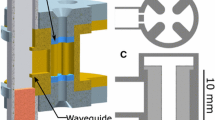
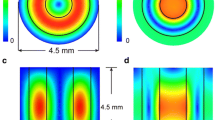
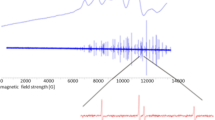
Abstract
Cavity resonators are often used for electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR). Rectangular TE102 and cylindrical TE011 are common modes at X-band even though the field varies cosinusoidally along the Z-axis. The authors found a way to create a uniform field (UF) in these modes. A length of waveguide at cut-off was introduced for the sample region, and tailored end sections were developed that supported the microwave resonant mode. This work is reviewed here. The radio frequency (RF) magnetic field in loop-gap resonators (LGR) at X-band is uniform along the Z-axis of the sample, which is a benefit of LGR technology. The LGR is a preferred structure for EPR of small samples. At Q-band and W-band, the LGR often exhibits nonuniformity along the Z-axis. Methods to trim out this nonuniformity, which are closely related to the methods used for UF cavity resonators, are reviewed. In addition, two transmission lines that are new to EPR, dielectric tube waveguide and circular ridge waveguide, were recently used in UF cavity designs that are reviewed. A further benefit of UF resonators is that cuvettes for aqueous samples can be optimum in cross section along the full sample axis, which improves quantification in EPR spectroscopy of biological samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In this work, we define the static magnetic field (H0) to be along the X-axis and, therefore, the RF magnetic fields along Y-axis and Z-axis give rise to EPR transitions.
References
Mett, R. R., Froncisz, W., & Hyde, J. S. (2001). Axially uniform resonant cavity modes for potential use in electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 72, 4188–4200.
Anderson, J. R., Mett, R. R., & Hyde, J. S. (2002). Cavities with axially uniform fields for use in electron paramagnetic resonance. II. Free space generalization. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 73, 3027–3037.
Hyde, J. S., Mett, R. R., & Anderson, J. R. (2002). Cavities with axially uniform fields for use in electron paramagnetic resonance. III. Re-entrant geometries. Rev Sci Instrum, 73, 4003–4009.
Hyde J. S., Mett R. R., Froncisz W., Anderson J. R. (2004) Cavity resonator for electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy having axially uniform field, US Patent 6,828,789.
Sidabras, J. W., Sarna, T., Mett, R. R., & Hyde, J. S. (2017). Uniform field loop-gap resonator and rectangular TEU02 for aqueous sample EPR at 94GHz. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 282, 129–135.
Mett, R. R., Sidabras, J. W., & Hyde, J. S. (2007). Uniform radio frequency fields in loop-gap resonators for EPR spectroscopy. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 31, 573.
Hyde, J. S., & Mett, R. R. (2017). EPR uniform field signal enhancement by dielectric tubes in cavities. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 48, 1185–1204.
Sidabras, J. W., Reijerse, E. J., & Lubitz, W. (2017). Uniform field re-entrant cylindrical TE01U cavity for pulse electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy at Q-band. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 48, 1301–1314.
Hyde, J. S., Eaton, S. S., & Eaton, G. R. (2006). EPR at work. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance, 28A, 82.
Hyde, J. S., & Froncisz, W. (1989). Loop gap resonators. In A. J. Hoff ed, Advanced EPR, Applications in Biology and Biochemistry (pp. 277–306). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Rempel R. C., Ward C. E., Sullivan R. T., St. Clair M. W., Weaver H. E. (1964) Gyromagnetic resonance method and apparatus, US Patent 3,122,703.
Sidabras, J. W., Mett, R. R., & Hyde, J. S. (2017). Extruded dielectric sample tubes of complex cross section for EPR signal enhancement of aqueous samples. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 277, 45–51.
Hyde, J. S., & Mett, R. R. (2002). Aqueous sample considerations in uniform field resonators for electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Current Topics in Biophysics, 26, 7–14.
Wood, R. L., Froncisz, W., & Hyde, J. S. (1984). The loop-gap resonator. II. Controlled return flux three-loop, two-gap microwave resonators for ENDOR and ESR spectroscopy. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 58, 243–253.
Froncisz, W., Oles, T., & Hyde, J. S. (1986). Q‐band loop‐gap resonator. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 57, 1095–1099.
Hyde, J. S., Yin, J.-J., Subczynski, W. K., Camenisch, T. G., Ratke, J. J., & Froncisz, W. (2004). Spin-label EPR T1 values using saturation recovery from 2 to 35 GHz. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 108, 9524–9529.
Sidabras, J. W., Mett, R. R., Froncisz, W., Camenisch, T. G., Anderson, J. R., & Hyde, J. S. (2007). Multipurpose EPR loop-gap resonator and cylindrical TE011 cavity for aqueous samples at 94 GHz. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 78, 034701.
Hyde, J. S., Strangeway, R. A., Camenisch, T. G., Ratke, J. J., & Froncisz, W. (2010). W-band frequency-swept EPR. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 205, 93–101.
Strangeway, R. A., Hyde, J. S., Camenisch, T. G., Sidabras, J. W., Mett, R. R., Anderson, J. R., Ratke, J. J., & Subczynski, W. K. (2017). Broadband W-band rapid frequency sweep considerations for Fourier transform EPR. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 75, 259–273.
Mainali, L., Sidabras, J. W., Camenisch, T. G., Ratke, J. J., Raguz, M., Hyde, J. S., & Subczynski, W. K. (2014). Spin-label W-band EPR with seven-loop-six-gap resonator: Application to lens membranes derived from eyes of a single donor. Applied Magnetic Resonance, 45, 1343–1358.
Chen, C.-C. (1974). Quadruple ridge-loaded circular waveguide phased arrays. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 22, 481–483.
Sangster, A. J., & Grant, J. (2009). Mode degeneracy in circular cylindrical ridge waveguides. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 9, 75–83.
Slater, J. C. (1950). Microwave electronics, D. Princeton, NJ: Van Nostrand.
Rong, Y., & Zaki, K. A. (2000). Characteristics of generalized rectangular and circular ridge waveguides. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 48, 258–265.
Mett, R. R., & Hyde, J. S. (2003). Aqueous flat cells perpendicular to the electric field for use in electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 165, 137–152.
Sidabras, J. W., Mett, R. R., & Hyde, J. S. (2005). Aqueous flat-cells perpendicular to the electric field for use in electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, II: design. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 172, 333–341.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant P41 EB001980 from the National Institutes of Health. Jason W. Sidabras is currently funded by the European Union Horizon 2020 Marie Skłodowska-Curie Fellowship (Act-EPR; http://act-epr.org) and the Max Planck Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyde, J.S., Sidabras, J.W. & Mett, R.R. Uniform Field Resonators for EPR Spectroscopy: A Review. Cell Biochem Biophys 77, 3–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-018-0845-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-018-0845-6