Abstract
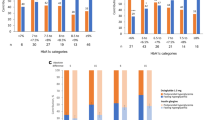
Exenatide is a new injectable medication for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes. Due to limited information of exenatide use in Asians and Pacific Islanders (API), we retrospectively reviewed API patients’ responses to exenatide treatment and compared the efficacy and safety of treatment to Caucasian patients. A total of 92 patients (70 API, 21 Caucasians, and 1 Hispanic) with type 2 diabetes were treated with exenatide. In all patients, there was a significant decrease in A1c level, BMI, and weight after 6 months of exenatide treatment (A1c from 8.63 ± 1.46 to 8.23 ± 1.46; P = 0.03, BMI from 34.54 ± 7.07 to 32.14 ± 6.41; P < 0.01, and weight from 215.24 ± 52.04 to 202.50 ± 49.90; P < 0.01 at 95% CI, N = 51). However, differences in mean change of A1c level, BMI, and weight between API and Caucasian patients were not observed at 3 and 6 months of treatment. Side effects and discontinuation of exenatide treatment between API and Caucasian patients were similar. In conclusion, exenatide is an effective anti-hyperglycemic agent in API patients with responses similar to that observed for Caucasian patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Dungan, J.B. Buse, Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for type 2 diabetes: a focus on exenatide. Clin. Diabetes 23, 56–62 (2005)
M.-B. Toft-Nielsen, M.B. Damholt, S. Madsbad, L.M. Hilsted, T.E. Hughes, B.K. Michelsen, J.J. Holst, Determinants of the impaired secretion of glucagons-like peptide-1 in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. 86(8), 3717–3723 (2001)
M.-B. Toft-Nielsen, S. Madsbad, J.J. Holst, Determinants of the effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide-1 in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. 86(8), 3853–3860 (2001)
D.J. Drucker, M.A. Nauck, The incretin system: glucacon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes Lancet 368(9548), 1696–1705 (2006)
J. Schirra, B. Goke, The physiological role of GLP-1 in human: incretin, ileal brake or more? Regul. Pept. 128, 109–115 (2005)
R.A. DeFronzo, R.E. Ratner, J. Han, D.D. Kim, M.S. Fineman, A.D. Baron, Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glycemic control and weight over 30 weeks in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 28(5), 1092–1100 (2005)
D.M. Kendall, M.C. Riddle, J. Rosenstock, D. Zhuang, D.D. Kim, M.S. Fineman, A.D. Baron, Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glycemic control over 30 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin and a sulfonylurea. Diabetes Care 28(5), 1083–1091 (2005)
J.B. Buse, R.R. Henry, J. Han, D.D. Kim, M.S. Fineman, A.D. Baron, Exenatide-113 Clinical Study Group. Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glycemic control over 30 weeks in sulfonylurea-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27(11), 2628–2635 (2004)
J.A. Loh, S.C. Clement, Efficacy of exenatide therapy over 12 months in a “real world” setting (Abstract). Diabetes 56(supplement1) A512; 570-P. (2007)
A.B. King, G. Wolfe, S. Healy, Clinical observations of exenatide treatment. Diabetes Care 29, 1984 (2006)
R.J. Heine, L.F. Van Gaal, D. Johns, M.J. Mihm, M.H. Widel, R.G. Brodows, GWAA study group, Exenatide versus insulin glargine in patients with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes. Ann. Intern. Med. 143, 559–569 (2005)
L. Blonde, E.J. Klein, J. Han, B. Zhang, S.M. Mac, T.H. Poon, K.L. Taylor, M.E. Trautmann, D.D. Kim, D.M. Kendal, Interim analysis of the effects of exenatide treatment on A1c, weight and cardiovascular risk factors over 82 weeks in 314 overweight patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 8, 436–447 (2006)
M.A. Nauck, S. Duran, D. Kim, D. Johns, A comparison of twice-daily exenatide and biphasic insulin aspart in patients with type 2 diabetes who were suboptimally controlled with sulfonylurea and metformin: a non-inferiority study. Diabetologia. 50, 259–267 (2007)
M.C. Riddle, R.R. Henry, T.H. Poon, B. Zhang, S.M. Mac, J.H. Holcombe, D.D. Kim, D.G. Maggs, Exenatide elicits sustained glycaemic control and progressive reduction of body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by sulphonylureas with or without metformin. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 22(6), 483–491 (2006)
R.E. Ratner, D. Maggs, L.L. Nielsen, A.H. Stonehouse, T. Poon, B. Zhang, T.A. Bicsak, R.G. Brodows, D.D. Kim, Long-term effects of exenatide therapy over 82 weeks on glycaemic control and weight in over-weight metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 8(4), 419–428 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chokrungvaranon, N., Chentanez, T. & Arakaki, R.F. Clinical experience with exenatide in predominantly Asian and Pacific Islander patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr 32, 311–316 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-008-9042-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-008-9042-5