Abstract
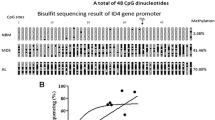
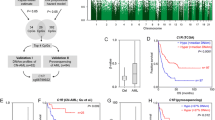
Aberrant methylation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) promoter has been observed in acute myeloid leukemia. However, little is known about CEBPA promoter in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). The purpose of this study was to investigate the alteration of CEBPA promoter in MDS patients and further determine the association with CEBPA expression and mutation. CEBPA promoter was significantly methylated in 105 MDS patients compared to 22 controls (median 0.016 vs. 0.000) (P < 0.0001). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis discriminated all patients or cytogenetically normal patients from normal controls. Three cases (3 %) were identified with single-mutated CEBPA and one (1 %) with double-mutated CEBPA. CEBPA methylation and mutation occurred mutually exclusive. No significant correlation was found between CEBPA expression and methylation (P = 0.586). Our findings indicate that CEBPA methylation is a common event in MDS, but could not act as a prognostic biomarker for MDS patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koschmieder S, Halmos B, Levantini E, Tenen DG. Dysregulation of the C/EBPalpha differentiation pathway in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:619–28.
Ossipow V, Descombes P, Schibler U. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein mRNA is translated into multiple proteins with different transcription activation potentials. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:8219–23.
Calkhoven CF, Bouwman PR, Snippe L, Ab G. Translation start site multiplicity of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha mRNA is dictated by a small 5′ open reading frame. Nucl Acids Res. 1994;22:5540–7.
Cammenga J, Mulloy JC, Berguido FJ, MacGrogan D, Viale A, Nimer SD. Induction of C/EBPalpha activity alters gene expression and differentiation of human CD34+ cells. Blood. 2003;101:2206–14.
Keeshan K, Santilli G, Corradini F, Perrotti D, Calabretta B. Transcription activation function of C/EBPalpha is required for induction of granulocytic differentiation. Blood. 2003;102:1267–75.
Zhang P, Iwasaki-Arai J, Iwasaki H, Fenyus ML, Dayaram T, Owens BM, Shigematsu H, Levantini E, Huettner CS, Lekstrom-Himes JA, Akashi K, Tenen DG. Enhancement of hematopoietic stem cell repopulating capacity and self-renewal in the absence of the transcription factor C/EBP alpha. Immunity. 2004;21:853–63.
Zhang DE, Hetherington CJ, Meyers S, Rhoades KL, Larson CJ, Chen HM, Hiebert SW, Tenen DG. CCAAT enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) and AML1 (CBF alpha2) synergistically activate the macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:1231–40.
Heath V, Suh HC, Holman M, Renn K, Gooya JM, Parkin S, Klarmann KD, Ortiz M, Johnson P, Keller J. C/EBPalpha deficiency results in hyperproliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells and disrupts macrophage development in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2004;104:1639–47.
Schepers H, Wierenga AT, van Gosliga D, Eggen BJ, Vellenga E, Schuringa JJ. Reintroduction of C/EBPalpha in leukemic CD34+ stem/progenitor cells impairs self-renewal and partially restores myelopoiesis. Blood. 2007;110:1317–25.
Pabst T, Mueller BU, Zhang P, Radomska HS, Narravula S, Schnittger S, Behre G, Hiddemann W, Tenen DG. Dominant-negative mutations of CEBPA, encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-alpha (C/EBPalpha), in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 2001;27:263–70.
Kirstetter P, Schuster MB, Bereshchenko O, Moore S, Dvinge H, Kurz E, Theilgaard-Mönch K, Månsson R, Pedersen TA, Pabst T, Schrock E, Porse BT, Jacobsen SE, Bertone P, Tenen DG, Nerlov C. Modeling of C/EBPalpha mutant acute myeloid leukemia reveals a common expression signature of committed myeloid leukemia-initiating cells. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:299–310.
Snaddon J, Smith ML, Neat M, Cambal-Parrales M, Dixon-McIver A, Arch R, Amess JA, Rohatiner AZ, Lister TA, Fitzgibbon J. Mutations of CEBPA in acute myeloid leukemia FAB types M1 and M2. Gene Chromosomes Cancer. 2003;37:72–8.
Gombart AF, Hofmann WK, Kawano S, Takeuchi S, Krug U, Kwok SH, Larsen RJ, Asou H, Miller CW, Hoelzer D, Koeffler HP. Mutations in the gene encoding the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemias. Blood. 2002;99:1332–40.
