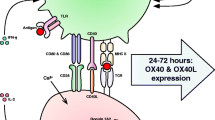
Abstract
Immunoglobulins are proteins with a highly variable antigen-binding domain and a constant region (Fc domain) that binds to a cell surface receptor (FcR). Activation of FcRs in immune cells (lymphocytes, macrophages, and mast cells) triggers effector responses including cytokine production, phagocytosis, and degranulation. In addition to their roles in normal responses to infection or tissue injury, and in immune-related diseases, FcRs are increasingly recognized for their involvement in neurological disorders. One or more FcRs are expressed in microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons. Aberrant activation of FcRs in such neural cells may contribute to the pathogenesis of major neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, ischemic stroke, and multiple sclerosis. On the other hand, FcRs may play beneficial roles in counteracting pathological processes; for e.g., FcRs may facilitate removal of amyloid peptides from the brain and so protect against Alzheimer’s disease. Knowledge of the functions of FcRs in the nervous system in health and disease is leading to novel preventative and therapeutic strategies for stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurological disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson, J., & Pecht, I. (2007). Regulation of the mast cell response to the type 1 Fc epsilon receptor. Immunological Reviews, 217, 231–254.
Akilesh, S., et al. (2008). Podocytes use FcRn to clear IgG from the glomerular basement membrane. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 967–972.
Akiyama, H., et al. (2000). Cell mediators of inflammation in the Alzheimer disease brain. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 14, S47–S53.
Alliot, F., et al. (1999). Microglia derive from progenitors, originating from the yolk sac, and which proliferate in the brain. Brain Research. Developmental Brain Research, 117, 145–152.
Amir-Moazami, O., et al. (2008). Phospholipid scramblase 1 modulates a selected set of IgE receptor-mediated mast cell responses through LAT-dependent pathway. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283, 25514–25523.
Andersson, J., et al. (2005). Intravenous immune globulin affects cytokine production in T lymphocytes and monocytes/macrophages. Clinical And Experimental Medicine, 5, 135–140.
Andoh, T., & Kuraishi, Y. (2004a). Direct action of immunoglobulin G on primary sensory neurons through Fc gamma receptor I. FASEB Journal, 18, 182–184.
Andoh, T., & Kuraishi, Y. (2004b). Expression of Fc epsilon receptor I on primary sensory neurons in mice. Neuroreport, 15, 2029–2031.
Appel, S., et al. (1992). Nigral damage and dopaminergic hypofunction in mesencephalon-immunized guinea pigs. Annals of Neurology, 32, 494–501.
Arumugam, T. V., et al. (2005). Stroke and T-cells. Neuromolecular Medicine, 7, 229–242.
Arumugam, T. V., et al. (2006). Gamma secretase-mediated notch signaling worsens brain damage and functional outcome in ischemic stroke. Nature Medicine, 12, 621–623.
Arumugam, T. V., et al. (2007). Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) protects the brain against experimental stroke by preventing complement-mediated neuronal cell death. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 14104–14109.
Arumugam, T. V., et al. (2009). Neuroprotection in stroke by complement inhibition and immunoglobulin therapy. Neuroscience, 158, 1074–1089.
Bacskai, B. J., et al. (2002). Non-Fc-mediated mechanisms are involved in clearance of amyloid-beta in vivo by immunotherapy. Journal of Neuroscience, 22, 7873–7878.
Baerenwaldt, A., & Nimmerjahn, F. (2008). Immune regulation: FcgammaRIIB–regulating the balance between protective and autoreactive immune responses. Immunology and Cell Biology, 86, 482–484.
Bard, F., et al. (2000). Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid beta-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nature Medicine, 6, 916–919.
Bard, F., et al. (2003). Epitope and isotype specificities of antibodies to beta -amyloid peptide for protection against Alzheimer’s disease-like neuropathology. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 2023–2028.
Bayry, J., et al. (2007). Monoclonal antibody and intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for rheumatic diseases: Rationale and mechanisms of action. Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology, 3, 262–272.
