Abstract
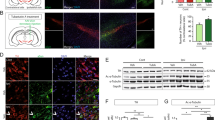
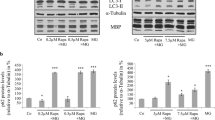
Proteinaceous inclusions in nerve cells and glia are a defining neuropathological hallmark in a variety of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), and corticobasal degeneration (CBD). Their occurrence may be related to malfunctions of the proteolytic degradation systems. In cultured oligodendrocytes, proteasomal inhibition leads to protein aggregate formation resembling coiled bodies, which are characteristic for PSP and CBD. Large protein aggregates are excluded from the proteasome and can only be degraded by autophagy, a lysosomal pathway. Autophagy is a highly selective process, which requires a variety of receptor proteins for ubiquitinated proteins, such as p62 and histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6). HDAC6 is mainly localized in the cytoplasm, and alpha-tubulin is its major substrate. HDAC6 is considered as a sensor of proteasomal stress; it is involved in the autophagosomal pathway and can mediate the retrograde transport of ubiquitinated proteins along the microtubules. As we have shown recently, HDAC6 is present in oligodendrocytes and its inhibition leads to morphological alterations, microtubule bundling, modulation of acetylation, and phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau. The present study was undertaken to investigate whether HDAC6 is involved in protein aggregate formation in oligodendrocytes and whether its inhibition modifies the consequences of MG-132-induced inhibition of the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS). The data show that HDAC6 and acetylated tau are recruited to protein aggregates after proteasomal inhibition. Pharmacological inhibition of HDAC6 by the selective inhibitor tubastatin A (TST) and its small hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated downregulation alters the assembly of MG-132-induced compact protein aggregates. After TST treatment, they appear more diffusely dispersed throughout the cytoplasm. This is not a protective means but promotes the onset of apoptotic cell death. Furthermore, the heat shock response is altered, and TST suppresses the MG-132-stimulated induction of HSP70. To test whether the alteration of protein aggregate formation is related to the influence of HDAC6 on the autophagic degradation system, an oligodendroglial cell line, i.e., OLN-93 cells stably expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP)-microtubule associated protein light chain 3 (LC3) and tau, was used. During autophagosome formation, endogenous LC3 is processed to LC3-I, which is then converted to LC3-II. An increase of LC3-II is used as a reliable marker for autophagosome formation and abundance. It is demonstrated that inhibition of HDAC6 leads to the accumulation of LC3-positive autophagosomal vacuoles and an increase in LC3-II immunoreactivity, but the autophagic flux is rather impaired. Hence, the inhibition or dysregulation of HDAC6 contributes to stress responses and pathological processes in oligodendrocytes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asthana J, Kapoor S, Mohan R, Panda D (2013) Inhibition of HDAC6 deacetylase activity increases its binding with microtubules and suppresses microtubule dynamic instability in MCF-7 cells. J Biol Chem 288:22516–26
Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:663–72
Banreti A, Sass M, Graba Y (2013) The emerging role of acetylation in the regulation of autophagy. Autophagy 9:819–29
Bauer NG, Richter-Landsberg C (2006) The dynamic instability of microtubules is required for aggresome formation in oligodendroglial cells after proteolytic stress. J Mol Neurosci 29:153–68
Boyault C, Gilquin B, Zhang Y et al (2006) HDAC6-p97/VCP controlled polyubiquitin chain turnover. EMBO J 25:3357–66
Boyault C, Sadoul K, Pabion M, Khochbin S (2007) HDAC6, at the crossroads between cytoskeleton and cell signaling by acetylation and ubiquitination. Oncogene 26:5468–76
Butler KV, Kalin J, Brochier C, Vistoli G, Langley B, Kozikowski AP (2010) Rational design and simple chemistry yield a superior, neuroprotective HDAC6 inhibitor, tubastatin A. J Am Chem Soc 132:10842–6
Chiba Y, Takei S, Kawamura N et al (2012) Immunohistochemical localization of aggresomal proteins in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 38:559–71
