Abstract
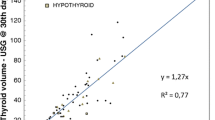
In multinodular goitre (MNG), low radioiodine (RAI) activity after recombinant human (rh) TSH is able to reduce thyroid volume (TV) and improve symptoms. Our aim was to evaluate the long-term outcome of RAI after rhTSH treatment in patients who were divided according to their baseline TSH levels. Eighteen patients (69.2 ± 6.1 year) presented non-toxic (TSH >0.3 mIU/l) MNG (TV: 61.0 ± 3.8 ml; group 1), while 13 patients (74.1 ± 7.9 year) had non-autoimmune pre-toxic (TSH <0.3 mIU/l) MNG (TV: 82.6 ± 14.4 ml; group 2). TSH, thyroid hormones, TV (by ultrasonography), body mass index (BMI), symptoms and quality of life (QoL) were evaluated. Treatment induced short-term thyrotoxicosis in both groups, but this was slightly more marked in group 2 than in group 1. The number and severity of adverse events were similar. The follow-up period was 55.3 ± 4.1 months in group 1 and 57.2 ± 5.1 months in group 2. The final TV reduction was similar in groups 1 (63.4 ± 3.6 %) and 2 (57.2 ± 4.6 %) and TV reduction positively correlated only with initial TV. At the last examination, 14 group-1 subjects were on L-T4 therapy, while 2 group-2 subjects were on methimazole. An increase in BMI was noted only in group 2. MNG-related symptoms were significantly reduced in both groups. Symptoms related to sub-clinical hyperthyroidism improved in group 2, while no significant changes in QoL were noted in either group. This study confirms the effectiveness of rhTSH adjuvant treatment in reducing TV after low RAI activities, irrespective of baseline thyroid status. TSH levels <0.3 mIU/l proved to be predictive of a more severe thyrotoxic phase after rhTSH and RAI, while initial TSH levels >0.3 mIU/l were more frequently followed by a need for L-T4 therapy. Compressive symptoms improved in the majority of subjects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Hegedus, S.J. Bonnema, F.N. Bennedback, Management of simple nodular goiter: current status and future perspectives. Endocr. Rev. 24, 102–132 (2003). doi:10.1210/er.2002-0016
S.J. Bonnema, L. Hegedus, A 30-year perspective on radioiodine therapy of benignant non-toxic multinodular goiter. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 16, 379–384 (2009). doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e32832ff2e1
R.H. Grogan, E.J. Mitmaker, J. Hwang, J.E. Gosnell, Q.-Y. Duh, O.H. Clark, W.T. Shen, A population-based prospective cohort study of complication after thyroidectomy in the elderly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97, 1645–1653 (2012). doi:10.1210/jc.2011-1162
S.J. Bonnema, H. Bertelsen, J. Mortensen, P.B. Andersen, D.U. Knudsen, L. Bastholt, L. Hegedus, The feasibility of high dose iodine 131 treatment as an alternative to surgery in patients with a very large goiter: effect of thyroid function and size and pulmonary function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 3638–3641 (1999). doi:10.1210/jc.84.10.3636
D. Huysmans, A. Hermus, M. Edelbroek, J. Barentsz, F. Corstens, P. Kloppenborg, Radioiodine for non-toxic multinodular goiter. Thyroid 7, 235–239 (1997)
B. Nygaard, L. Hegedus, M. Gervil, H. Hjalgrim, P. Soe-Jensen, J.M. Hansen, Radioiodine treatment of multinodular non-toxic goitre. BMJ 307, 828–832 (1993). doi:10.1136/bmj.307.6908.828
D.A. Huysmans, W.A. Nieuwlaat, R.J. Erdtsieck, A.P. Schellekens, J.W. Bus, B. Bravenboer, A.R. Hermus, Administration of a single low dose of recombinant human thyrotropin significantly enhances thyroid radioiodine uptake in nontoxix nodular goiter. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 3592–3596 (2000). doi:10.1210/jc.85.10.3592
W.A. Nieuwlaat, A.R. Hermus, F. Sicro-Prndelj, F.H. Corstens, D.A. Huysmans, Pretreatment with recombinant human TSH changes the regional distribution of radioiodine on thyroid scintigrams of nodular goiters. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 5330–5336 (2001). doi:10.1210/jc.86.11.5330