Beard, C. M., et al. (1998). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and Alzheimer’s disease: A case–control study in Rochester, Minnesota, 1980 through 1984. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 73, 951–955.
Bernstein, J. J., et al. (1993). Sequestering of immunoglobulins by astrocytes after cortical lesion and homografting of fetal cortex. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 11, 117–124.
Bracke, M., et al. (1998). Analysis of signal transduction pathways regulating cytokine-mediated Fc receptor activation on human eosinophils. Journal of Immunology, 161, 6768–6774.
Brauweiler, A. M., & Cambier, J. C. (2003). Fc gamma RIIB activation leads to inhibition of signalling by independently ligated receptors. Biochemical Society Transactions, 31, 281–285.
Breckwoldt, M. O., et al. (2008). Tracking the inflammatory response in stroke in vivo by sensing the enzyme myeloperoxidase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 18584–18589.
Bruhns, P., et al. (2000). Molecular basis of the recruitment of the SH2 domain-containing inositol 5-phosphatases SHIP1 and SHIP2 by fcgamma RIIB. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 37357–37364.
Chen, S., et al. (1998). Experimental destruction of substantia nigra initiated by Parkinson disease immunoglobulins. Archives of Neurology, 55, 1075–1080.
Coggeshall, K. M. (2002). Regulation of signal transduction by the Fc gamma receptor family members and their involvement in autoimmunity. Current Directions in Autoimmunity, 5, 1–29.
Cote-Vélez, M. J., et al. (1999). Low affinity Fc gamma receptors on murine macrophages: Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and AP-1 DNA binding activity. Immunology Letters, 67, 251–255.
Cox, D., & Greenberg, S. (2001). Phagocytic signaling strategies: Fc(gamma)receptor-mediated phagocytosis as a model system. Seminars in Immunology, 13, 339–345.
Dahlström, A., et al. (1990). Investigations on auto-antibodies in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, using defined neuronal cultures. Journal of Neural Transmission, 29, 195–206.
Das, P., et al. (2003). Amyloid-beta immunization effectively reduces amyloid deposition in FcRgamma−/− knock-out mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 8532–8538.
Davis, R. S., et al. (2001). Identification of a family of Fc receptor homologs with preferential B cell expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 9772–9777.
Davis, R. S., et al. (2002). Fc receptor homologs: Newest members of a remarkably diverse Fc receptor gene family. Immunological Reviews, 190, 123–136.
Deane, R., et al. (2005). IgG-assisted age-dependent clearance of Alzheimer’s amyloid beta peptide by the blood–brain barrier neonatal Fc receptor. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 11495–11503.
Deane, R., et al. (2009). Clearance of amyloid-beta peptide across the blood–brain barrier: Implication for therapies in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets, 8, 16–30.
Dessaint, J. P., & Capron, A. (1990). Fc epsilon receptor II-positive macrophages and platelets: Potent effector cells in allergy and defence against helminth parasites. Springer Seminars in Immunopathology, 12, 349–363.
Dierks, S. E., et al. (1993). The oligomeric nature of the murine Fc epsilon RII/CD23. Implications for function. Journal of Immunology, 150, 2372–2382.
Ebel, C., et al. (2001). Signal transduction via both human low-affinity IgG Fc receptors, Fc gamma RIIa and Fc gamma RIIIb, depends on the activity of different families of intracellular kinases. Immunobiology, 203, 616–628.
Falsig, J., et al. (2008). Molecular basis for detection of invading pathogens in the brain. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 86, 1434–1447.
Frangione, B., & Wolfenstein-Todel, C. (1972). Partial duplication in the “hinge” region of IgA 1 myeloma proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 69, 3673–3676.
Galon, J., et al. (1996). Soluble Fcgamma receptor type III (FcgammaRIII, CD16) triggers cell activation through interaction with complement receptors. Journal of Immunology, 157, 1184–1192.
Goldstein, B., et al. (2002). Modeling the early signaling events mediated by FcepsilonRI. Molecular Immunology, 38, 1213–1219.
Gould, H. J., & Sutton, B. J. (2008). IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nature Reviews Immunology, 8, 205–217.
