Abstract
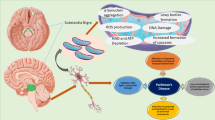
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a powerful early sign of Parkinson’s disease (PD), but the pathogenetic mechanism involved in RBD remains largely unexplored. α-Synuclein has been verified to form Lewy bodies in the orexin neurons, whose activity and function rely on the orexin 1 receptor (OX1R). Dysfunction of the OX1R may induce the occurrence of RBD. Here, we determined the role of the interaction between α-Synuclein and OX1R in the pathogenesis of RBD, in vitro and in vivo. We found that injection of α-Synuclein into the lateral hypothalamus area (LHA) damaged orexin neurons and induced the RBD-like sleep pattern, to further damage dopaminergic neurons and result in locomotor dysfunction in mice. α-Synuclein interacted with OX1R, promoting the degradation of OX1R through proteasomal and lysosomal pathways. In addition, overexpression of α-Synuclein downregulated OX1R-mediated signaling, subsequently leading to orexin neuron damage. We conclude that α-Synuclein induced the occurrence of RBD via interaction with OX1R and modulated its degradation. These findings provide evidence for a novel mechanism by which the association of α-Synuclein with OX1R was attributed to α-Synuclein-induced orexin neuron damage, which may be a new molecular target for an effective therapeutic strategy for RBD pathology.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bae, E. J., Choi, M., Kim, J. T., Kim, D. K., Jung, M. K., Kim, C., Kim, T. K., Lee, J. S., Jung, B. C., Shin, S. J., Rhee, K. H., & Lee, S. J. (2022). TNF-α promotes α-synuclein propagation through stimulation of senescence-associated lysosomal exocytosis. Experimental and Molecular Medicine, 54(6), 788–800.
Baimel, C., Lau, B. K., Qiao, M., & Borgland, S. L. (2017). Projection-target-defined effects of orexin and dynorphin on VTA dopamine neurons. Cell Reports, 18(6), 1346–1355.
Bjørnarå, K. A., Pihlstrøm, L., Dietrichs, E., & Toft, M. (2018). Risk variants of the α-synuclein locus and REM sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson’s disease: a genetic association study. BMC Neurology, 18(1), 15.
Blanco-Centurion, C., Luo, S., Spergel, D. J., Vidal-Ortiz, A., Oprisan, S. A., Van den Pol, A. N., Liu, M., & Shiromani, P. J. (2019). Dynamic network activation of hypothalamic MCH neurons in REM sleep and exploratory behavior. Journal of Neuroscience, 39(25), 4986–4998.
Blanco-Centurion, C., Bendell, E., Zou, B., Sun, Y., Shiromani, P. J., & Liu, M. (2018). VGAT and VGLUT2 expression in MCH and orexin neurons in double transgenic reporter mice. IBRO Reports, 4, 44–49.
Boeve, B. F., Silber, M. H., Ferman, T. J., Lucas, J. A., & Parisi, J. E. (2001). Association of REM sleep behavior disorder and neurodegenerative disease may reflect an underlying synucleinopathy. Movement Disorder, 16(4), 622–630.
Brewer, G. J. (1997). Isolation and culture of adult rat hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 71(2), 143–155.
Chang, X., Zhao, Y., Ju, S., & Guo, L. (2015). Orexin-A regulates cell apoptosis in human H295R adrenocortical cells via orexin receptor type 1 through the AKT signaling pathway. Molecular Medicine Reports, 12(5), 7582–7588.
Chen, K. S., Xu, M., Zhang, Z., Chang, W. C., Gaj, T., Schaffer, D. V., & Dan, Y. (2018). A hypothalamic switch for REM and non-REM sleep. Neuron, 97(5), 1168-1176.e4.
Danieli, A., & Martens, S. (2018). p62-mediated phase separation at the intersection of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy. Journal of Cell Science, 131(19), 15.
Di Maio, R., Barrett, P. J., Hoffman, E. K., Barrett, C. W., Zharikov, A., Borah, A., Hu, X., McCoy, J., Chu, C. T., Burton, E. A., Hastings, T. G., & Greenamyre, J. T. (2016). α-Synuclein binds to TOM20 and inhibits mitochondrial protein import in Parkinson’s disease. Science Translational Medicine, 8(342), 58.
Doppler, K., Mammadova, S., Kuzkina, A., Reetz, K., Michels, J., Hermann, W., Sommerauer, M., Volkmann, J., Oertel, W. H., Janzen, A., & Sommer, C. (2022). Association between probable REM sleep behavior disorder and increased dermal alpha-synuclein deposition in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, 99, 58–61.