Barjesteh van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani S, Erpelinck C, Meijer J, van Oosterhoud S, van Putten WL, Valk PJ, Berna Beverloo H, Tenen DG, Löwenberg B, Delwel R. Biallelic mutations in the CEBPA gene and low CEBPA expression levels as prognostic markers in intermediate-risk AML. Hematology J. 2003;4:31–40.
Quintana-Bustamante O, Lan-Lan Smith S, Griessinger E, Reyal Y, Vargaftig J, Lister TA, Fitzgibbon J, Bonnet D. Overexpression of wild-type or mutants forms of CEBPA alters normal human hematopoiesis. Leukemia. 2012;26:1537–46.
Chim CS, Wong AS, Kwong YL. Infrequent hypermethylation of CEBPA promotor in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2002;119:988–90.
Griffiths EA, Gore SD, Hooker CM, Mohammad HP, McDevitt MA, Smith BD, Karp JE, Herman JG, Carraway HE. Epigenetic differences in cytogenetically normal versus abnormal acute myeloid leukemia. Epigenetics. 2010;5:590–600.
Lu Y, Chen W, Chen W, Stein A, Weiss LM, Huang Q. C/EBPA gene mutation and C/EBPA promoter hypermethylation in acute myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics. Am J Hematol. 2010;85:426–30.
Hollink IH, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, Arentsen-Peters ST, Zimmermann M, Peeters JK, Valk PJ, Balgobind BV, Sonneveld E, Kaspers GJ, de Bont ES, Trka J, Baruchel A, Creutzig U, Pieters R, Reinhardt D, Zwaan CM. Characterization of CEBPA mutations and promoter hypermethylation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2011;96:384–92.
Lin TC, Hou HA, Chou WC, Ou DL, Yu SL, Tien HF, Lin LI. CEBPA methylation as a prognostic biomarker in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2011;25:32–40.
Santana-Lemos BA, de Lima Lange AP, de Lira Benício MT, José TD, Lucena-Araújo AR, Krause A, Thomé CH, Rego EM. The CEBPA gene is down-regulated in acute promyelocytic leukemia and its upstream promoter, but not the core promoter, is highly methylated. Haematologica. 2011;96:617–20.
Szankasi P, Ho AK, Bahler DW, Efimova O, Kelley TW. Combined testing for CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPA) mutations and promoter methylation in acute myeloid leukemia demonstrates shared phenotypic features. Leuk Res. 2011;35:200–7.
Alberich-Jordà M, Wouters B, Balastik M, Shapiro-Koss C, Zhang H, Di Ruscio A, Radomska HS, Ebralidze AK, Amabile G, Ye M, Zhang J, Lowers I, Avellino R, Melnick A, Figueroa ME, Valk PJ, Delwel R, Tenen DG. C/EBPgamma deregulation results in differentiation arrest in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:4490–504.
Fasan A, Alpermann T, Haferlach C, Grossmann V, Roller A, Kohlmann A, Eder C, Kern W, Haferlach T, Schnittger S. Frequency and prognostic impact of CEBPA proximal, distal and core promoter methylation in normal karyotype AML: a study on 623 cases. PLoS One. 2013;8:e54365.
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM, Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A, Bloomfield CD. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–51.
Lin J, Chen Q, Yang J, Qian J, Deng ZQ, Qian W, Chen XX, Ma JC, Xiong DS, Ma YJ, An C, Tang CY. DDX43 promoter is frequently hypomethylated and may predict a favorable outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2014;38:601–7.
Hackanson B, Bennett KL, Brena RM, Jiang J, Claus R, Chen SS, Blagitko-Dorfs N, Maharry K, Whitman SP, Schmittgen TD, Lübbert M, Marcucci G, Bloomfield CD, Plass C. Epigenetic modification of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3142–51.
Chen Q, Lin J, Yao DM, Qian J, Qian W, Yang J, Chai HY, Ma JC, Deng ZQ, Wang CZ, Li Y. Aberrant hypomethylation of DDX43 promoter in myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2012;158:293–6.
Lin J, Yao DM, Qian J, Chen Q, Qian W, Li Y, Yang J, Wang CZ, Chai HY, Qian Z, Xiao GF, Xu WR. Recurrent DNMT3A R882 mutations in Chinese patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26906.