Grant, J. A., et al. (1997). High-affinity IgE receptor Fc epsilon RI expression in allergic reactions. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 113, 376–378.
Gu, H., et al. (2001). Essential role for Gab2 in the allergic response. Nature, 412, 186–190.
Haberman, F., et al. (2007). Soluble neuroprotective antioxidant uric acid analogs ameliorate ischemic brain injury in mice. Neuromolecular Medicine, 9, 315–323.
He, Y., et al. (2002). Role of Fcgamma receptors in nigral cell injury induced by Parkinson disease immunoglobulin injection into mouse substantia nigra. Experimental Neurology, 176, 322–327.
Heyman, B. (2000). Regulation of antibody responses via antibodies, complement, and Fc receptors. Annual Review of Immunology, 18, 709–737.
Hill, J. M., et al. (1985). Transferrin receptors in rat brain: Neuropeptide-like pattern and relationship to iron distribution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 82, 4553–4557.
Hirsch, E. C., & Hunot, S. (2009). Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: A target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurology, 8, 382–397.
Holtzman, D. M., et al. (2002). Abeta immunization and anti-Abeta antibodies: Potential therapies for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 54, 1603–1613.
Huang, Z. Y., et al. (2003). The effect of phosphatases SHP-1 and SHIP-1 on signaling by the ITIM- and ITAM-containing Fcgamma receptors FcgammaRIIB and FcgammaRIIA. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 73, 823–829.
Hulse, K. E., & Woodfolk, J. A. (2008). Targeting allergen to Fc gammaRI: A strategy to treat allergic disease? Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 8, 547–552.
Hunot, S., et al. (1999). FcepsilonRII/CD23 is expressed in Parkinson’s disease and induces, in vitro, production of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in glial cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 19, 3440–3447.
Ishikawa, M., et al. (2005). CD40/CD40 ligand signaling in mouse cerebral microvasculature after focal ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation, 111, 1690–1696.
Ivashkiv, L. B. (2009). Cross-regulation of signaling by ITAM-associated receptors. Nature Immunology, 10, 340–347.
Jabril-Cuenod, B., et al. (1996). Sykdependent phosphorylation of Shc: A potential link between FcepsilonRI and the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway through SOS and Grb2. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 16268–16272.
Jakus, Z., et al. (2009). Critical role of phospholipase Cgamma2 in integrin and Fc receptor-mediated neutrophil functions and the effector phase of autoimmune arthritis. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 206, 577–593.
Jin, C. Y., et al. (2006). Piceatannol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB-related proinflammatory mediators in BV2 microglia. Pharmacological Research, 54, 461–467.
Johnson, S. A., et al. (1995). Phosphorylated immunoreceptor signaling motifs (ITAMs) exhibit unique abilities to bind and activate Lyn and Syk tyrosine kinases. Journal of Immunology, 155, 4596–4603.
Johnson, S., et al. (1996). Perforant path transection induces complement C9 deposition in hippocampus. Experimental Neurology, 138, 198–205.
Joshi, T., et al. (2006). Molecular analysis of expression and function of hFcgammaRIIbl and b2 isoforms in myeloid cells. Molecular Immunology, 43, 839–850.
Kaur, C., & Ling, E. A. (1999). Increased expression of transferrin receptors and iron in amoeboid microglial cells in postnatal rats following an exposure to hypoxia. Neuroscience Letters, 262, 183–186.
Kimata, H. (2007). Specific allergen enhances IgE production via galectin-3 in surface IgE+ B cells. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 37, 1001–1002.
Kitaura, J., et al. (2000). Akt-dependent cytokine production in mast cells. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 192, 729–740.
Komine-Kobayashi, M., et al. (2004). Dual role of Fcgamma receptor in transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke, 35, 958–963.
Kopeć, A., Panaszek, B., & Fal, A. M. (2006). Intracellular signaling pathways in IgE-dependent mast cell activation. Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis, 54, 393–401.
Lakshmi Tamma, S. M., et al. (2001). IgD receptor-mediated signal transduction in T cells. Cellular Immunology, 207, 110–117.
