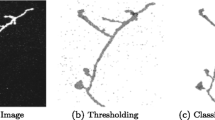
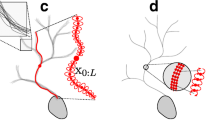
Abstract
Digital reconstruction of a single neuron occupies an important position in computational neuroscience. Although many novel methods have been proposed, recent advances in molecular labeling and imaging systems allow for the production of large and complicated neuronal datasets, which pose many challenges for neuron reconstruction, especially when discontinuous neuronal morphology appears in a strong noise environment. Here, we develop a new pipeline to address this challenge. Our pipeline is based on two methods, one is the region-to-region connection (RRC) method for detecting the initial part of a neurite, which can effectively gather local cues, i.e., avoid the whole image analysis, and thus boosts the efficacy of computation; the other is constrained principal curves method for completing the neurite reconstruction, which uses the past reconstruction information of a neurite for current reconstruction and thus can be suitable for tracing discontinuous neurites. We investigate the reconstruction performances of our pipeline and some of the best state-of-the-art algorithms on the experimental datasets, indicating the superiority of our method in reconstructing sparsely distributed neurons with discontinuous neuronal morphologies in noisy environment. We show the strong ability of our pipeline in dealing with the large-scale image dataset. We validate the effectiveness in dealing with various kinds of image stacks including those from the DIADEM challenge and BigNeuron project.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bas, E., & Erdogmus, D. (2011). Principal curves as skeletons of tubular objects. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 181–191.
Bas, E., Erdogmus, D., Draft, R. W., & Lichtman, J. W. (2012). Local tracing of curvilinear structures in volumetric color images: application to the Brainbow analysis. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 23, 1260–1271.
Bria A, Iannello G, Peng H. (2015). An open-source VAA3D plugin for real-time 3D visualization of terabyte-sized volumetric images. 2015 I.E. 12th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). IEEE, 2015: 520–523.
Brown, K., Barrionuevo, G., Canty, A., De Paola, V., Hirsch, J., Jefferis, G., et al. (2011). The DIADEM data sets: representative light microscopy images of neuronal morphology to advance automation of digital reconstructions. Neuroinformatics, 9(2), 143–157.
Chen, H., Xiao, H., Liu, T., & Peng, H. (2015). SmartTracing: self-learning-based neuron reconstruction. Brain Informatics, 2, 135–144.
Cohen, A.R., Roysam, B. & Turner, J.N. (1994). Automated tracing and volume measurements of neurons from 3-D confocal fluorescence microscopy data. J Microsc, 173, 103–114.
Donohue, D. E., & Ascoli, G. A. (2011). Automated reconstruction of neuronal morphology: an overview. Brain Research Reviews, 67(1–2), 94–102.
Gala, R., Chapeton, J., Jitesh, J., Bhavsar, C., & Stepanyants, A. (2014). Active learning of neuron morphology for accurate automated tracing of neurites. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 8(37), 1–14.
Gong, H., Zeng, S., Yan, C., Lv, X., Yang, Z., Xu, T., Feng, Z., Ding, W., Qi, X., Li, A., Wu, J., & Luo, Q. (2013). Continuously tracing brain-wide long-distance axonal projections in mice at a one-micron voxel resolution. NeuroImage, 74, 87–98.
Hastie, T., & Stuetzle, W. (1989). Principal curves. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 84(406), 502–516.
Jefferis, G., & Livet, J. (2012). Sparse and combinatorial neuron labeling. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 22, 101–110.
Jefferis, G., Potter, C., Chan, A., Marin, E., Rohlfing, T., Maurer, C., et al. (2007). Comprehensive maps of Drosophila higher olfactory centers: spatially segregated fruit and pheromone representation. Cell, 128(6), 1187–1203.
Josh Huang, Z., & Zeng, H. (2013). Genetic approaches to neural circuits in the mouse. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 36, 183–215.
Lu, J. (2011). Neuronal tracing for Connectomic studies. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 159–166.
Luo, L., Callaway, E. M., & Svoboda, K. (2008). Genetic dissection of neural circuits. Neuron, 57(5), 634–660.
Luo, G., Sui, D., Wang, K., et al. (2015). Neuron anatomy structure reconstruction based on a sliding filter. BMC Bioinformatics, 16(1), 342.
Meijering, E. (2010). Neuron tracing in perspective. Cytometry Part A, 77A(7), 693–704.
Ming, X., Li, A., Wu, J., Yan, C., Ding, W., Gong, H., Zeng, S., & Liu, Q. (2013). Rapid reconstruction of 3D neuronal morphology from light microscopy images with augmented rayburst sampling. PloS One, 8(12), e84–557.
Neurolucida (2014). MBF Bioscience: stereology and neuron morphology quantitative analysis. http://www.mbfbioscience.com.
Parekh, R., & Ascoli, G. A. (2013). Neuronal morphology goes digital: a research hub for cellular and system neuroscience. Neuron, 77(6), 1017–1038.
Peng, H., Long, F., & Myers, G. (2011). Automatic 3D neuron tracing using all-path pruning. Bioinformatics, 27(13), i239.
Peng, H., Hawrylycz, M., Roskams, J., et al. (2015a). BigNeuron: large-scale 3D neuron reconstruction from optical microscopy images. Neuron, 87(2), 252–256.
Peng, H., Meijering, E., & Ascoli, G. A. (2015b). From DIADEM to BigNeuron. Neuroinformatics, 13, 259–260.
Quan, T., et al. (2013). NeuroGPS: automated localization of neurons for brain circuits using L1minimization model. Scientific Reports, Rep. 3, 1414.
