Abstract
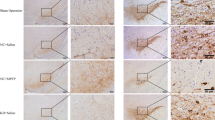
Neuro-inflammation and dysfunction of blood–brain barrier play an important role in the occurrence, development, and neuronal degeneration of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Studies have demonstrated that a variety of cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β destroy the structure and function of blood–brain barrier. The damage to blood–brain barrier results in death of dopaminergic neurons, while protection of blood–brain barrier slows down the progression of PD. Also, it has been shown that activation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) plays an important role in causing damage to blood–brain barrier. In addition, the PARP inhibitor 3-AB has been shown to protect blood–brain barrier from damage and has neuroprotective effects. In this study, using a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced PD rat model, we investigated whether 3-AB protects blood–brain barrier and dopaminergic neurons from functional damage. LPS significantly increased Evans blue content in the substantia nigra which peaked at 12 h, while administration of 3-AB significantly inhibited the LPS-induced increase in Evans blue content and also significantly increased the expression of the tight junction-associated proteins claudin-5, occludin and ZO-1. 3-AB also increased the number of tyrosine hydroxylase positive cells and reduced the IL-1β and TNF-α content significantly. According to western blot analysis, 3-AB significantly reduced the p-ERK1/2 expression, while the expression of p-p38MAPK increased. These results suggest that 3-AB protects the blood–brain barrier from functional damage in an LPS-induced PD rat model and dopaminergic neurons are protected from degeneration by upregulation of tight junction-associated proteins. These protective effects of 3-AB may be related to modulation of the ERK1/2 pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carvey PM, Zhao CH, Hendey B, Lum H, Trachtenberg J, Desai BS, Snyder J, Zhu YG, Ling ZD (2005) 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced alterations in blood–brain barrier permeability. Eur J Neurosci 22(5):1158–1168
Castaño A, Herrera AJ, Cano J, Machado A (1998) Lipopolysaccharide intranigral injection induces inflammatory reaction and damage in nigrostriatal dopaminergic system. J neurochem 70(4):1584–1592
Chen X, Lan X, Roche I, Liu R, Geiger JD (2008) Caffeine protects against MPTP-induced blood–brain barrier dysfunction in mouse striatum. J Neurochem 107(4):1147–1157
Cohen-Armon M, Visochek L, Rozensal D, Kalal A, Geistrikh I, Klein R, Bendetz-Nezer S, Yao Z, Seger R (2007) DNA-independent PARP-1 activation by phosphorylated ERK2 increases Elk1 activity: a link to histone acetylation. Mol Cell 25(2):297–308
D’Amours D, Desnoyers S, D’Silva I, Poirier GG (1999) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reactions in the regulation of nuclear functions. Biochem J 342(Pt 2):249–268
Feng D, Ling WH, Duan RD (2010) Lycopene suppresses LPS-induced NO and IL-6 production by inhibiting the activation of ERK, p38MAPK, and NF-kappaB in macrophages. Inflamm Res 59(2):115–121
Hassa PO, Haenni SS, Elser M, Hottiger MO (2006) Nuclear ADP-ribosylation reactions in mammalian cells: where are we today and where are we going? Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70(3):789–829
Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS (2000) Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysacchride-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci 20(16):6309–6316
Kim MY, Zhang T, Kraus WL (2005) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by PARP-1: ‘PAR-laying’ NAD + into a nuclear signal. Genes Dev 19(17):1951–1967
Koh SH, Park Y, Song CW, Kim JG, Kim K, Kim J, Kim MH, Lee SR, Kim DW, Yu HJ, Chang DI, Hwang SJ, Kim SH (2004) The effect of PARP inhibitor on ischaemic cell death, its related inflammation and survival signals. Eur J Neurosci 20(6):1461–1472
Kortekaas R, Leenders KL, van Oostrom JC, Vaalburg W, Bart J, Willemsen AT, Hendrikse NH (2005) Blood–brain barrier dysfunction in parkinsonian midbrain in vivo. Ann Neurol 57(2):176–179
Lee HS, Ryu DS, Lee GS, Lee DS (2012) Anti-inflammatory effects of dichloromethane fraction from Orostachys japonicus in RAW 264.7 cells: suppression of NF-κB activation and MAPK signaling. J Ethnopharmacol 140(2):271–276
Lenzsér G, Kis B, Snipes JA, Gáspár T, Sándor P, Komjáti K, Szabó C, Busija DW (2007) Contribution of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase to postischemic blood–brain barrier damage in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(7):1318–1326