Lalancette-Hébert, M., et al. (2007). Selective ablation of proliferating microglial cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 2596–2605.
Lang, M. L., & Kerr, M. A. (2000). Characterization of FcalphaR-triggered Ca(2+) signals: Role in neutrophil NADPH oxidase activation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 276, 749–755.
Le, W. D., et al. (1995). Experimental autoimmune nigral damage in guinea pigs. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 57, 45–53.
Le, W. D., et al. (1999). Effects of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Parkinson disease on dopaminergic cells. Archives of Neurology, 56, 194–200.
Lees, A. J., et al. (2009). Parkinson’s disease. Lancet, 373, 2055–2066.
Levites, Y., et al. (2006). Insights into the mechanisms of action of anti-Abeta antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. FASEB Journal, 20, 2576–2578.
Li, Y. N., et al. (2008). Alterations of Fc gamma receptor I and Toll-like receptor 4 mediate the antiinflammatory actions of microglia and astrocytes after adrenaline-induced blood–brain barrier opening in rats. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 86, 3556–3565.
Liesz, A., et al. (2009). Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nature Medicine, 15, 192–199.
Loughlin, A. J., et al. (1992). Regulation of Fc receptor and major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on isolated rat microglia by tumour necrosis factor, interleukin-1 and lipopolysaccharide: Effects on interferon-gamma induced activation. Immunology, 75, 170–175.
Loughlin, A. J., et al. (1993). Modulation of interferon-gamma-induced major histocompatibility complex class II and Fc receptor expression on isolated microglia by transforming growth factor-beta 1, interleukin-4, noradrenaline and glucocorticoids. Immunology, 79, 125–130.
Love, S. (1999). Oxidative stress in brain ischemia. Brain Pathology, 9, 119–131.
Lyden, T. W., et al. (2001). The Fc receptor for IgG expressed in the villus endothelium of human placenta is Fc gamma RIIb2. Journal of Immunology, 166, 3882–3889.
Ma, Y., et al. (2006). Toll-like receptor 8 functions as a negative regulator of neurite outgrowth and inducer of neuronal apoptosis. Journal of Cell Biology, 175, 209–215.
Malbec, O., et al. (2002). Negative regulation of mast cell proliferation by FcgammaRIIB. Molecular Immunology, 38, 1295–1299.
Manetz, T. S., et al. (2001). Vav1 regulates phospholipase cgamma activation and calcium responses in mast cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 21, 3763–3774.
Mangin, P., et al. (2003). Signaling role for phospholipase C gamma 2 in platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha calcium flux and cytoskeletal reorganization. Involvement of a pathway distinct from FcR gamma chain and Fc gamma RIIA. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 32880–32891.
Mash, D. C., et al. (1990). Characterization and distribution of transferrin receptors in the rat brain. Journal of Neurochemistry, 55, 1972–1979.
Mattson, M. P. (2004). Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature, 430, 631–639.
McGeer, P. L., et al. (2006). Inflammation, anti-inflammatory agents and Alzheimer disease: The last 12 years. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 9, 271–276.
McRae-Degueurce, A., et al. (1988). Immunocytochemical investigations on the presence of neuron-specific antibodies in the CSF of Parkinson’s disease cases. Neurochemical Research, 13, 679–684.
Mélik-Parsadaniantz, S., & Rostène, W. (2008). Chemokines and neuromodulation. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 198, 62–68.
Merrill, J. E., et al. (1980a). A T lymphocyte subpopulation in multiple sclerosis patients bearing Fc receptors for both IgG and IgM1. Journal of Immunology, 124, 2758–2764.
Merrill, J. E., et al. (1980b). Identification of three FcR-positive T cell subsets (T gamma, T mu and T gamma mu) in the cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 42, 345–354.
Mina-Osorio, P., & Ortega, E. (2004). Signal regulators in FcR-mediated activation of leukocytes? Trends in Immunology, 25, 529–535.
Minskoff, S. A., et al. (1998). Fc gamma RII-B1 regulates the presentation of B cell receptor-bound antigens. Journal of Immunology, 161, 2079–2083.