Feng, H., Wen, S. Y., Qiao, Q. C., Pang, Y. J., Wang, S. Y., Li, H. Y., Cai, J., Zhang, K. X., Chen, J., Hu, Z. A., Luo, F. L., Wang, G. Z., Yang, N., & Zhang, J. (2020). Orexin signaling modulates synchronized excitation in the sublaterodorsal tegmental nucleus to stabilize REM sleep. Nature Communications, 11(1), 3661.
Fronczek, R., Overeem, S., Lee, S. Y. Y., Hegeman, I. M., van Pelt, J., van Duinen, S. G., Lammers, G. J., & Swaab, D. F. (2007). Hypocretin (orexin) loss in Parkinson’s disease. Brain, 130(6), 1577–1585.
Hu, Y., Yu, S. Y., Zuo, L. J., Cao, C. J., Wang, F., Chen, Z. J., Du, Y., Lian, T. H., Wang, Y. J., Chan, P., Chen, S. D., Wang, X. M., & Zhang, W. (2015). Parkinson disease with REM sleep behavior disorder: Features, alpha-synuclein, and inflammation. Neurology, 84(9), 888–894.
Hungs, M., & Mignot, E. (2001). Hypocretin/orexin, sleep and narcolepsy. BioEssays, 23(5), 397–408.
Ip, C. W., Klaus, L. C., Karikari, A. A., Visanji, N. P., Brotchie, J. M., Lang, A. E., Volkmann, J., & Koprich, J. B. (2017). AAV1/2-induced overexpression of A53T-α-synuclein in the substantia nigra results in degeneration of the nigrostriatal system with Lewy-like pathology and motor impairment: A new mouse model for Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathologica Communications, 5(1), 11.
Iranzo, A. (2018). The REM sleep circuit and how its impairment leads to REM sleep behavior disorder. Cell and Tissue Research, 373(1), 245–266.
Iranzo, A., Stockner, H., Serradell, M., Seppi, K., Valldeoriola, F., Frauscher, B., Molinuevo, J. L., Vilaseca, I., Mitterling, T., Gaig, C., Vilas, D., Santamaria, J., Högl, B., Tolosa, E., & Poewe, W. (2014). Five-year follow-up of substantia nigra echogenicity in idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorder. Movement Disorder, 29(14), 1774–1780.
Iranzo, A., Tolosa, E., Gelpi, E., Molinuevo, J. L., Valldeoriola, F., Serradell, M., Sanchez-Valle, R., Vilaseca, I., Lomeña, F., Vilas, D., Ladó, A., Gaig, C., & Santamaria, J. (2013). Neurodegenerative disease status and post-mortem pathology in idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: An observational cohort study. The Lancet Neurology, 12(5), 443–453.
Ivins, J. K., Colognato, H., Kreidberg, J. A., Yurchenco, P. D., & Lander, A. D. (1998). Neuronal receptors mediating responses to antibodyactivated laminin-1. Journal of Neuroscience, 18(23), 9703–9715.
Izawa, S., Chowdhury, S., Miyazaki, T., Mukai, Y., Ono, D., Inoue, R., Ohmura, Y., Mizoguchi, H., Kimura, K., Yoshioka, M., Terao, A., Kilduff, T. S., & Yamanaka, A. (2019). REM sleep-active MCH neurons are involved in forgetting hippocampus-dependent memories. Science, 365(6459), 1308–1313.
Jaeger, W. C., Seeber, R. M., Eidne, K. A., & Pfleger, K. D. G. (2014). Molecular determinants of orexin receptor-arrestin-ubiquitin complex formation. British Journal of Pharmacology, 171(2), 364–374.
Ju, S. J., Zhao, Y., Chang, X., & Guo, L. (2014). Orexin A protects cells from apoptosis by regulating FoxO1 and mTORC1 through the OX1R/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in hepatocytes. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 34(1), 153–159.
Korotkova, T. M., Sergeeva, O. A., Eriksson, K. S., Haas, H. L., & Brown, R. E. (2003). Excitation of ventral tegmental area dopaminergic and nondopaminergic neurons by orexins/hypocretins. Journal of Neuroscience, 23(1), 7–11.
Lee, H. J. (2005). Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of α-synuclein and its aggregates. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(25), 6016–6024.
Li, M. M., Madara, J. C., Steger, J. S., Krashes, M. J., Balthasar, N., Campbell, J. N., Resch, J. M., Conley, N. J., Garfield, A. S., & Lowell, B. B. (2019). The paraventricular hypothalamus regulates satiety and prevents obesity via two genetically distinct circuits. Neuron, 102(3), 653-667.e6.
Liu, W. J., Ye, L., Huang, W. F., Guo, L. J., Xu, Z. G., Wu, H. L., Yang, C., & Liu, H. F. (2016). p62 links the autophagy pathway and the ubiqutin–proteasome system upon ubiquitinated protein degradation. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 21(1), 15.
Lu, J., Sherman, D., Devor, M., & Saper, C. B. (2006). A putative flip–flop switch for control of REM sleep. Nature, 441(7093), 589–594.
