Abstract
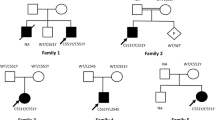
Infantile Sandhoff disease is an autosomal recessive inherited disease primarily characterized by cherry red spots in the retina, muscle weakness, seizure, truncal hypotonia, hyperacusis, developmental delay and regression. The pathogenic genetic defects of the HEXB gene, which encodes the β subunit of the hexosaminidase A (ɑβ) and hexosaminidase B (ββ) enzymes, cause deficiency of both the Hex A and Hex B enzymes, resulting in the deposition of GM2 ganglion glycerides in the lysosomes of the central nervous system and somatic cells. The aim of this study was to discover disease-causing variants of the HEXB gene in two Chinese families through the use of exome sequencing. By characterizing three novel variants by molecular genetics, bioinformatics analysis, and three-dimensional structure modeling, we showed that all these novel variants influenced the protein structure. The results broaden the variant spectrum of HEXB in different ethnic groups. Furthermore, not all patients diagnosed with infantile Sandhoff disease had characteristic cranial imaging findings, which can only be used as supplementary information for diagnosis. The results of this study may contribute to clinical management, genetic counseling, and gene-targeted treatments for Sandhoff disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SD:
-
Sandhoff disease
- Hex A:
-
Hexosaminidase A
- Hex B:
-
Hexosaminidase B
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CT:
-
Computer tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- RRI:
-
Recurrent Respiratory Infections
References
Bley AE, Giannikopoulos OA, Hayden D, Kubilus K, Tifft CJ, Eichler FS (2011) Natural history of infantile G(M2) gangliosidosis. Pediatrics 128:e1233–e1241. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-0078
Gaignard P, Fagart J, Niemir N et al (2013) Characterization of seven novel mutations on the HEXB gene in French Sandhoff patients. Gene 512:521–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.09.124
Gort L, de Olano N, Macias-Vidal J, Coll MA, Spanish GM2 Working Group (2012) GM2 gangliosidoses in Spain: analysis of the HEXA and HEXB genes in 34 Tay-Sachs and 14 Sandhoff patients. Gene 506:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.06.080
Hittmair K, Wimberger D, Bernert G, Mallek R, Schindler EG (1996) MRI in a case of Sandhoff’s disease. Neuroradiology 38:S178–S180
Huang Y, Xie T, Zheng J, Zhao X, Liu H, Liu L (2014) Clinical and molecular characteristics of a child with juvenile Sandhoff disease. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 52:313–316
Jain A, Kohli A, Sachan D (2010) Infantile Sandhoff’s disease with peripheral neuropathy. Pediatr Neurol 42:459–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2010.02.007
Karimzadeh P, Jafari N, Nejad BH et al (2014) GM2-Gangliosidosis (Sandhoff and Tay Sachs disease): diagnosis and neuroimaging findings (an Iranian pediatric case series). Iran J Child Neurol 8:55–60
Kleiman FE, de Kremer RD, de Ramirez AO, Gravel RA, Argaraña CE (1994) Sandhoff disease in Argentina: high frequency of a splice site mutation in the HEXB gene and correlation between enzyme and DNA-based tests for heterozygote detection. Hum Genet 94:279–282
Koelfen W, Freund M, Jaschke W, Koenig S, Schultze C (1994) GM2 gangliosidois (Sandhoff’s disease): two year follow up by MRI. Neuroradiology 36:152–154
Nalini A, Christopher R (2004) Cerebral Glycolipidoses: clinical characteristics of 41 pediatric patients. J Child Neurol 19:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1177/088307380401900610
O’Dowd BF, Klavins MH, Willard HF, Gravel R, Lowden JA, Mahuran DJ (1986) Molecular heterogenicity in the infantile and juvenile forms of Sandhoff disease (O-variant GM2 gangliosidosis). J Biol Chem 261:12680–12685
Sandhoff K, Andreae U, Jatzkewitz H (1968) Deficient hexosaminidase activity in an exceptional case of Tay-Sachs disease with additional storage of kidney globoside in visceral organs. Pathol Eur 3:278–285
Saouab R, Mahi M, Abilkacem R et al (2011) A case report of Sandhoff disease. Clin Neuroradiol 21:83–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-010-0035-4
Smith NJ, Winston AM, Stellitano L, Cox TM, Verity CM (2012) GM2 gangliosidosis in a UK study of children with progressive neurodegeneration: 73 cases reviewed. Dev Med Child Neurol 54:176–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.04160.x
Tavasoli AR, Parvaneh N, Ashrafi MR, Rezaei Z, Zschocke J, Rostami P (2018) Clinical presentation and outcome in infantile Sandhoff disease: a case series of 25 patients from Iranian neurometabolic bioregistry with five novel mutations. Orphanet J Rare Dis 13:130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-018-0876-5
Wu T, Li X, Wang Q et al (2013) HEXB gene study and prenatal diagnosis for a family affected by infantile Sandhoff disease. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 42:403–410
Yüksel A, Yalçinkaya C, Işlak C, Gündüz E, Seven M (1999) Neuroimaging findings of four patients with Sandhoff disease. Pediatr Neurol 21:562–565
Yun YM, Lee SN (2005) A case Refort of Sandhoff disease. Korean J Ophthalmol 19:68–72. https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2005.19.1.68
Zampieri S, Filocamo M, Buratti E et al (2009) Molecular and functional analysis of the HEXB gene in Italian patients affected with Sandhoff disease: identification of six novel alleles. Neurogenetics 10:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-008-0145-1
Zhang W, Zeng H, Huang Y et al (2016) Clinical, biochemical and molecular analysis of five Chinese patients with Sandhoff disease. Metab Brain Dis 31:861–867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9819-9
Acknowledgements
We would wish to thank the patients, their families for their cooperation and contribution.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Suzhou Science and Technology Support Program (No.SS201647), Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program (No. BE2018661), Suzhou City Key Clinical Disease Treatment Technology Program (LCZX201810) and The Fifteenth Batch of Jiangsu Province Funds for Selection and Training of High-level Talents (WSN-028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was based on the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and authorized by the Institutional Review Committee of Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University. All participants have signed the written informed consent.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Huang, D., Wang, H. et al. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of Two Chinese Children with Infantile Sandhoff Disease and Review of the Literature. J Mol Neurosci 70, 481–487 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01409-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01409-6