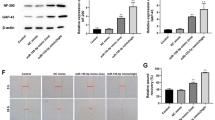
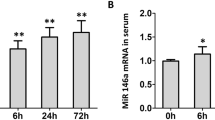
Abstract
Mechanical trauma injury is a severe insult to neural cells. Subsequent secondary injury involves the release of inflammatory factors that have dramatic consequences for undamaged cells, leading to normal cell death after the initial injury. The present study investigated the capacity for arctigenin (ARC) to prevent secondary effects and evaluated the mechanism underlying the action of microRNA (miRNA)-199a and miRNA-16 in a mechanical trauma injury (MTI) model using SH-SY5Y cells in vitro. SH-SY5Y cells are often applied to in vitro models of neuronal function and differentiation. Recently, miRNAs have been demonstrated to play a crucial role in NF-κB and cholinergic signaling, which can regulate inflammation. The cell model was established by scratch-induced injury of human SH-SY5Y cells, which mimics the characteristics of MTI. A cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL), and immunocytochemistry were used to measure cell viability. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to evaluate the inflammatory cytokine and cholinesterase (CHE) content. The lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) content was measured to assess the degree of cell injury. The mRNA levels were measured by RT-PCR to analyze ARC’s mechanism of action. miRNA inhibitors and mimics were used to inhibit and strengthen the expression of miRNAs. Protein expression was detected by western blotting analysis. ARC treatment reduced the TNF-α and IL-6 levels as well as the number of TUNEL+ apoptotic SH-SY5Y cells surrounding the scratch and increased the IL-10 level compared to the controls. ARC attenuated the increase of the cell damage degree and LDH content induced by scratching, indicating increased cell survival. Mechanistic studies showed that ARC upregulated the miRNA-16 and miRNA-199a levels to reduce upstream protein (IKKα and IKKβ) expression and inhibit NF-κB signaling pathway activity; moreover, the increased miRNA-199a suppresses cholinesterases to increase cholinergic signaling, resulting in decreased expression of proinflammatory cytokines. ARC treatment confers protection for SH-SY5Y cells through positive regulation of miRNA expression, thereby reducing the inflammatory response. In turn, these effects accelerate injury repair in the scratch-induced injury model. These results might provide insights into the pharmacological role of ARC in anti-inflammation and neuroprotection in neural cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Muneer PM, Chandra N, Haorah J (2015) Interactions of oxidative stress and neurovascular inflammation in the pathogenesis of traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol 51(3):966–979
Abemayor E, Sidell N (1989) Human neuroblastoma cell lines as models for the in vitro study of neoplastic and neuronal cell differentiation. Environ Health Perspect 80:3
Aggarwal BB, Kohr WJ, Hass PE, Moffat B, Spencer SA, Henzel WJ, ... & Harkins RN (1985) Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem 260: 2345–2354
Aravindan S, Natarajan M, Herman TS, Aravindan N (2013) Radiation-induced TNFα cross signaling-dependent nuclear import of NF-κB favors metastasis in neuroblastoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 30(6):807–817
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, ... & Tracey KJ (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405(6785), 458–462
Brown ER, Charles KA, Hoare SA, Rye RL, Jodrell DI, Aird RE., ... & DeWitte M. (2008). A clinical study assessing the tolerability and biological effects of infliximab, a TNF-α inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. Ann Oncol 19(7): 1340–1346
Burgos-Tiburcio A, Santos ES, Arango BA, Raez LE (2011) Development of targeted therapy for squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 11(3):373–386
Campbell IL, Abraham CR, Masliah E, Kemper P, Inglis JD, Oldstone MB, Mucke L (1993) Neurologic disease induced in transgenic mice by cerebral overexpression of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:10061–10065
Chen JW, Chen YH, Lin SJ (2006) Long-term exposure to oxidized low-density lipoprotein enhances tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated endothelial adhesiveness of monocytes by activating superoxide generation and redox-sensitive pathways. Free Radic Biol Med 40:817–826
Chen R, Alvero AB, Silasi DA, Kelly MG, Fest S, Visintin I, ... & Mor G (2008). Regulation of IKKβ by miR-199a affects NF-κB activity in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 27(34): 4712–4723
Cheng SB, Sharma S (2015) Interleukin-10: a pleiotropic regulator in pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol 73(6):487–500