Luk, K. C., Kehm, V., Carroll, J., Zhang, B., O’Brien, P., Trojanowski, J. Q., & Lee, V. M. (2012). Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science, 338(6109), 949–953.
Luppi, P., Clement, O., Sapin, E., Peyron, C., Gervasoni, D., Léger, L., & Fort, P. (2012). Brainstem mechanisms of paradoxical (REM) sleep generation. Pflügers Archiv, 463(1), 43–52.
Luppi, P., Peyron, C., & Fort, P. (2013). Role of MCH neurons in paradoxical (REM) sleep control. Sleep, 36(12), 1775–1776.
Mavanji, V., Georgopoulos, A. P., & Kotz, C. M. (2022). Orexin enhances neuronal synchronization in adult rat hypothalamic culture: A model to study hypothalamic function. Journal of Neurophysiology, 127(5), 1221–1229.
Miglis, M. G., Adler, C. H., Antelmi, E., Arnaldi, D., Baldelli, L., Boeve, B. F., Cesari, M., Dall’Antonia, I., Diederich, N. J., Doppler, K., Dušek, P., Ferri, R., Gagnon, J., Gan-Or, Z., Hermann, W., Högl, B., Hu, M. T., Iranzo, A., Janzen, A., … Oertel, W. H. (2021). Biomarkers of conversion to α-synucleinopathy in isolated rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder. The Lancet Neurology, 20(8), 671–684.
Ohayon, M. M., Caulet, M., & Priest, R. G. (1997). Violent behavior during sleep. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 58(8), 369–376.
Overeem, S., Scammell, T. E., & Lammers, G. J. (2002). Hypocretin/orexin and sleep: Implications for the pathophysiology and diagnosis of narcolepsy. Current Opinion in Neurology, 15(6), 739–745.
Parmeggiani, P. L., Azzaroni, A., & Calasso, M. (1998). A pontine-hypothalamic temperature difference correlated with cutaneous and respiratory heat loss. Respiration Physiology, 114(1), 49–56.
Pasban-Aliabadi, H., Esmaeili-Mahani, S., & Abbasnejad, M. (2017). Orexin-A protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity: Involvement of PKC and PI3K signaling pathways. Rejuvenation Research, 20(2), 125–133.
Perez-Bonilla, P., Santiago-Colon, K., & Leinninger, G. M. (2020). Lateral hypothalamic area neuropeptides modulate ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons and feeding. Physiology & Behavior, 223, 112986.
Poewe, W., Seppi, K., Tanner, C. M., Halliday, G. M., Brundin, P., Volkmann, J., Schrag, A., & Lang, A. E. (2017). Parkinson disease. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 3(1), 15.
Postuma, R. B., Iranzo, A., Hu, M., Högl, B., Boeve, B. F., Manni, R., Oertel, W. H., Arnulf, I., Ferini-Strambi, L., Puligheddu, M., Antelmi, E., Cochen De Cock, V., Arnaldi, D., Mollenhauer, B., Videnovic, A., Sonka, K., Jung, K., Kunz, D., Dauvilliers, Y., … Pelletier, A. (2019). Risk and predictors of dementia and parkinsonism in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder: A multicentre study. Brain, 142(3), 744–759.
Postuma, R. B., Poewe, W., Litvan, I., Lewis, S., Lang, A. E., Halliday, G., Goetz, C. G., Chan, P., Slow, E., Seppi, K., Schaffer, E., Rios-Romenets, S., Mi, T., Maetzler, C., Li, Y., Heim, B., Bledsoe, I. O., & Berg, D. (2018). Validation of the MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorder, 33(10), 1601–1608.
Roberts, H., & Brown, D. (2015). Seeking a mechanism for the toxicity of oligomeric α-synuclein. Biomolecules, 5(2), 282–305.
Schenck, C. H., Boeve, B. F., & Mahowald, M. W. (2013). Delayed emergence of a parkinsonian disorder or dementia in 81% of older men initially diagnosed with idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: A 16-year update on a previously reported series. Sleep Medicine, 14(8), 744–748.
Shen, Y., Yu, W., Shen, B., Dong, H., Zhao, J., Tang, Y., Fan, Y., Yang, Y., Sun, Y., Luo, S., Chen, C., Liu, F., Wu, J., Xiao, B., Yu, H., Koprich, J. B., Huang, Z., & Wang, J. (2020). Propagated α-synucleinopathy recapitulates REM sleep behaviour disorder followed by parkinsonian phenotypes in mice. Brain, 143(11), 3374–3392.
Simitsi, A. M., Koros, C., Stamelou, M., Papadimitriou, D., Leonardos, A., Bougea, A., Papagiannakis, N., Pachi, I., Angelopoulou, E., Lourentzos, K., Bonakis, A., & Stefanis, L. (2021). REM sleep behavior disorder and other sleep abnormalities in p A53T SNCA mutation carriers. Sleep, 44(5), 15.
