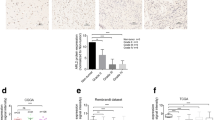
Abstract
This study was conducted to evaluate the role of tumor suppressor gene ras homologue member I (ARHI) in human glioma tumors. We examined expression of ARHI in human glioma tumors and normal brain tissue and also in 4 different glioma cell lines. Furthermore, the effects of ARHI over-expression produced by cellular transfection on the growth of human glioma U251 cells cultured in vitro were also studied. Expression of ARHI was evaluated in samples of glioma tumors obtained from 59 patients who underwent surgery at the Department of Neurosurgery, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, China. Ten samples of normal brain tissue were used as controls. Additionally, in vitro studies were conducted in which a recombinant vector carrying ARHI cDNA was constructed and transfected into U251 glioma cells with reduced expression of ARHI. Following transfection, the MTT assay, flow cytometry, TUNEL procedure, Transwell assay, and wound-healing test were employed to evaluate the biological functions of ARHI in U251 glioma cells in vitro. Analyses of mRNA and protein expression revealed that ARHI was significantly down-regulated in glioma tissues as well as in 4 malignant glioma cell lines. Over-expression of ARHI resulted in suppression of glioma cell proliferation, arrest of cell cycle progression, reduction in cell migration and invasion, and promotion of cell apoptosis. Collectively, our data highlight the importance of ARHI in glioma progression and provide the first biological basis for ARHI as a novel candidate target for gene therapy of glioma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hess KR, Broglio KR, Bondy ML. Adult glioma incidence trends in the United States, 1977–2000. Cancer. 2004;101:2293–9.
Goodenberger ML, Jenkins RB. Genetics of adult glioma. Cancer Genet. 2012;205(12):613–21.
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, Chin L, DePinho RA, Cavenee WK. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21(21):2683–710.
An S, Nam K, Choi S, Bai CZ, Lee Y, Park JS. Nonviral gene therapy in vivo with PAM-RG4/apoptin as a potential brain tumor therapeutic. Int J Nanomed. 2013;8:821–34.
Marsh JC, Goldfarb J, Shafman TD, Diaz AZ. Current status of immunotherapy and gene therapy for high-grade gliomas. Cancer Control. 2013;20(1):43–8.
Peng H, Xu F, Pershad R, Hunt KK, Frazier ML, Berchuck A, Gray JW, Hogg D, Bast RC Jr, Yu Y. ARHI is the center of allelic deletion on chromosome 1p31 in ovarian and breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 2000;86:690–4.
Hu YQ, Si LJ, Ye ZS, Lin ZH, Zhou JP. Inhibitory effect of ARHI on pancreatic cancer cells and NF-κB activity. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(4):1180–4.
Huang J, Lin Y, Li L, Qing D, Teng XM, Zhang YL, Hu X, Hu Y, Yang P, Han ZG. ARHI, as a novel suppressor of cell growth and downregulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma, could contribute to hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48:130–40.
Wu X, Liang L, Dong L, Yu Z, Fu X. Effect of ARHI on lung cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and invasion in vitro. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(3):2671–8.
Lu X, Qian J, Yu Y, Yang H, Li J. Expression of the tumor suppressor ARHI inhibits the growth of pancreatic cancer cells by inducing G1 cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep. 2009;22(3):635–40.
Yu Y, Luo R, Lu Z, Wei Feng W, Badgwell D, Issa JP, Rosen DG, Liu J, Bast RC. Biochemistry and biology of ARHI (DIRAS3), an imprinted tumor suppressor gene whose expression is lost in ovarian and breast cancers. Methods Enzymol. 2006;407:455–68.
Yu Y, Xu F, Peng H, Fang X, Zhao S, Li Y, Cuevas B, Kuo WL, Gray JW, Siciliano M, Mills GB, Bast RC Jr. NOEY2 (ARHI), an imprinted putative tumor suppressor gene in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:214–9.
Janssen EA, Øvestad IT, Skaland I, Søiland H, Gudlaugsson E, Kjellevold KH, Nysted A, Søreide JA, Baak JP. LOH at 1p31 (ARHI) and proliferation in lymph node-negative breast cancer. Cell Oncol. 2009;31(5):335–43.
Mitra A, Fillmore RA, Metge BJ, Rajesh M, Xi Y, King J, Ju J, Pannell L, Shevde LA, Samant RS. Large isoform of MRJ (DNAJB6) reduces malignant activity of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:R22.
Khwaja FW, Duke-Cohan JS, Brat DJ, Van Meir EG. Attractin is elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with malignant astrocytoma and mediates glioma cell migration. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6331–6.
Hisatomi H, Nagao K, Wakita K, Kohno N. ARHI/NOEY2 inactivation may be important in breast tumor pathogenesis. Oncology. 2002;62:136–40.
Li Y, Shi L, Han C, Wang Y, Yang J, Cao C, Jiao S. Effects of ARHI on cell cycle progression and apoptosis levels of breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2012;33(5):1403–10.
Lu Z, Bast RC Jr. The tumor suppressor gene ARHI (DIRAS3) inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration through multiple mechanisms. Cell Adh Migr. 2013;7(2):232–6.
Weber F, Aldred MA, Morrison CD, Plass C, Frilling A, Broelsch CE, Waite KA, Eng C. Silencing of the maternally imprinted tumor suppressor ARHI contributes to follicular thyroid carcinogenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:1149–55.
Luo RZ, Fang X, Marquez R, Liu SY, Mills GB, Liao WS, Yu Y, Bast RC. ARHI is a Ras-related small G-protein with a novel N-terminal extension that inhibits growth of ovarian and breast cancers. Oncogene. 2003;22:2897–909.
Bao JJ, Le XF, Wang RY, Yuan J, Wang L, Atkinson EN, LaPushin R, Andreeff M, Fang B, Yu Y, Bast RC Jr. Re-expression of the tumor suppressor gene ARHI induces apoptosis in ovarian and breast cancer cells through a caspase-independent calpain-dependent pathway. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7264–72.
Zhang H, Zhu W, Su X, Wu S, Lin Y, Li J, Wang Y, Chen J, Zhou Y, Qiu P, Yan G, Zhao S, Hu J, Zhang J. Triptolide inhibits proliferation and invasion of malignant glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 2012;109(1):53–62.
Roomi MW, Ivanov V, Kalinovsky T, Niedzwiecki A, Rath M. Inhibition of glioma cell line A-172 MMP activity and cell invasion in vitro by a nutrient mixture. Med Oncol. 2007;24:231–8.
Xu L, Ding X, Tan H, Qian J. Correlation between B7-H3 expression and matrix metalloproteinases 2 expression in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013;13(1):81.
Singh N, Das P, Datta Gupta S, Sahni P, Pandey RM, Gupta S, Chauhan SS, Saraya A. Prognostic significance of extracellular matrix degrading enzymes-cathepsin L and matrix metalloproteases-2 [MMP-2] in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Invest. 2013;31(7):461–71.
Wang G, Wang W, Zhou J, Yang X. Correlation between telomerase activity and matrix metalloproteinases 2 expression in gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2013;13(1):21–8.
Honda T, Yamamoto I, Inagawa H. Angiogenesis-, metastasis- and signaling pathway-related factor dynamics in human colon cancer cells following interaction with monocytes. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(7):2895–900.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Young Scientist Project of Fujian Province Science Foundation (2013J05113).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Shi, S., Yang, W. et al. Over-expression of ARHI decreases tumor growth, migration, and invasion in human glioma. Med Oncol 31, 846 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0846-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0846-2