Cohen TJ, Guo JL, Hurtado DE et al (2011) The acetylation of tau inhibits its function and promotes pathological tau aggregation. Nat Commun 2:252
Cook C, Carlomagno Y, Gendron TF et al (2014) Acetylation of the KXGS motifs in tau is a critical determinant in modulation of tau aggregation and clearance. Hum Mol Genet 23:104–16
d’Ydewalle C, Bogaert E, Van Den Bosch L (2012) HDAC6 at the intersection of neuroprotection and neurodegeneration. Traffic 13:771–9
Ding H, Dolan PJ, Johnson GV (2008) Histone deacetylase 6 interacts with the microtubule-associated protein tau. J Neurochem 106:2119–30
Dohm CP, Kermer P, Bahr M (2008) Aggregopathy in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic implication. Neurodegener Dis 5:321–38
Fiesel FC, Voigt A, Weber SS et al (2010) Knockdown of transactive response DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) downregulates histone deacetylase 6. EMBO J 29:209–21
Fort P, Marty L, Piechaczyk M et al (1985) Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res 13:1431–42
Goldbaum O, Richter-Landsberg C (2004) Proteolytic stress causes heat shock protein induction, tau ubiquitination, and the recruitment of ubiquitin to tau-positive aggregates in oligodendrocytes in culture. J Neurosci 24:5748–57
Goldbaum O, Oppermann M, Handschuh M et al (2003) Proteasome inhibition stabilizes tau inclusions in oligodendroglial cells that occur after treatment with okadaic acid. J Neurosci 23:8872–80
Goldbaum O, Vollmer G, Richter-Landsberg C (2006) Proteasome inhibition by MG-132 induces apoptotic cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured rat brain oligodendrocytes but not in astrocytes. Glia 53:891–901
Goldbaum O, Riedel M, Stahnke T, Richter-Landsberg C (2009) The small heat shock protein HSP25 protects astrocytes against stress induced by proteasomal inhibition. Glia 57:1566–77
He C, Klionsky DJ (2009) Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 43:67–93
Irwin DJ, Cohen TJ, Grossman M et al (2012) Acetylated tau, a novel pathological signature in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Brain 135:807–18
Janen SB, Chaachouay H, Richter-Landsberg C (2010) Autophagy is activated by proteasomal inhibition and involved in aggresome clearance in cultured astrocytes. Glia 58:1766–74
Jellinger KA (2012) Interaction between pathogenic proteins in neurodegenerative disorders. J Cell Mol Med 16:1166–83
Johansen T, Lamark T (2011) Selective autophagy mediated by autophagic adapter proteins. Autophagy 7:279–96
Kawaguchi Y, Kovacs JJ, McLaurin A, Vance JM, Ito A, Yao TP (2003) The deacetylase HDAC6 regulates aggresome formation and cell viability in response to misfolded protein stress. Cell 115:727–38
Kirkin V, McEwan DG, Novak I, Dikic I (2009) A role for ubiquitin in selective autophagy. Mol Cell 34:259–69
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H et al (2012) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy 8:445–544
Kopito RR (2000) Aggresomes, inclusion bodies and protein aggregation. Trends Cell Biol 10:524–30
Lee JY, Koga H, Kawaguchi Y et al (2010) HDAC6 controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective quality-control autophagy. EMBO J 29:969–80
Li Y, Shin D, Kwon SH (2013) Histone deacetylase 6 plays a role as a distinct regulator of diverse cellular processes. FEBS J 280:775–93
Matsuyama A, Shimazu T, Sumida Y et al (2002) In vivo destabilization of dynamic microtubules by HDAC6-mediated deacetylation. EMBO J 21:6820–31
Matthias P, Yoshida M, Khochbin S (2008) HDAC6 a new cellular stress surveillance factor. Cell Cycle 7:7–10
Miki Y, Mori F, Tanji K, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K (2011) Accumulation of histone deacetylase 6, an aggresome-related protein, is specific to Lewy bodies and glial cytoplasmic inclusions. Neuropathology 31:561–8
Miller DW, Cookson MR, Dickson DW (2004) Glial cell inclusions and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Neuron Glia Biol 1:13–21
Min SW, Cho SH, Zhou Y et al (2010) Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy. Neuron 67:953–66
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Levine B (2010) Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell 140:313–26