Mohamed, H. A., et al. (2002). Immunoglobulin Fc gamma receptor promotes immunoglobulin uptake, immunoglobulin-mediated calcium increase, and neurotransmitter release in motor neurons. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 69, 110–116.
Monteiro, R. C., & Van De Winkel, J. G. (2003). IgA Fc receptors. Annual Review of Immunology, 21, 177–204.
Moos, T., et al. (1999). Iron-independent neuronal expression of transferrin receptor mRNA in the rat. Brain Research. Developmental Brain Research, 72, 231–234.
Moura, I. C., et al. (2001). Identification of the transferrin receptor as a novel immunoglobulin (Ig)A1 receptor and its enhanced expression on mesangial cells in IgA nephropathy. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 194, 417–425.
Mukhopadhyay, S., et al. (2001). Bruton’s tyrosine kinase associates with the actin-based cytoskeleton in activated platelets. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 81, 659–665.
Muraille, E., et al. (2000). The SH2 domain containing inositol 5-phosphatase SHIP2 associates to the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif of Fc gammaRIIB in B cells under negative signaling. Immunology Letters, 72, 7–15.
Nakahara, J., & Aiso, S. (2006). Fc receptor-positive cells in remyelinating multiple sclerosis lesions. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 65, 582–591.
Nakahara, J., et al. (2003a). Signaling via immunoglobulin Fc receptors induces oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation. Developmental Cell, 4, 841–852.
Nakahara, J., et al. (2003b). Expression of Fc receptor for immunoglobulin M in oligodendrocytes and myelin of mouse central nervous system. Neuroscience Letters, 337, 73–76.
Nakamura, T., et al. (1993). Characterization of an IgM Fc-binding receptor on human T cells. Journal of Immunology, 151, 6933–6941.
Nakamura, K., et al. (2007). CD3 and immunoglobulin G Fc receptor regulate cerebellar functions. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 27, 5128–5134.
Nimmerjahn, F., & Ravetch, J. V. (2008). Fcgamma receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nature Reviews Immunology, 8, 34–47.
Nimmerjahn, F., et al. (2005). FcgammaRIV: A novel FcR with distinct IgG subclass specificity. Immunity, 23, 41–51.
Ninomiya, N., et al. (1994). Involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in Fc gamma receptor signaling. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269, 22732–22737.
Nishizumi, H., & Yamamoto, Y. (1997). Impaired tyrosine phosphorylation and Ca2+ mobilization, but not degranulation, in Lyn-deficient bone marrow-derived mast cells. Journal of Immunology, 158, 2350–2355.
Nitta, T., et al. (1992). Expression of Fc gamma receptors on astroglial cell lines and their role in the central nervous system. Neurosurgery, 31, 83–87.
Ohno, T., et al. (1990). Biochemical nature of an Fc mu receptor on human B-lineage cells. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 172, 1165–1175.
Okun, E., et al. (2009). Toll-like receptors in neurodegeneration. Brain Research Reviews, 59, 278–292.
Olivera, A., et al. (2006). IgE-dependent activation of sphingosine kinases 1 and 2 and secretion of sphingosine 1-phosphate requires Fyn kinase and contributes to mast cell responses. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 2515–2525.
Orita, T., et al. (1990). Transferrin receptors in injured brain. Acta Neuropathologica, 79, 686–688.
Orr, C. F., et al. (2005). A possible role for humoral immunity in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Brain, 128, 2665–2674.
Ouadrhiri, Y., et al. (2002). Effect of IgA on respiratory burst and cytokine release by human alveolar macrophages: Role of ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-kappaB. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 26, 315–332.
Pardridge, W. M., et al. (1987). Human blood–brain barrier transferrin receptor. Metabolism, 36, 892–895.
Park, R. K., et al. (1999). Role of Src in the modulation of multiple adaptor proteins in FcalphaRI oxidant signaling. Blood, 94, 2112–2120.
Peress, N. S., et al. (1993). Identification of Fc gamma RI, II and III on normal human brain ramified microglia and on microglia in senile plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 48, 71–79.