Clark RS, Chen J, Watkins SC, Kochanek PM, Chen M, Stetler RA, ... & Graham SH (1997) Apoptosis-suppressor gene bcl-2 expression after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurosci 17: 9172–9182
Fan T, Jiang WL, Zhu J, Feng Zhang Y (2012) Arctigenin protects focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats through inhibiting neuroinflammation. Biol Pharm Bull 35:2004–2009
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Yu JW, Datta P, Wu J, Alnemri ES (2009) AIM2 activates the inflammasome and cell death in response to cytoplasmic DNA. Nature 458:509–513
Francis F, Koulakoff A, Boucher D, Chafey P, Schaar B, Vinet M C, ... & McConnell S K. (1999). Doublecortin is a developmentally regulated, microtubule-associated protein expressed in migrating and differentiating neurons. Neuron 23(2): 247–256
Friocourt G, Koulakoff A, Chafey P, Boucher D, Fauchereau F, Chelly J, Francis F (2003) Doublecortin functions at the extremities of growing neuronal processes. Cereb Cortex 13(6):620–626
Gao K, Wang CR, Jiang F, Wong AYK, Su N, Jiang JH, ... & Jiang YW (2013) Traumatic scratch injury in astrocytes triggers calcium influx to activate the JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 pathway and switch on GFAP expression. Glia 61(12): 2063–2077
Genovese T, Mazzon E, Esposito E, Di Paola R, Caminiti R, Meli R, ... & Cuzzocrea S (2008) Effect of thalidomide on signal transduction pathways and secondary damage in experimental spinal cord trauma. Shock 30: 231–240
Gu Y, Qi C, Sun X, Ma X, Zhang H, Hu L, ... & Yu Q (2012) Arctigenin preferentially induces tumor cell death under glucose deprivation by inhibiting cellular energy metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol 84: 468–476
He H, Zhu D, Sun J, Pei R, Jia S (2011) The novel protein TSR2 inhibits the transcriptional activity of nuclear factor-κB and induces apoptosis. Mol Biol 45(3):451–457
Hu Y, Wen Q, Liang W, Kang T, Ren L, Zhang N, ... & Yang J (2013) Osthole reverses beta-amyloid peptide cytotoxicity on neural cells by enhancing cyclic AMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation. Biol Pharm Bull 36:1950–1958
Huang C, Wang Y, Wang J, Yao W, Chen X, Zhang W (2013) 2-O-β-D-glucoside) suppresses induction of pro-inflammatory factors by attenuating the binding activity of nuclear factor-κB in microglia. J Neuroinflammation 10:129
Hyam SR, Lee IA, Gu W, Kim KA, Jeong JJ, Jang SE, ... & Kim DH (2013) Arctigenin ameliorates inflammation in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway and polarizing M1 macrophages to M2-like macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol 708: 21–29
Ji-wen Y, Tong-yan T, Qi-lin H (2013) Protective effect of astrocyte-conditioned medium on neurons following hypoxia and mechanical injury. Chin J Traumatol 16(1):3–9
Kang HS, Lee JY, Kim CJ (2008) Anti-inflammatory activity of arctigenin from ForsythiaeFructus. J Ethnopharmacol 116:305–312
Karin M, Greten FR (2005) NF-κB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 5(10):749–759
Krishnan RK, Nolte H, Sun T, Kaur H, Sreenivasan K, Looso M, ... & Swiercz, JM. (2015). Quantitative analysis of the TNF-[alpha]-induced phosphoproteome reveals AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC as an IKK [beta] substrate. Nat Commun 6. doi:10.1038/ncomms7658
Laplaca MC, Lee VMY, Thibault LE (1997) An in vitro model of traumatic neuronal injury: loading rate-dependent changes in acute cytosolic calcium and lactate dehydrogenase release. J Neurotrauma 14(6):355–368
Lee JY, Cho BJ, Park TW, Park BE, Kim SJ, Sim SS, Kim CJ (2010) Dibenzylbutyrolactone lignans from forsythia koreana fruits attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced inducible nitric oxide synthetase and cyclooxygenase-2 expressions through activation of nuclear factor-. KAPPA. B and mitogen-activated protein kinase in RAW264. 7 Cells. Biol Pharm Bull 33(11):1847–1853
Li Y, Bader M, Tamargo I, Rubovitch V, Tweedie D, Pick CG, Greig NH (2015) Liraglutide is neurotrophic and neuroprotective in neuronal cultures and mitigates mild traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurochem 135(6):1203–1217
Liu M, Lee DF, Chen CT, Yen CJ, Li LY, Lee HJ, ... & Xia W (2012) IKKα activation of NOTCH links tumorigenesis via FOXA2 suppression. Mol Cell 45(2): 171–184
Logsdon AF, Lucke-Wold BP, Turner RC, Huber JD, Rosen CL, Simpkins JW (2015) Role of microvascular disruption in brain damage from traumatic brain injury. Compr Physiol 5(3):1147–1160
Ma X, Buscaglia LEB, Barker JR, Li Y (2011a) MicroRNAs in NF-κB signaling. J Mol Cell Biol 3(3):159–166