W.A. Nieuwlaat, D.A. Huysmans, H.C. Van den Bosch, G.C. Sweep, H.A. Ross, F.H. Corstens, A.R. Hermus, Pretreatment with a single, low dose of recombinant human thyrotropin allows dose reduction of radioiodine therapy in patients with nodular goiter. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 3121–3129 (2003). doi:10.1210/jc.2002-021554
C.C. Albino, C.O. Mesa Jr, M. Olandoski, C.E. Ueda, L.C. Woellner, C.A. Goedert, A.M. Souza, H. Graf, Recombinant human thyrotropin as adjuvant in the treatment of multinodular goiters with radioiodine. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 2775–2780 (2005). doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0458
C.C. Albino, H. Graf, G. Paz-Filho, L.A. Diehl, M. Olandoski, A. Sabbag, C. Buchpiguel, Radioiodine plus recombinant human thyrotropin do not cause acute airway compression and are effective in reducing multinodular goiter. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 43, 303–309 (2010)
S.J. Bonnema, V.E. Nielsen, H. Boel-Jorgensen, P. Gruppe, P.B. Anderson, L. Bastholt, L. Hegedus, Improvement of goiter volume reduction after 0.3 mg recombinant human thyrotorpin-stimulated radioiodine therapy in patients with a very large goiter: a double-blinded, randomised trail. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92, 3424–3428 (2007). doi:10.1210/jc.2007-0501
O. Cohen, J. Ilany, C. Hoffman, D. Olchovsky, S. Dabhi, A. Karasik, E. Goshen, G. Rotenberg, S.T. Zwas, Low-dose recombinant human thyrotropin-aided radioiodine treatment of large, multinodular goiters in elderly patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 154, 243–252 (2006). doi:10.1530/eje.1.02094
E.R. Cubas, G.J. Paz-Filho, M. Olandoski, C.A. Goedert, L.C. Woellner, G.A. Carvalho, H. Graf, Recombinant human TSH increases the efficacy of a fixed activity of radioiodine for treatment of multinodular goitre. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 63, 583–590 (2009). doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2008.01904.x
S. Fast, L. Hegedus, P. Grupe, V.E. Nielsen, C. Bluhme, L. Bastholt, S.J. Bonnema, Recombinant human thyrotropin-stimulated radioiodine therapy of nodular goiter allows major reduction of the radiation burden with retained efficacy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95, 3719–3725 (2010). doi:10.1210/jc.2010-0634
M. Giusti, C. Cappi, B. Santaniello, E. Ceresola, C. Augeri, C. Lagasio, F. Minuto, Safety and efficacy of administering 0.2 mg of recombinant human TSH for two consecutive days as an adjuvant to therapy with low radioiodine doses in elderly out-patients with large multinodular goiter. Minerva Endocrinol. 31, 191–209 (2006)
M. Giusti, M. Caputo, I. Calamia, M.C. Bagnara, E. Ceresola, M. Schiavo, M. Mussap, D. Ferone, F. Minuto, M. Bagnasco, Long-term outcome of low-activity radioiodine administration preceded by adjuvant recombinant human TSH pretreatment in elderly subjects with multinodular goiter. Thyroid Res. 2, 6 (2009). doi:10.1186/1756-6614-2-6
V.E. Nielsen, S.J. Bonnema, H. Boel-Jorgensen, P. Gruppe, L. Hegedus, Stimulation with 0.3-mg recombinant human thyrotropin prior to iodine 131 therapy to improve the size reduction of benign nontoxic goiter: a prospective randomised double-blind trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 166, 1476–1482 (2006). doi:10.1001/archint.166.14.1476
G.J. Paz-Filho, C.O. Mesa-Junior, M. Olandoski, L.C. Woellner, C.A. Goedert, C.L. Boguszewski, G.A. Carvalho, H. Graf, Effect of 30 mCi radioiodine on multinodular goiter previously treated with recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 40, 1661–1670 (2007)
R. Romao, I.G.S. Rubio, E.K. Tominori, Y. Camargo, M. Knobel, G. Medeiros-Neto, High prevalence of side effect after recombinant human thyrotropin-stimulated radioiodine treatment with 30 mCi in patients with multinodular goiter and subclinical/clinical hyperthyroidism. Thyroid 19, 945–951 (2009)
