus officinalis attenuate ischemic myocardial damage by decreasing oxidative stress and regulating the production of cardiac vasoactive agents. International Journal Molecules Science, 18, 2412.
Finley, L. W., Carracedo, A., Lee, J., Souza, A., Egia, A., Zhang, J., Teruya-Feldstein, J., Moreira, P. I., Cardoso, S. M., Clish, C. B., Pandolfi, P. P., & Haigis, M. C. (2011). SIRT3 opposes reprogramming of cancer cell metabolism through HIF1α destabilization. Cancer Cell, 19, 416–428.
Acun, A., & Zorlutuna, P. (2017). Engineered myocardium model to study the roles of HIF-1α and HIF1A-AS1 in paracrine-only signaling under pathological level oxidative stress. Acta Biomaterialia, 58, 323–336.
Ren, H., Shao, Y., Wu, C., Lv, C., Zhou, Y., & Wang, Q. (2020). VASH-1 regulates oxidative stress and fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease via SIRT1/HIF1α and TGFβ1/Smad3 signaling pathways. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, 7, 137.
Luo, Z., Wu, F., Xue, E., Huang, L., Yan, P., Pan, X., & Zhou, Y. (2019). Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival by inducing HIF-1α in injured neuronal cells derived exosomes culture system. Cell Death & Disease, 10, 134.
Hill, M., & Tran, N. (2018). MicroRNAs regulating MicroRNAs in cancer. Trends Cancer, 4, 465–468.
Dallaire, A., Frédérick, P. M., & Simard, M. J. (2018). Somatic and germline microRNAs form distinct silencing complexes to regulate their target mRNAs differently. Developmental Cell, 47, 239-247.e4.
Lindholm, E. M., Ragle, A. M., Haugen, M. H., Kleivi, S. K., Kristensen, V. N., Nebdal, D., Børresen-Dale, A. L., Lingjaerde, O. C., & Engebraaten, O. (2019). miRNA expression changes during the course of neoadjuvant bevacizumab and chemotherapy treatment in breast cancer. Molecular Oncology, 13, 2278–2296.
Beavers, K. R., Nelson, C. E., & Duvall, C. L. (2015). MiRNA inhibition in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 88, 123–137.
Huang, W., Hu, H., Zhang, Q., Wu, X., Wei, F., Yang, F., Gan, L., Wang, N., Yang, X., & Guo, A. Y. (2019). Regulatory networks in mechanotransduction reveal key genes in promoting cancer cell stemness and proliferation. Oncogene, 38, 6818–6834.
Yang, L., Han, X., Zhang, C., Sun, C., Huang, S., Xiao, W., Gao, Y., Liang, Q., Luo, F., Lu, W., Fu, J., & Zhou, Y. (2020). Hsa_circ_0060450 negatively regulates type I interferon-induced inflammation by serving as miR-199a-5p sponge in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Frontier Immunology, 11, 576903.
Raimondi, L., Amodio, N., Di Martino, M. T., Altomare, E., Leotta, M., Caracciolo, D., Gullà, A., Neri, A., Taverna, S., D’Aquila, P., Alessandro, R., Giordano, A., Tagliaferri, P., & Tassone, P. (2014). Targeting of multiple myeloma-related angiogenesis by miR-199a-5p mimics: In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity. Oncotarget, 5, 3039–3054.
Li, X., Tian, Y., Tu, M. J., Ho, P. Y., Batra, N., & Yu, A. M. (2019). Bioengineered miR-27b-3p and miR-328-3p modulate drug metabolism and disposition via the regulation of target ADME gene expression. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 9, 639–647.
Geng, L., Tang, X., Zhou, K., Wang, D., Wang, S., Yao, G., Chen, W., Gao, X., Chen, W., Shi, S., Shen, N., Feng, X., & Sun, L. (2019). MicroRNA-663 induces immune dysregulation by inhibiting TGF-β1 production in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 16, 260–274.
Ma, Y., Wu, Y., Chen, J., Huang, K., Ji, B., Chen, Z., Wang, Q., Ma, J., Shen, S., & Zhang, J. (2019). miR-10a-5p promotes chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by targeting HOXA1. Molecules Therapy Nucleic Acids, 14, 398–409.
Wang, R., Zuo, X., Wang, K., Han, Q., Zuo, J., Ni, H., Liu, W., Bao, H., Tu, Y., & Xie, P. (2018). MicroRNA-485-5p attenuates cell proliferation in glioma by directly targeting paired box 3. American Journal of Cancer Research, 8, 2507–2517.
Ling, S., Shan, Q., Zhan, Q., Ye, Q., Liu, P., Xu, S., He, X., Ma, J., Xiang, J., Jiang, G., Wen, X., Feng, Z., Wu, Y., Feng, T., Xu, L., Chen, K., Zhang, X., Wei, R., Zhang, C., … Xu, X. (2020). USP22 promotes hypoxia-induced hepatocellular carcinoma stemness by a HIF1α/USP22 positive feedback loop upon TP53 inactivation. Gut, 69, 1322–1334.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou City (201804010067) and Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2017ZC0064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HY., Lu, J., Wang, ZK. et al. Hsa-miR-199a-5p Protect Cell Injury in Hypoxia Induces Myocardial Cells Via Targeting HIF1α. Mol Biotechnol 64, 482–492 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00423-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00423-7