Abstract
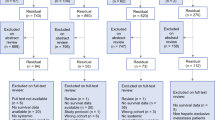
To investigate the effectiveness of monoclonal antibody (131I-chTNT) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) combination therapy in treating middle-advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Thirty-four patients diagnosed with HCC patients, divided into two groups comprised of 22 and 12 cases were included in this retrospective study. The two groups received RFA with or without (131I-chTNT) therapy, respectively. The patients in these groups were followed up for a median of 31 and 35 months, respectively. Patient survival was evaluated using Kaplan–Meier method and safety profiles were determined by analyzing liver, thyroid, and bone marrow toxicities. This retrospective study showed that survival time of the patients who received combination therapy was significantly longer than that of the RFA group (P = 0.052). The median progress-free survival of patients in the two groups was 23 and 7 months, respectively, and the difference was significant (P = 0.04). Tumor recurred in 3.5–8.7 months in four of the combination group patients, among which three had newly developed lesions. The red blood cells and platelets counts were not altered on day 7 and 1 month of the treatment, however, number of white blood cells was significantly increased on day 7 which was reversed back to the normal range in 2 weeks. The ALT and AST were also not significantly altered on day 7 and 1 month of therapy. In middle-advanced stage HCC patients, the combination of 131I-chTNT and RFA therapy was found to be significantly more effective than the RFA treatment alone as assessed in short-term follow-up. However, the dose we used was insufficient to completely block the local recurrence of the lesions with a diameter of 5 cm or larger.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewandowski, R. J., Mulcahy, M. F., Kulik, L. M., et al. (2010). Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma comprehensive imaging and survival analysis in a 172-patient cohort. Radiology, 255, 955–965.
Ye, S. L., Takayama, T., Geschwind, J., et al. (2010). Current approaches to the treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist, 15, 34–41.
Yin, J. H., Li, N., Han, Y. F., et al. (2013). Effect of antiviral treatment with nucleotide/nucleoside analogs on postoperative prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A two-stage longitudinal clinical study. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 31, 3647–3655.
Feng, K., Yan, J., Li, X. W., et al. (2012). A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Hepatology, 57, 794–802.
Lencioni, R., & Crocetti, L. (2012). Local-regional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology, 262, 43–58.
Livraghi, T., Meloni, F., Morabito, A., & Vettori, C. (2004). Multimodal image-guided tailored therapy of early and intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma: Long-term survival in the experience of a single radiologic referral center. Liver Transplantation, 10(2 suppl 1), S98–S106.
Shiina, S., Teratani, T., Obi, S., et al. (2005). A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology, 129(1), 122–130.
Kong, W.-T., Zhang, W.-W., Qiu, Y.-D., et al. (2009). Major complications after radiofrequency ablation for liver tumors: Analysis of 255 patients. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 15(21), 2651–2656.
Seror, O. N., Kontchou, G., Ibraheem, M., et al. (2008). Large (≥5.0 cm) HCCs: Multipolar RF ablation with three internally cooled bipolar electrodes—initial experience in 26 patients. Radiology, 248, 288–296.
Vincenzo, A., Stefano, P., Claudio, M. P., et al. (2008). Complications of laser ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter study. Radiology, 246, 944–955.
Lau, W., & Lai, C. H. (2008). Hepatocellular carcinoma current management and recent advances. Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Diseases International, l7, 237–257.
Boerman, O. C., Koppe, M. J., Postema, E. J., et al. (2007). Radionuclide therapy of cancer with radiolabeled antibodies. Anticancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 7, 335–343.
Guglielmi, A., Ruzzenente, A., Valdegamberi, A., et al. (2008). Radiofrequency ablation versus resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, 12, 192–198.
Goldberg, S. N., Girnan, G. D., Lukyanov, A. N., et al. (2002). Percutaneous tumor ablation: Increased necrosis with combined radio-frequency ablation and intravenous liposomal doxorubicin in a rat breast tumor model. Radiology, 222(3), 797–804.
Yamakado, K., Nakatsuka, A., Takaki, H., et al. (2008). Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization versus hepatectomy. Radiology, 247, 260–266.
Harris, D. A., Pellikka, R., Gasser, O., et al. (2009). In-line radiolabeling: A novel continuous-flow system for commercial-scale protein labeling. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 50, 1178–1186.
Jong, G. M., Boerman, O. C., Heskamp, S., et al. (2009). Radioimmunotherapy prevents local recurrence of colonic cancer in an experimental model. British Journal of Surgery, 96, 314–321.
Chen, S. L., Like, Yu., Jiang, C. Y., et al. (2005). Pivotal study of iodine-131-labeled chimeric tumor necrosis treatment radioimmunotherapy in patients with advanced lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 23, 1538–1547.
Wilder, R., DeNardo, G., & DeNardo, S. (1996). Radioimmunotherapy: Recent results and future directions. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 14, 1383–1400.
Meredith, R., LoBuglio, A., & Spencer, E. (1997). Recent Progress in Radioimmunotherapy for Cancer. Oncology, 11, 979–984.
Knox, S., & Meredith, R. (2000). Clinical Radioimmunotherapy. Seminars in Radiation Oncology, 10, 73–93.
Zheng, S.-G., Xu, H.-X., Guo, L.-H., Liu, L.-N., & Lu, F. (2014). The safety and treatment response of combination therapy of radioimmunotherapy and radiofrequency ablation for solid tumor: A study in vivo. PLoS One, 9(5), e96539.
Yu, L., Ju, D. W., Chen, W., et al. (2006). 131I-chTNT Radioimmunotherapy of 43 Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer. Cancer Biotherapy Radiopharmaceuticals, 21(1), 5–14.
Gao, J., & Zhu, J. Y. (2012 [2011 edition]). Read of the primary liver cancer diagnosis and treatment norms by The Ministry of Health. Chinese Journal of General Surgery, 27(8), 693–699.
Llovet, J. M., Di Bisceglie, A. M., Bruix, J., et al. (2008). Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 100, 698–711.
Li, Bl., Chen, S. L., & Xu, Z. Q. (2009). Biodistribution of iodine-131-labeled chimeric monoclonal antibody in patients following intratumoral administration in advanced lung carcinoma. Fudan University Journal of Medical Sciences, 36, 475–478.
Shibata, T., Isoda, H., Hirokawa, Y., et al. (2009). Small hepatocellular carcinoma: Is radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization more effective than radiofrequency ablation alone for treatment? Radiology, 252, 905–913.
Peng, Z. W., Zhang, Y. J., Chen, M. S., et al. (2013). Radiofrequency ablation with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective randomized trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 31, 426–432.
Zhu, A. X., & Salem, R. (2013). Combining transarterial chemoembolization with radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: One step forward? Journal of Clinical Oncology, 31, 406–408.
Zhang, Y.-J., Liang, H.-H., Chen, M.-S., et al. (2007). Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radiofrequency ablation with or without ethanol injection: A prospective randomized trial. Radiology, 244, 599–607.
Takaki, H., Yamakado, K., Nakatsuka, A., et al. (2007). Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma 5 cm or smaller: Risk factors for local tumor progression. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 18(7), 856–861.
Kuang, M., Lu, M.-D., Xie, X.-Y., et al. (2009). Ethanol ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma up to 5.0 cm by using a multipronged injection needle with high-dose strategy. Radiology, 253, 552–561.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Program for Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (2010C33113).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no disclosures to make.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, J., Ji, J., Wu, F. et al. Effectiveness of Combined 131I-chTNT and Radiofrequency Ablation Therapy in Treating Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Biochem Biophys 71, 777–784 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0262-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0262-4