Abstract
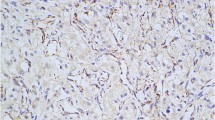
The objective of this article is to evaluate Heparanase-1 and Cyclooxygenase-2 as tissue-based markers of pheochromocytoma prognosis. Ninety-two sporadic pheochromocytoma patients with a minimum of 8-year follow-up post-diagnosis were enrolled. Slides of normal adrenal glands in nephrectomy specimens from 20 patients with benign renal tumors were as control. Heparanase-1 and Cyclooxygenase-2 expression as well as microvessel density were examined using immunohistochemistry in tissues from these patients. Positive staining for Heparanase-1 was observed in 23.68% of the benign and 77.78% of the malignant cases, whereas none of the normal adrenal controls showed positive staining. Similarly, Cyclooxygenase-2 staining was seen in 23.68% of the benign versus 83.33% of the malignant cases, and none of the normal controls appeared positive for Cyclooxygenase-2. Using both HPA-1 and Cox-2 combined, the positive predictive value of malignancy was significantly increased to 0.72, compared to about 0.45 by their own. Malignant cases showed higher microvessel density compared to benign tumors and normal controls (36.41, 21.43, and 13.36%, respectively). Heparanase-1 and Cyclooxygenase-2 may contribute to the invasive characteristics of malignant pheochromocytomas. Heparanase-1 and Cyclooxygenase-2 combined is better than their own to be used as a marker to distinguish malignant from benign pheochromocytoma.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Eisenhofer, S.R. Bornstein, F.M. Brouwers et al., Malignant pheochromocytoma: current status, initiatives for future progress. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 11, 423–436 (2004)
R.I. Linnoila, H.R. Keiser, S.M. Steinberg, E.E. Lack, Histopathology of benign versus malignant sympathoadrenal paragangliomas: clinicopathologic study of 120 cases including unusual histologic features. Hum. Pathol. 21, 1168–1180 (1999)
E.E. Lack, Adrenal medullary hyperplasia and pheochromocytoma, in Pathology of the Adrenal Glands, ed. by E.E. Lack (Churchill Livingstone, New York, 1990), pp. 173–235
M. Toyoshima, M. Nakajima, Human heparanase: purification, characterization, cloning, expression. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 24153–24160 (1999)
R.M. Quiros, A.W. Kim, J. Maxhimer, P. Gattuso, X. Xu, R.A. Prinz, Differential heparanase-1 expression in malignant, benign pheochromocytoma. J. Surg. Res. 108, 44–50 (2002)
K. Merati, M. said Siadaty, A. Andea et al., Expression of inflammatory modulator CoX-2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, its relationship to pathologic, clinical parameters. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 447–452 (2001)
N. Weidner, Intratumor microvessel density as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 147, 9–19 (1995)
H.C. Klingler, P.J. Klingler, J.K. Martin Jr., R.C. Smallridge, S.L. Smith, R.A. Hinder, Pheochromocytoma. Urology 57, 1025–1032 (2001)
I. Vlodavsky, Y. Friedmann, M. Elkin et al., Mammalian heparanase: gene cloning, expression, function in tumor progression, metastasis. Nat. Med. 5, 793–802 (1999)
M.D. Hulett, C. Freeman, B.J. Hamdorf, R.T. Baker, M.J. Harris, C.R. Parish, Cloning of mammalian heparanase, an important enzyme in tumor invasion, metastasis. Nat. Med. 5, 803–809 (1999)
A. Koliopanos, H. Friess, J. Kleeff et al., Heparanase expression in primary, metastatic pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 61, 4655–4659 (2001)
K. Gohji, H. Hirano, M. Okamoto et al., Expression of three extracellular matrix degradative enzymes in bladder cancer. Int. J. Cancer 95, 295–301 (2001)
A. Ferrandez, S. Prescott, R.W. Burt, CoX-2, colorectal cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 9, 2229–2251 (2003)
D. Brattström, K. Wester, M. Bergqvist et al., HER-2, EGFR, CoX-2 expression status correlated to microvessel density, survival in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Oncol. 43, 80–86 (2004)
B.S. Sheu, H.B. Yang, S.M. Sheu, A.H. Huang, J.J. Wu, Higher gastric cycloxygenase-2 expression, precancerous change in Helicobacter pylori-infected relatives of gastric cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 9, 5245–5251 (2003)
G.S. Gupta, M. Srivastava, N. Ahmad, D.G. Bostwick, H. Mukhtar, Over expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human prostate adenocarcinoma. Prostate 42, 73–78 (2001)
R. Yoshimura, H. Sano, M. Mitsuhashi, M. Kohno, J. Chargui, S. Wada, Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in patients with bladder carcinoma. J. Urol. 165, 1468–1472 (2001)
R. Yoshimura, M. Matsuyama, Y. Kawahito et al., Study of cyclooxygenase-2 in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 13, 229–233 (2004)
K. Saukkonen, J. Rintahaka, A. Sivula et al., Cyclooxygenase-2, gastric carcinogenesis. APMIS 111, 915–925 (2003)
K. Salmenkivi, C. Haglund, A. Ristimäki, J. Arola, P. Heikkilä, Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in malignant pheochromocytomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 5615–5619 (2001)
J.B. Laforga, F.I. Aranda, Angiogenic index: a new method for assessing microvascularity in breast carcinoma with possible prognostic implications. Breast J. 6, 103–107 (2000)
M. Elkin, N. Ilan, R. Ishai-Michaeli et al., Heparanase as mediator of angiogenesis: mode of action. FASEB J. 15, 1661–1663 (2001)
T. Imada, J. Matsuoka, T. Nobuhisa et al., CoX-2 induction by heparanase in the progression of breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 17, 221–228 (2006)
T. Okawa, Y. Naomoto, T. Nobuhisa et al., Heparanase is involved in angiogenesis in esophageal cancer through induction of cyclooxygenase-2. Clin. Cancer Res. 11, 7995–8005 (2005)
Y. Ohtawa, Y. Naomoto, Y. Shirakawa et al., The close relationship between heparanase, cyclooxygenase-2 expressions in signet-ring cell carcinoma of the stomach. Hum. Pathol. 37, 1145–1152 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Shanghai Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. 09ZR1418500), grant from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hong-chao is listed as co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., He, Hc., Yuan, F. et al. Heparanase-1 and Cyclooxygenase-2: prognostic indicators of malignancy in pheochromocytomas. Endocr 38, 93–99 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-010-9356-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-010-9356-y