Abstract
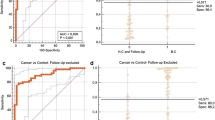
For bladder cancer, a new diagnostic marker is needed to avoid painful cystoscopy. The aim of this study was to explore the efficacy of urinary miRNA-96 as molecular marker in bladder cancer diagnosis and its relation to bilharziasis. Urine cytology, serologic assessment of schistosomiasis and estimation of miRNA-96 by real-time PCR were carried out for 94 bladder cancer patients, 30 benign bladder lesions and 60 healthy individuals. Expression of miRNA-96 showed a significant difference among the three tested groups and also between benign and malignant bilharzial cases. Urinary miRNA-96 is a good noninvasive diagnostic biomarker for bladder cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avritscher EB, Cooksley CD, Grossman HB, Sabichi AL, Hamblin L, Dinney CP, Elting LS. Clinical model of lifetime cost of treating bladder cancer and associated complications. Urology. 2006;68:549–53.
Cortez MA, Bueso-Ramos CB, Ferdin J, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Calin GA. MicroRNAs in body fluids the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8:467–77.
Dyrskjøt L, Ostenfeld MS, Bramsen JB, Silahtaroglu AN, Lamy P, Ramanathan R, Fristrup N, Jensen JL, Andersen CL, Zieger K, Kauppinen S, Ulhøi BP, Kjems J, Borre M, Orntoft TF. Genomic profiling of microRNAs in bladder cancer: miR-129 is associated with poor outcome and promotes cell death in vitro. Cancer Res. 2010;69:4851–60.
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer; 2010. p. 497–505.
Gui M, Idris MA, Shi YE, Muhling A, Ruppel A. Reactivity of Schistosoma japonicum and S. mansoni antigen preparations in indirect haemagglutination (IHA) with sera of patients with homologous and heterogonous schistosomiasis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1991;85:599–604.
Guttilla IK, White BA. Coordinate regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:23204–16.
Han Y, Chen J, Zhao X, Liang C, Wang Y, Sun L, Jiang Z, Zhang Z, Yang R, Chen J. MicroRNA expression signatures of bladder cancer revealed by deep sequencing. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e18286.
Konety BR. Molecular markers in bladder cancer: a critical appraisal. Urol Oncol. 2006;24(4):326–37.
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Ochiya T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:2087–92.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:1046–54.
Liu C, Yu J, Yu S, Lavker RM, Cai L, Liu W, Yang K, He X, Chen S. MicroRNA-21 acts as an oncomir through multiple targets in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2010;53:98–107.
Lotan Y, Svatek RS, Sagalowsky AI. Should we screen for bladder cancer in a high-risk population: a cost per life-year saved analysis. Cancer. 2006;107:982–90.
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T, Toyoda H, Okanoue T, Shimotohno K. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene. 2006;25:2537–45.
Myatt SS, Wang J, Monteiro LJ. Definition of microRNAs that repress expression of the tumor suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:367–77.
Papanicolaou GN, Marshall VF. Urine sediment smears as a diagnostic procedure in cancers of the urinary tract. Science. 1945;101:519.
Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Ménard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin GA, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce CM. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7065–70.
Proctor I, Stoeber K, Williams GH. Biomarkers in bladder cancer. Histopathology. 2010;57:1–13.
Sobin LH, Wittkind CH. UICC TNM classification of malignant tumors. 5th ed. New York: Wiley Liss; 1997. p. 187.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110:13–21.
Wang Y, Luo H, Li Y, Chen T, Wu S, Yang L. hsa-miR-96 up-regulates (MAP4K1 and IRS1 and may function as a promising diagnostic marker in human bladder urothelial carcinomas. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5(1):260–5.
Yamada Y, Enokida H, Kojima S, Kawakami K, Chiyomaru T, Tatarano S, Yoshino H, Kawahara K, Nishiyama K, Seki N, Nakagawa M. MiR-96 and miR-183 detection in urine serve as potential tumor markers of urothelial carcinoma: correlation with stage and grade, and comparison with urinary cytology. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:522–9.
Yan B, Fu Q, Lai L, Tao X, Fei Y, Shen J, Chen Z, Wang Q. Down regulation of microRNA 99a in oral squamous cell carcinomas contributes to the growth and survival of oral cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6:675–81.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, Calin GA, Liu CG, Croce CM, Harris CC. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:189–98.
Yu S, Lu Z, Liu C, Meng Y, Ma Y, Zhao W, Liu J, Yu J, Chen J. miRNA-96 suppresses KRAS and functions as a tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:6015–25.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ain Shams University Research Projects 2013-14. The authors acknowledge Prof. Nahla Awad, at the early cancer detection unit, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, for her help in the cytological examinations of urine samples and Dr. Yosif Kotb at Urology department.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eissa, S., Habib, H., Ali, E. et al. Evaluation of urinary miRNA-96 as a potential biomarker for bladder cancer diagnosis. Med Oncol 32, 413 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0413-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0413-x