M.N. Silva, I.G.S. Rubio, R. Romao, E.M.M.S. Gebrin, C. Buchpiguel, E. Tomimori, R. Camargo, M.S. Cardia, G. Medeiros-Neto, Administration of a single dose of recombinant human thyrotrophin enhances the efficacy of radioiodine treatment of large compressive multinodular goiter. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 60, 300–308 (2004). doi:10.1046/j.1365-2265.2003.01918.x
S. Fast, V.E. Nielsen, P. Groupe, B. Boel-Jorgensen, L. Bastholt, P.B. Andersen, S.J. Bonnema, L. Hegedus, Prestimulation with recombinant human thyrotropin (rhTSH) improves the long-term outcome of radioiodine therapy for multinodular nontoxic goiter. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97, 2653–2660 (2012). doi:10.1210/jc.2011-3335
M.S. Cardia, I.G. Rubio, G. Medeiros-Neto, Prolonged follow-up of multinodular goitre patients treated with radioiodine preceded or not by human recombinant TSH. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 64, 474 (2006). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02419.x
G.J. Paz-Filho, C.O. Mesa, G.A. Carvalho, C.A. Goedert, H. Graf, Recombinant human TSH associated with radioiodine does not have further effects on thyroid volume and function after 2 years. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 69, 345–346 (2008). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.03165.x
A.C. Traino, F. Di Martino, M. Lazzeri, M.G. Stabia, Influence of thyroid volume reduction on calculated dose in radioiodine therapy of Graves’ hyperthyroidism. Phys. Med. Biol. 45, 121–129 (2000). doi:10.1088/0031-9155/45/1/309
W.Z. Billewicz, R.S. Chapman, J. Crooks, M.E. Day, J. Gossage, E. Wayne, J.A. Young, Statistical methods applied to the diagnosis of hypothyroidism. Q. J. Med. 150, 255–266 (1969)
M. Giusti, G. Melle, M. Fenocchio, L. Mortara, F. Cecoli, V. Caorsi, D. Ferone, F. Minuto, E. Rasore, Five-year longitudinal evaluation of quality of life in a cohort of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J. Zehjiang Univ. Sci. B. 12, 163–173 (2011). doi:10.1631/jzus.B.1000382
V.E. Nielsen, S.J. Bonnema, L. Hegedus, Transient goiter enlargement after administration of 0.3 mg of recombinant human thyrotropin in patients with benign nontoxic nodular goiter: a randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 1317–1322 (2006). doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2137
H. Graf, S. Fast, F. Pacini, A. Pinchera, A. Leung, M. Vaisman, C. Reiners, J.L. Wemeau, D. Huysmans, W. Harper, A. Driedger, H. de Noemberg Souza, M.G. Castagna, L. Antonangeli, L. Braverman, R. Corbo, C. Duren, E. Proust-Lemoine, A. Edelbroek, C. Mariott, I. Rachinsky, P. Gruppe, T. Watt, J. Magner, L. Hegedus, Modified-Release Recombinant Human TSH (MRrhTSH) augments the effect of ¹³¹I therapy in benign multinodular goiter; results from a multicenter international, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, 1368–1376 (2011). doi:10.1210/jc.2010-1193
R. Crevenna, G. Zetting, M. Keilani, M. Posch, M. Schmidinger, C. Pirich, M. Nuhr, M. Wolzt, M. Quittan, V. Fialka-Moser, Quality of life in patients with non-metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer under thyroxine supplementation therapy. Support Care Center 11(9), 597–603 (2003). doi:10.1007/s00520-003-0474-4
J. Lee, M.J. Yun, K.H. Nam, W.Y. Choung, E.Y. Soh, C.S. Park, Quality of life and effectiveness comparisons of thyroxine withdrawal, triiodothyronine withdrawal, and recombinant thyroid-stimulating hormone administration for low-dose radioiodine remnant ablation of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 20, 173–179 (2010)
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giusti, M., Caorsi, V., Mortara, L. et al. Long-term outcome after radioiodine therapy with adjuvant rhTSH treatment: comparison between patients with non-toxic and pre-toxic large multinodular goitre. Endocrine 45, 221–229 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-9959-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-9959-1