Perry, V. H., et al. (1985). Immunohistochemical localization of macrophages and microglia in the adult and developing mouse brain. Neuroscience, 15, 313–326.
Rakover, I., et al. (2007). Immunotherapy against APP beta-secretase cleavage site improves cognitive function and reduces neuroinflammation in Tg2576 mice without a significant effect on brain abeta levels. Neurodegenerative Diseases, 4, 392–402.
Ravetch, J. V., & Bolland, S. (2001). IgG Fc receptors. Annual Review of Immunology, 19, 275–290.
Ravetch, J. V., et al. (2001). Anti-inflammatory activity of IVIG mediated through the inhibitory Fc receptor. Science, 291, 484–486.
Renedo, M. A., et al. (2001). FcgammaRIIA exogenously expressed in HeLa cells activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by a mechanism dependent on the endogenous expression of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk. European Journal of Immunology, 31, 1361–1369.
Rivera, J., et al. (2008). New insights on mast cell activation via the high affinity receptor for IgE. Advances in Immunology, 98, 85–120.
Robbie-Ryan, M., et al. (2003). Cutting edge: Both activating and inhibitory Fc receptors expressed on mast cells regulate experimental allergic encephalomyelitis disease severity. Journal of Immunology, 170, 1630–1634.
Roccatello, D., Quattrocchio, G., Cacace, G., Coppo, R., Sena, L. M., et al. (1993). Removal systems of immunoglobulin A and immunoglobulin A containing complexes in IgA nephropathy and cirrhosis patients. The role of asialoglycoprotein receptors. Laboratory Investigation, 69, 714–723.
Roopenian, D. C., & Akilesh, S. (2007). FcRn: The neonatal Fc receptor comes of age. Nature Reviews Immunology, 7, 715–725.
Rose, D. M., et al. (1997). Interferon-gamma and transforming growth factor-beta modulate the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production induced by Fc gamma-receptor stimulation in murine macrophages. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 238, 256–260.
Sada, K., & Yamamura, H. (2003). Protein-tyrosine kinases and adaptor proteins in FcepsilonRI-mediated signaling in mast cells. Current Molecular Medicine, 3, 85–94.
Scali, C. (2000). Brain inflammatory reaction in an animal model of neuronal degeneration and its modulation by an anti-inflammatory drug: Implication in Alzheimer’s disease. European Journal of Neuroscience, 12, 1900–1912.
Seiwa, C., et al. (2007). Restoration of FcRgamma/Fyn signaling repairs central nervous system demyelination. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 85, 954–966.
Shichita, T., et al. (2009). Pivotal role of cerebral interleukin-17-producing gammadeltaT cells in the delayed phase of ischemic brain injury. Nature Medicine, 15, 946–950.
Sibéril, S., et al. (2006). Molecular aspects of human FcgammaR interactions with IgG: Functional and therapeutic consequences. Immunology Letters, 106, 111–118.
Song, X., et al. (2002). Fcgamma receptor I- and III-mediated macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha induction in primary human and murine microglia. Infection and Immunity, 70, 5177–5184.
Song, X., et al. (2004). Fcgamma receptor signaling in primary human microglia: Differential roles of PI-3K and Ras/ERK MAPK pathways in phagocytosis and chemokine induction. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 75, 1147–1155.
Stevens, B., et al. (2007). The classical complement cascade mediates CNS synapse elimination. Cell, 131, 1164–1178.
Stockert, R. J. (1995). The asialoglycoprotein receptor: Relationships between structure, function, and expression. Physiological Reviews, 75, 591–609.
Suzuki, T., et al. (2000). Differential involvement of Src family kinases in Fc gamma receptor-mediated phagocytosis. Journal of Immunology, 165, 473–482.
Takai, T., et al. (2003). Fc receptors as potential targets for the treatment of allergy, autoimmune disease and cancer. Current Drug Targets. Immune, Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders, 3, 187–197.
Tang, S. C., et al. (2007). Pivotal role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain injury and functional deficits. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 13798–13803.