Neuhoff V, Philipp K, Zimmer HG, Mesecke S (1979) A simple, versatile, sensitive and volume-independent method for quantitative protein determination which is independent of other external influences. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem 360:1657–70
Nixon RA (2006) Autophagy in neurodegenerative disease: friend, foe or turncoat? Trends Neurosci 29:528–35
Noack M, Leyk J, Richter-Landsberg C (2014) HDAC6 inhibition results in tau acetylation and modulates tau phosphorylation and degradation in oligodendrocytes. Glia 62:535–47
Odagiri S, Tanji K, Mori F et al (2013) Brain expression level and activity of HDAC6 protein in neurodegenerative dementia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 430:394–9
Pandey UB, Nie Z, Batlevi Y et al (2007) HDAC6 rescues neurodegeneration and provides an essential link between autophagy and the UPS. Nature 447:859–63
Richter-Landsberg C (2007) Heat shock proteins: expression and functional roles in nerve cells and glia, in heat shock proteins in neural cells. Landes Bioscience, New York, pp 1–12
Richter-Landsberg C (2008) The cytoskeleton in oligodendrocytes. Microtubule dynamics in health and disease. J Mol Neurosci 35:55–63
Richter-Landsberg C, Bauer NG (2004) Tau-inclusion body formation in oligodendroglia: the role of stress proteins and proteasome inhibition. Int J Dev Neurosci 22:443–51
Richter-Landsberg C, Gorath M (1999) Developmental regulation of alternatively spliced isoforms of mRNA encoding MAP2 and tau in rat brain oligodendrocytes during culture maturation. J Neurosci Res 56:259–70
Richter-Landsberg C, Heinrich M (1996) OLN-93: a new permanent oligodendroglia cell line derived from primary rat brain glial cultures. J Neurosci Res 45:161–73
Richter-Landsberg C, Leyk J (2013) Inclusion body formation, macroautophagy, and the role of HDAC6 in neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol 126:793–807
Richter-Landsberg C, Vollgraf U (1998) Mode of cell injury and death after hydrogen peroxide exposure in cultured oligodendroglia cells. Exp Cell Res 244:218–29
Roach A, Boylan K, Horvath S, Prusiner SB, Hood LE (1983) Characterization of cloned cDNA representing rat myelin basic protein: absence of expression in brain of shiverer mutant mice. Cell 34:799–806
Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A (2009) Targeting proteins for destruction by the ubiquitin system: implications for human pathobiology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:73–96
Schwarz L, Goldbaum O, Bergmann M, Probst-Cousin S, Richter-Landsberg C (2012) Involvement of macroautophagy in multiple system atrophy and protein aggregate formation in oligodendrocytes. J Mol Neurosci 47:256–66
Seiberlich V, Borchert J, Zhukareva V, Richter-Landsberg C (2013) Inhibition of protein deubiquitination by PR-619 activates the autophagic pathway in OLN-t40 oligodendroglial cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 67:149–60
Taylor JP, Tanaka F, Robitschek J et al (2003) Aggresomes protect cells by enhancing the degradation of toxic polyglutamine-containing protein. Hum Mol Genet 12:749–57
van Stipdonk MJ, Willems AA, Plomp AC, van Noort JM, Boog CJ (2000) Tolerance controls encephalitogenicity of alphaB-crystallin in the Lewis rat. J Neuroimmunol 103:103–11
Xilouri M, Stefanis L (2011) Autophagic pathways in Parkinson disease and related disorders. Expert Rev Mol Med 13:e8
Zilberman Y, Ballestrem C, Carramusa L, Mazitschek R, Khochbin S, Bershadsky A (2009) Regulation of microtubule dynamics by inhibition of the tubulin deacetylase HDAC6. J Cell Sci 122:3531–41
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the German Science Foundation (DFG RI 384/17-1). We thank Dr. Virginia Lee, CNDR, University of Pennsylvania Medical School, Philadelphia, PA, USA, for generously providing antibodies against acetylated K280 tau. Dr. Philip Kahle, Hertie Institute for clinical brain research, Tübingen, Germany, generously provided human full-length cDNA-encoding HDAC6. We thank Irina Fomins and Angelika Spanjer for the excellent technical help, and Dr. Sven Jänen for cloning and preparing the HDAC6 shRNA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leyk, J., Goldbaum, O., Noack, M. et al. Inhibition of HDAC6 Modifies Tau Inclusion Body Formation and Impairs Autophagic Clearance. J Mol Neurosci 55, 1031–1046 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0460-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0460-y