Lin J, Yao DM, Qian J, Chen Q, Qian W, Li Y, Yang J, Wang CZ, Chai HY, Qian Z, Xiao GF, Xu WR. IDH1 and IDH2 mutation analysis in Chinese patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Ann Hematol. 2012;91:519–25.
Cilloni D, Carturan S, Gottardi E, Messa F, Messa E, Fava M, Diverio D, Guerrasio A, Lo-Coco F, Saglio G. Down-modulation of the C/EBPalpha transcription factor in core binding factor acute myeloid leukemias. Blood. 2003;102:2705–6.
Grossmann V, Bacher U, Kohlmann A, Butschalowski K, Roller A, Jeromin S, Dicker F, Kern W, Schnittger S, Haferlach T, Haferlach C. Expression of CEBPA is reduced in RUNX1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2012;2:e86.
Valent P, Horny HP, Bennett JM, Fonatsch C, Germing U, Greenberg P, Haferlach T, Haase D, Kolb HJ, Krieger O, Loken M, van de Loosdrecht A, Ogata K, Orfao A, Pfeilstöcker M, Rüter B, Sperr WR, Stauder R, Wells DA. Definitions and standards in the diagnosis and treatment of the myelodysplastic syndromes: consensus statements and report from a working conference. Leuk Res. 2007;31:727–36.
Jiang H, Xue Y, Wang Q, Pan J, Wu Y, Zhang J, Bai S, Wang Q, He G, Sun A, Wu D, Chen S. The utility of fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis in diagnosing myelodysplastic syndromes is limited to cases with karyotype failure. Leuk Res. 2012;36:448–52.
Wouters BJ, Löwenberg B, Erpelinck-Verschueren CA, van Putten WL, Valk PJ, Delwel R. Double CEBPA mutations, but not single CEBPA mutations, define a subgroup of acute myeloid leukemia with a distinctive gene expression profile that is uniquely associated with a favorable outcome. Blood. 2009;113:3088–91.
Pabst T, Eyholzer M, Fos J, Mueller BU. Heterogeneity within AML with CEBPA mutations; only CEBPA double mutations, but not single CEBPA mutations are associated with favourable prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:1343–6.
Dufour A, Schneider F, Metzeler KH, Hoster E, Schneider S, Zellmeier E, Benthaus T, Sauerland MC, Berdel WE, Büchner T, Wörmann B, Braess J, Hiddemann W, Bohlander SK, Spiekermann K. Acute myeloid leukemia with biallelic CEBPA gene mutations and normal karyotype represents a distinct genetic entity associated with a favorable clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:570–7.
Taskesen E, Bullinger L, Corbacioglu A, Sanders MA, Erpelinck CA, Wouters BJ, van der van der Poel-van de Luytgaarde SC, Damm F, Krauter J, Ganser A, Schlenk RF, Löwenberg B, Delwel R, Döhner H, Valk PJ, Döhner K. Prognostic impact, concurrent genetic mutations, and gene expression features of AML with CEBPA mutations in a cohort of 1182 cytogenetically normal AML patients: further evidence for CEBPA double mutant AML as a distinctive disease entity. Blood. 2011;117:2469–75.
Kaeferstein A, Krug U, Tiesmeier J, Aivado M, Faulhaber M, Stadler M, Krauter J, Germing U, Hofmann WK, Koeffler HP, Ganser A, Verbeek W. The emergence of a C/EBPalpha mutation in the clonal evolution of MDS towards secondary AML. Leukemia. 2003;17:343–9.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science foundation of China (81270630, 81172592), Science and Technology Special Project in Clinical Medicine of Jiangsu Province (BL2012056), 333 Project of Jiangsu Province (BRA2013136), Jiangsu Government Scholarship for Overseas Studies, Social Development Foundation of Zhenjiang (SH2013042, SH2013082, SH2014044), Research and Development Foundation of Clinical Medicine of Jiangsu University (JLY20120013, JLY20120011), Key Medical Talent Program of Zhenjiang, and Science and Technology Infrastructure Program of Zhenjiang (SS2012003).
Conflict of interest
The authors stated that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiang-mei Wen and Jia-bo Hu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, Xm., Hu, Jb., Yang, J. et al. CEBPA methylation and mutation in myelodysplastic syndrome. Med Oncol 32, 192 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0605-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0605-z