Tang, S. C., et al. (2008). Toll-like receptor-4 mediates neuronal apoptosis induced by amyloid beta-peptide and the membrane lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. Experimental Neurology, 213, 114–121.
Tarasenko, T., et al. (2007). FcgammaRIIB as a modulator of autoimmune disease susceptibility. Autoimmunity, 40, 409–417.
Ting, A. T., et al. (1995). Interaction between lck and syk family tyrosine kinases in Fc gamma receptor-initiated activation of natural killer cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 270, 16415–16421.
Tkaczyk, C., et al. (2003). The phospholipase C gamma 1-dependent pathway of Fc epsilon RI-mediated mast cell activation is regulated independently of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 48474–48484.
Turner, H., & Kinet, J. P. (1999). Signalling through the high-affinity IgE receptor Fc epsilonRI. Nature, 402, B24–B30.
Ueyama, T., et al. (2004). Superoxide production at phagosomal cup/phagosome through beta I protein kinase C during Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis in microglia. Journal of Immunology, 173, 4582–4589.
Ulvestad, E., et al. (1994). Reactive microglia in multiple sclerosis lesions have an increased expression of receptors for the Fc part of IgG. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 121, 125–131.
Underhill, D. M., & Goodridge, H. S. (2007). The many faces of ITAMs. Trends in Immunology, 28, 66–73.
Urich, E., et al. (2006). Autoantibody-mediated demyelination depends on complement activation but not activatory Fc-receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 18697–18702.
Urtz, N., et al. (2004). Early activation of sphingosine kinase in mast cells and recruitment to FcepsilonRI are mediated by its interaction with Lyn kinase. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 24, 8765–8777.
Van den Herik-Oudijk, I. E., et al. (1995). Identification of signaling motifs within human Fc gamma RIIa and Fc gamma RIIb isoforms. Blood, 85, 2202–2211.
Vedeler, C., et al. (1994). Fc receptor for IgG (FcR) on rat microglia. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 49, 19–24.
Wang, H. H., et al. (2009). Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via a p42/p44 and JNK-dependent AP-1 pathway in brain astrocytes. Glia, 57, 24–38.
Wilcock, D. M., & Colton, C. A. (2009). Immunotherapy, vascular pathology, and microhemorrhages in transgenic mice. CNS & Neurological Disorders Drug Targets, 8, 50–64.
Wilcock, D. M., Gordon, M. N., Morgan, D., et al. (2003). Intracranially administered anti-Abeta antibodies reduce beta-amyloid deposition by mechanisms both independent of and associated with microglial activation. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 3745–3751.
Williams, M. R., et al. (2000). The role of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in activating AGC kinases defined in embryonic stem cells. Current Biology, 10, 439–448.
Wines, B. D., & Hogarth, P. M. (2006). IgA receptors in health and disease. Tissue Antigens, 68, 103–114.
Woodroofe, M. N., et al. (1989). Fc receptor density, MHC antigen expression and superoxide production are increased in interferon-gamma-treated microglia isolated from adult rat brain. Immunology, 68, 421–426.
Wurzburg, B. A., et al. (2006). Structural changes in the lectin domain of CD23, the low-affinity IgE receptor, upon calcium binding. Structure, 14, 1049–1058.
Yenari, M. A., et al. (2006). Microglia potentiate damage to blood–brain barrier constituents: Improvement by minocycline in vivo and in vitro. Stroke, 37, 1087–1093.
Yilmaz, G., et al. (2006). Role of T lymphocytes and interferon-gamma in ischemic stroke. Circulation, 113, 2105–2112.
Yoo, E. M., & Morrison, S. L. (2005). IgA: An immune glycoprotein. Clinical Immunology, 116, 3–10.
Yu, M., et al. (2006). Scaffolding adapter Grb2-associated binder 2 requires Syk to transmit signals from FcepsilonRI. Journal of Immunology, 176, 2421–2429.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okun, E., Mattson, M.P. & Arumugam, T.V. Involvement of Fc Receptors in Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Neuromol Med 12, 164–178 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-009-8099-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-009-8099-5