Quan, T., et al. (2014). Digital reconstruction of the cell body in dense neural circuits using a spherical-coordinated variational model. Scientific Reports, 4, 4970.
Quan, T., et al. (2016). NeuroGPS-Tree: automatic reconstruction of a large-scale neuronal population with dense neurites. Nature Methods, 13(1), 51–54.
Radojevie, M., Smal, I. & Meijering, E. (2015). Automated neuron morphology reconstruction using fuzzy-logic detection and Bayesian tracing algorithms. Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2015 I.E. 12th International Symposium on, 885–888.
Rodriguez, A., Ehlenberger, D., Hof, P., & Wearne, S. (2006). Rayburst sampling, an algorithm for automated three- dimensional shape analysis from laser scanning microscopy images. Nature Protocols, 1(4), 2152–2161.
Rodriguez, A., Ehlenberger, D., Hof, P., & Wearne, S. (2009). Three-dimensional neuron tracing by voxel scooping. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 184(1), 169–175.
Rotolo, T., Smallwood, P., Williams, J., & Nathans, J. (2008). Genetically-directed, cell type-specific sparse labeling for the analysis of neuronal morphology. PloS One, 3(12), 1–13.
Santamaría-Pang, A., Hernandez-Herrera, P., Papadakis, M., Saggau, P., & Kakadiaris, A. I. (2015). Automatic morphological reconstruction of neurons from multiphoton and confocal microscopy images using 3D tubular models. Neuroinformatics, 13(3), 297–320.
Schwarz, L., & Luo, L. (2015). Organization of the Locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system. Current Biology, 25(21), 1051–1056.
Silvestri, L., Bria, A., Sacconi, L., Iannello, G., & Pavone, F. (2012). Confocal light sheet microscopy: micron-scale neuroanatomy of the entire mouse brain. Optics Express, 20(18), 20582–20598.
Srinivasan, R., Li, Q., Zhou, X., Lu, J., Lichtman, J., & Wong, S. (2010). Reconstruction of the neuromuscular junction connectome. Bioinformatics, 26(12), i64–i70.
Turetken, E., Benmansour, F. & Fua, P. (2012). Automated reconstruction of tree structures using path classifiers and mixed integer programming. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 566–573). Rhode Island.
Turetken, E., Benmansour, F., Andres, B., Pfister, H. & Fua, P. (2013). Reconstructing loopy curvilinear structures using integer programming. In Proceedings of the IEEE, CVPR (pp. 1822–1829). Portland.
Turetken, E., Benmansour, F., Andres, B., Głowacki, P. &Pfister, H. (2014). Reconstructing Curvilinear Networks using Path Classifiers and Integer Programming. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Wang, Y., Narayanaswamy, A. & Roysam, B. (2011a). Novel 4-D open-curve active contour and curve completion approach for automated tree structure extraction. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE (pp. 1105–1112). Colorado Springs.
Wang, Y., Narayanaswamy, A., Tsai, C.-L., & Roysam, B. (2011b). A broadly applicable 3-D neuron tracing method based on open curve snake. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 193–217.
Wilt, B. A., Burns, L. D., Wei Ho, E. T., Ghosh, K. K., Mukamel, E. A., & Schnitzer, M. J. (2009). Advances in light microscopy for neuroscience. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 32, 435–506.
Xiao, H., & Peng, H. (2013). APP2: automatic tracing of 3D neuron morphology based on hierarchical pruning of a gray-weighted image distance-tree. Bioinformatics, 29(11), 1448–1454.
Xiong, H., Zhou, Z., Zhu, M., Lv, X., Li, A., Li, S., Li, L., Yang, T., Wang, S., Yang, Z., Xu, T., Luo, Q., Gong, H., & Zeng, S. (2014). Chemical reactivation of quenched fluorescent protein molecules enables resin-embedded fluorescence microimaging. Nature Communications, 5, 4992.
Yang, J., Gonzalez-Bellido, P. T., & Peng, H. (2013). A distance-field based automatic neuron tracing method. BMC Bioinformatics, 14(1), 93.
Yang, T., Zheng, T., Shang, Z., Wang, X., Lv, X., Yuan, J., & Zeng, S. (2015). Rapid imaging of large tissues using high-resolution stage-scanning microscopy. Biomedical Optics Express, 6(5), 1867–1875.
Yuan, X., Trachtenberg, J., Potter, S., & Roysam, B. (2009). MDL constrained 3-D grayscale skeletonization algorithm for automated extraction of dendrites and spines from fluorescence confocal images. Neuroinformatics, 7, 213–232.
Zhao, T., Xie, J., Amat, F., Clack, F., Ahammad, P., Peng, H., Long, F., & Myers, E. (2011). Automated reconstruction of neuronal morphology based on local geometrical and global structural models. Neuroinformatics, 9(2–3), 247–261.
Zheng, T., et al. (2013). Visualization of brain circuits using two-photon fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography. Optics Express, 21(8), 9839–9850.
Zhou, Z., Sorensen, S. & Peng, H. (2015).Neuron crawler: an automatic tracing algorithm for very large neuron images, Proc. of IEEE 2015 International Symposiumon Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, 870–874.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 91232306, Grant No. 61205196), National Key Scientific Instrument & Equipment Development Program of China (Grant No. 2012YQ030260) and Science Fund for Creative Research Group of China (Grant No. 61121004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Zhou, H., Quan, T. et al. SparseTracer: the Reconstruction of Discontinuous Neuronal Morphology in Noisy Images. Neuroinform 15, 133–149 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-016-9317-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-016-9317-6