Abstract
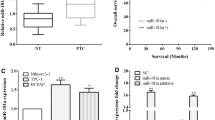
This study was set to study the molecular mechanism underlying how miR-200 regulates EGF/EGFR signaling to involve in epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) cells. Loss-of-function experiments of EGFR silencing by siRNA transfection was performed. Transfection of pre-miR-200s or anti-miR-200s was used to increase or decrease miR-200 transcripts. Real-time PCR, Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and transwell experiments were performed to determine the role of miR-200s in EMT and its role in EGF/EGFR-mediated EMT in vitro and in vivo. EGF/EGFR signaling activation increased the expression of mesenchymal marker vimentin in Nthy-ori 3-1 cells and decreased the expression of endothelial maker E-cadherin. EGF stimulation led to increased RhoA expression in Nthy-ori 3-1 cells. EGFR silencing resulted in decreased RhoA expression in SW1736 and ARO cells. EGF stimulation led to down-regulation of miR-200s and EMT. Restoration of miR-200 expression by pre-miR-200a/c transfection reversed the process, including increased E-cadherin and decreased vimentin. Down-regulation of miR-200 by anti-miR-200 effectively reduced miR-200. Matrigel invasion assay proved that restoration of miR-200 expression counteracted invasiveness. EGFR silencing decreased invasiveness in SW1736 cells, while down-regulation of miR-200s restored invasiveness. Xenograft tumors of SW1736 cells with cotransfection of anti-miR-200s and EGFR siRNA which kept the similar E-cadherin and vimentin expression with the untransfected controls. In ATC cells, miR-200s play a central role in EGF/EGFR-mediated invasiveness in vitro and EMT in vivo.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
30 July 2019
An amendment to this paper has been published and can be accessed via a link at the top of the paper.
References
Diaz-Lopez, A., et al. (2014). Zeb1 and Snail1 engage miR-200f transcriptional and epigenetic regulation during EMT. International Journal Cancer,. doi:10.1002/ijc.29177.
Tejero, R., et al. (2014). miR-141 and miR-200c as markers of overall survival in early stage non-small cell lung cancer adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE, 9(7), e101899.
Zhang, B., et al. (2013). KLF5 activates microRNA 200 transcription to maintain epithelial characteristics and prevent induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in epithelial cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 33(24), 4919–4935.
Engelsvold, D. H., et al. (2013). miRNA and mRNA expression profiling identifies members of the miR-200 family as potential regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pterygium. Experimental Eye Research, 115, 189–198.
David, M., et al. (2014). Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 modulates invasion and metastatic potential of colorectal cancer cells. MolOncol, 8(5), 942–955.
Guo, F., et al. (2014). Post-transcriptional regulatory network of epithelial-to-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions. Journal of Hematology Oncology, 7, 19.
Lu, Y., et al. (2014). MiR-200a inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer stem cell. BMC Cancer, 14, 85.
Jabbari, N., Reavis, A. N., & McDonald, J. F. (2014). Sequence variation among members of the miR-200 microRNA family is correlated with variation in the ability to induce hallmarks of mesenchymal-epithelial transition in ovarian cancer cells. Journal of Ovarian Research, 7(1), 12.
Banyard, J., et al. (2013). Regulation of epithelial plasticity by miR-424 and miR-200 in a new prostate cancer metastasis model. Scientific Report, 3, 3151.
Lawrie, C. H., et al. (2014). Targeted next-generation sequencing and non-coding RNA expression analysis of clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma suggests distinct pathological mechanisms from other renal tumour subtypes. The Journal of Pathology, 232(1), 32–42.
Paterson, E. L., et al. (2013). Down-regulation of the miRNA-200 family at the invasive front of colorectal cancers with degraded basement membrane indicates EMT is involved in cancer progression. Neoplasia, 15(2), 180–191.
Ahmad, A., et al. (2012). Garcinol regulates EMT and Wnt signaling pathways in vitro and in vivo, leading to anticancer activity against breast cancer cells. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 11(10), 2193–2201.
Zhang, Z., et al. (2012). The miR-200 family regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by EGF/EGFR in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 30(4), 856–862.
Hill, L., Browne, G., & Tulchinsky, E. (2013). ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: at the crossroads of signal transduction in cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 132(4), 745–754.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lei XUE and Dongyue SU have contributed equally.
The Editor-in-Chief has retracted this article due to significant overlap with a previously published article by a different author group. The authors have not responded to any correspondence regarding this retraction.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, L., Su, D., Li, D. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: miR-200 Regulates Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer via EGF/EGFR Signaling. Cell Biochem Biophys 72, 185–190 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0435-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0435-1