Ma Y, Liu W, Wang Y, Chao X, Qu Y, Wang K, Fei Z (2011b) VEGF protects rat cortical neurons from mechanical trauma injury induced apoptosis via the MEK/ERK pathway. Brain Res Bull 86(5):441–446
Moore KW, de Waal MR, Coffman RL, O’Garra A (2001) Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 19(1):683–765
Mukhin AG, Ivanova SA, Knoblach SM, Faden AI (1997) New in vitro model of traumatic neuronal injury: evaluation of secondary injury and glutamate receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. J Neurotrauma 14(9):651–663
Mullen RJ, Buck CR, Smith AM (1992) NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development 116(1):201–211
Nadorp B, Soreq H (2014) Predicted overlapping microRNA regulators of acetylcholine packaging and degradation in neuroinflammation-related disorders. Novel roles of non-coding brain RNAs in health and disease 55
Pan H, Wang H, Wang X, Zhu L, Mao L (2012) The absence of Nrf2 enhances NF-B-dependent inflammation following scratch injury in mouse primary cultured astrocytes. Mediat Inflamm 2012. doi:10.1155/2012/217580
Pandey NR, Sultan K, Twomey E, Sparks DL (2009) Phospholipids block nuclear factor-kappa B and tau phosphorylation and inhibit amyloid-beta secretion in human neuroblastoma cells. Neuroscience 164(4):1744–1753
Park HR, Lee H, Park H, Jeon JW, Cho WK, Ma JY (2015) Neuroprotective effects of Liriope Platyphylla extract against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. BMC Complement Altern Med 15(1):171
Permpoonputtana K, Govitrapong P (2013) The anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin on methamphetamine-induced proinflammatory mediators in human neuroblastoma dopamine SH-SY5Y cell lines. Neurotox Res 23(2):189–199
Qin XY, Cheng Y, Yu LC (2010) Potential protection of curcumin against intracellular amyloid β-induced toxicity in cultured rat prefrontal cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 480(1):21–24
Sarray S, Almawi WY (2015) Contribution of reduced interleukin-10 levels to the pathogenesis of osteomyelitis in children with sickle cell disease. Clin Vaccine Immunol 22(9):1020–1024
Schmit A, Carol M, Robert F, Bontems P, Houben JJ, Van Gossum A, ... & Mascart F (2001) Dose-effect of interleukin-10 and its immunoregulatory role in Crohn’s disease. Eur Cytokine Netw 13: 298–305
Shin VY, Jin H, Ng EK., Cheng AS, Chong WW, Wong CY., ... & Chu KM (2011) NF-κB targets miR-16 and miR-21 in gastric cancer: involvement of prostaglandin E receptors. Carcinogenesis 32(2): 240–245
Stoica BA, Faden AI (2010) Cell death mechanisms and modulation in traumatic brain injury. Neurotherapeutics 7:3–12
Swarup V, Ghosh J, Mishra MK, Basu A (2008) Novel strategy for treatment of Japanese encephalitis using arctigenin, a plant lignan. J Antimicrob Chemother 61:679–688
Tsai WJ, Chang CT, Wang GJ, Lee TH, Chang SF, Lu SC, Kuo YC (2011) Arctigenin from Arctiumlappa inhibits interleukin-2 and interferon gene expression in primary human T lymphocytes. Chin Med 6:12
Voigt A, Zintl F (2003) Effects of retinoic acid on proliferation, apoptosis, cytotoxicity, migration, and invasion of neuroblastoma cells. Med Pediatr Oncol 40(4):205–213
Wilson MR, Choudhury S, Takata M (2005) Pulmonary inflammation induced by high-stretch ventilation is mediated by tumor necrosis factor signaling in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L599–L607
Zhai PP, Xu LH, Yang JJ, Jiang ZL, Zhao GW, Sun L, ... & Li X (2015) Reduction of inflammatory responses by l-serine treatment leads to neuroprotection in mice after traumatic brain injury. Neuropharmacology 95:1–11
Zhang WZ, Jiang ZK, He BX, Liu XB (2015) Arctigenin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary oxidative stress and inflammation in a mouse model via suppression of MAPK, HO-1, and iNOS signaling. Inflammation 38(4):1406–1414
Zhang YZ, Shen JF, Xu JY, Xiao JH, Wang JL (2007) Inhibitory effects of 2, 3, 5, 4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside on experimental inflammation and cyclooxygenase 2 activity. J Asian Nat Prod Res 9(4):355–363
Zhuang P, Zhang Y, Cui G, Bian Y, Zhang M, Zhang J, ... & Jiang Y (2012) Direct stimulation of adult neural stem/progenitor cells in vitro and neurogenesis in vivo by salvianolic acid B. PLoS One 7(4): e35636
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 30572336 and 81173580).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Li, N., Xia, Y. et al. Arctigenin Confers Neuroprotection Against Mechanical Trauma Injury in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells by Regulating miRNA-16 and miRNA-199a Expression to Alleviate Inflammation. J Mol Neurosci 60, 115–129 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0784-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0784-x