Stanojlovic, M., Pallais Yllescas, J. P., & Jr., Mavanji V., Kotz C. (2019). Chemogenetic activation of orexin/hypocretin neurons ameliorates aging-induced changes in behavior and energy expenditure. American Journal of Physiology, 316(5), R571–R583.
Stefani, A., Iranzo, A., Holzknecht, E., Perra, D., Bongianni, M., Gaig, C., Heim, B., Serradell, M., Sacchetto, L., Garrido, A., Capaldi, S., Sánchez-Gómez, A., Cecchini, M. P., Mariotto, S., Ferrari, S., Fiorini, M., Schmutzhard, J., Cocchiara, P., Vilaseca, I., … Zanusso, G. (2021). Alpha-synuclein seeds in olfactory mucosa of patients with isolated REM sleep behaviour disorder. Brain, 144(4), 1118–1126.
Stefanova, N., Schanda, K., Klimaschewski, L., Poewe, W., Wenning, G. K., & Reindl, M. (2003). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced cell death in U373 cells overexpressing alpha-synuclein. J Neuroscience Research, 73(3), 334–340.
Taguchi, T., Ikuno, M., Hondo, M., Parajuli, L. K., Taguchi, K., Ueda, J., Sawamura, M., Okuda, S., Nakanishi, E., Hara, J., Uemura, N., Hatanaka, Y., Ayaki, T., Matsuzawa, S., Tanaka, M., El-Agnaf, O. M. A., Koike, M., Yanagisawa, M., Uemura, M. T., … Takahashi, R. (2020). α-Synuclein BAC transgenic mice exhibit RBD-like behaviour and hyposmia: A prodromal Parkinson’s disease model. Brain, 143(1), 249–265.
Tsunematsu, T., Ueno, T., Tabuchi, S., Inutsuka, A., Tanaka, K. F., Hasuwa, H., Kilduff, T. S., Terao, A., & Yamanaka, A. (2014). Optogenetic manipulation of activity and temporally controlled cell-specific ablation reveal a role for MCH neurons in sleep/wake regulation. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(20), 6896–6909.
Wang, C. M., Yang, C. Q., Cheng, B. H., Chen, J., & Bai, B. (2018). Orexin-A protects SH-SY5Y cells against H2O2-induced oxidative damage via the PI3K/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology, 32, 2058738418785739.
Weil, R. S., & Morris, H. R. (2019). REM sleep behaviour disorder: An early window for prevention in neurodegeneration? Brain, 142(3), 498–501.
Wong, J. C., Li, J., Pavlova, M., Chen, S., Wu, A., Wu, S., & Gao, X. (2016). Risk factors for probable REM sleep behavior disorder: A community-based study. Neurology, 86(14), 1306–1312.
Yamanaka, A., Tabuchi, S., Tsunematsu, T., Fukazawa, Y., & Tominaga, M. (2010). Orexin directly excites orexin neurons through orexin 2 receptor. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(38), 12642–12652.
Zhan, S., Che, P., Zhao, X. K., Li, N., Ding, Y., Liu, J., Li, S., Ding, K., Han, L., Huang, Z., Wu, L., Wang, Y., Hu, M., Han, X., & Ding, Q. (2019). Molecular mechanism of tumour necrosis factor alpha regulates hypocretin (orexin) expression, sleep and behaviour. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 23(10), 6822–6834.
Zhang, L., Okada, T., Badawy, S. M. M., Hirai, C., Kajimoto, T., & Nakamura, S. (2017). Extracellular α-synuclein induces sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor subtype 1 uncoupled from inhibitory G-protein leaving β-arrestin signal intact. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 256.
Zhang, Y., Fan, J., Gu, L., Yang, H., Zhan, S., & Zhang, H. (2021). Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 inhibits α-synuclein-induced microglia inflammation to protect from neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 18(1), 58.
Acknowledgements
We thank International Science Editing ( http://www.internationalscienceediting.com ) for editing this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (81972231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HZ and LG conceived and designed research. JKF and MCW conducted experiments. JKF, MCW, and LG analyzed data. HZ and LG wrote the manuscript; HMY and JNZ revised the manuscript. HZ acquired the funding and financial support for the project. All authors read and approved the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical Approval
This study was reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of Capital Medical University (2019SY040). Written informed consent from all subjects was obtained. All animals experiments protocols were approved by the Committee on Animal Care and Usage of Capital Medical University (AEEI-2020-141).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, J.K., Wang, M.C., Yang, H.M. et al. α-Synuclein Induced the Occurrence of RBD via Interaction with OX1R and Modulated Its Degradation. Neuromol Med 25, 286–300 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-023-08735-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-023-08735-4