Lescot T, Fulla-Oller L, Palmier B, Po C, Beziaud T, Puybasset L, Plotkine M, Gillet B, Meric P, Marchand-Leroux C (2010) Effect of acute poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition by 3-AB on blood–brain barrier permeability and edema formation after focal traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 27(6):1069–1079
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, McGeer EG (1988) Expression of the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR in neurological disease. Acta Neuropathol 76(6):550–557
Moroni F (2008) Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase 1 (PARP-1) and postischemic rain damage. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8(1):96–103
Mota RA, Sánchez-Bueno F, Saenz L, Hernández-Espinosa D, Jimeno J, Tornel PL, Martínez-Torrano A, Ramírez P, Parrilla P, Yélamos J (2005) Inhibition of poly(ADP-ri-bose) polymerase attenuates the severity of acute pancreatitis and associated lung injury. Lab Investn 85(10):1250–1262
Qin L, Liu Y, Wang T, Wei SJ, Block ML, Wilson B, Liu B, Hong JS (2004) NADPH oxidase mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity and proinflammatory gene expression in activated microglia. J Biol Chem 279(2):1415–1421
Rite I, Machado A, Cano J, Venero JL (2007) Blood–brain barrier disruption induces in vivo degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons. J Neurochem 101(6):1567–1582
Scott GS, Kean RB, Mikheeva T, Fabis MJ, Mabley JG, Szabó C, Hooper DC (2004) The therapeutic effects of PJ34 [N-(6-oxo-5,6-dihydrophenanthridin-2-yl)-N,N-dimethylacetamide.HCl], a selective inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis are associated with immunomodulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310(3):1053–1061
Singh AK, Jiang Y, Gupta S (2007a) Effects of bacterial toxins on endothelial tight junction in vitro: a mechanism-based investigation. Toxicol Mech Methods 17(6):331–347
Singh AK, Jiang Y, Gupta S, Benlhabib E (2007b) Effects of chronic ethanol drinking on the blood brain barrier and ensuing neuronal toxicity in alcohol-preferring rats subjected to intraperitoneal LPS injection. Alcohol Alcohol 42(5):385–399
Tansey MG, McCoy MK, Frank-Cannon TC (2007) Neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: potential environmental triggers, pathways, and targets for early therapeutic intervention. Exp Neurol 208(1):1–25
Veres B, Radnai B, Gallyas F Jr, Varbiro G, Berente Z, Osz E, Sumegi B (2004) Regulation of kinase cascades and transcription factors by a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor, 4-hydroxyquinazoline, in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310(1):247–255
Whitton PS (2007) Inflammation as a causative factor in the aetiology of Parkinson’s disease. Br J Pharmacol 150(8):963–976
Wu TT, Chen TL, Loon WS, Tai YT, Cherng YG, Chen RM (2011) Lipopolysaccharide stimulates syntheses of toll-like receptor 2 and surfactant protein-A in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells through upregulating phosphorylation of MEK1 and ERK1/2 and sequential activation of NF-κB. Cytokine 55(1):40–47
Yokoyama H, Kuroiwa H, Tsukada T, Uchida H, Kato H, Araki T (2010) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerse inhibitor can attenuate the neuronal death after 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity in mice. J Neurosci Res 88(7):1522–1536
Zhao C, Ling Z, Newman MB, Bhatia A, Carvey PM (2007) TNF-alpha knockout and minocycline treatment attenuates blood–brain barrier leakage in MPTP-treated mice. Neurobiol Dis 26(1):36–46
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (81171131, 81172197, 81072056, 81272564, 81272795), the special fund for Scientific Research of Doctor-degree Subjects in Colleges and Universities (20102104110009), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province in China (no. 201102300), Liaoning Science and Technology Plan Projects (no. 2011225020), and Shenyang Science and Technology Plan Projects (nos. F13-220-9-15, F13-316-1-16, and F13-316-1-19).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
The effects of different PJ34 concentrations on BBB permeability at 12 h after LPS injection were detected by extravasation of EB. EB content is given as means ± SD (n = 5, each). *P < 0.05 versus 0 mg/kg group; # P < 0.05 versus 5 mg/kg group (JPEG 8 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Xl., Wang, P., Liu, Yh. et al. Effects of Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor 3-Aminobenzamide on Blood–Brain Barrier and Dopaminergic Neurons of Rats with Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Parkinson’s Disease. J Mol Neurosci 53, 1–9 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0175-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0175-5