Abstract
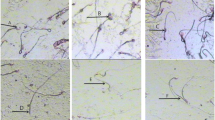
Cadmium (Cd), a heavy metal element, cumulates in the testis and can cause male reproductive toxicity. Although vitamin E (VE) as one of potential antioxidants protects the testis against toxicity of Cd, the underlying mechanism remained uncompleted clear. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the Nrf-2 pathway is involved with the protective effect of VE on testicular damages caused by sub-chronic Cd exposure. Thirty-two SD rats were divided into four groups and orally administrated with VE and/or Cd for 28 consecutive days: control group, VE group (100 mg VE/kg), Cd group (5 mg CdCl2/kg), and VE + Cd group (100 mg VE/kg + 5 mg CdCl2/kg). The results showed that 28-day exposure of Cd caused accumulation of Cd, histopathological lesions, and alternations of sperm parameters (elevated rate of abnormal sperm, decreased count of sperm, declined motility, and viability of sperm). Moreover, the rats exposed to Cd showed significant oxidative stress (increased contents of MDA and decreased levels or activities of T-AOC, GSH, CAT, SOD and GSH-Px) and inhibition of Nrf-2 signaling pathway (downregulation of Nrf-2, HO-1, NQO-1, GCLC, GCLM and GST) of the testes. In contrast, VE treatment significantly reduced the Cd accumulation, alleviated histopathological lesions and dysfunctions, activated Nrf-2 pathway, and attenuated the oxidative stress caused by Cd in the testes of rats. In conclusion, VE, through upregulating Nrf-2 pathway, could protect testis against oxidative damages induced by sub-chronic Cd exposure.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Alagawany M, El-Hack MEA, Farag MR, Elnesr SS, El-Kholy MS, Saadeldin IM, Swelum AA (2018) Dietary supplementation of Yucca schidigera extract enhances productive and reproductive performances, blood profile, immune function, and antioxidant status in laying Japanese quails exposed to lead in the diet. Poult Sci 97(9):3126–3137
Nguyen CC, Hugie CN, Kile ML, Navab-Daneshmand T (2019) Association between heavy metals and antibiotic-resistant human pathogens in environmental reservoirs: a review. Front Environ Sci Eng 13(3):46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-019-1129-0
Andráš P, Turisová I, Krnáč J, Dirner V, Voleková-Lalinská B, Buccheri G, Jeleň S (2012) Hazards of heavy metal contamination at L’ubietová Cu-Deposit (Slovakia). Procedia Environ Sci 14:3–21
Beccaloni E, Vanni F, Beccaloni M, Carere M (2013) Concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, lead and zinc in homegrown vegetables and fruits: estimated intake by population in an industrialized area of Sardinia, Italy. Microchem J 107:190–195
Khafaga AF, Abd El-Hack ME, Taha AE, Elnesr SS, Alagawany M (2019) The potential modulatory role of herbal additives against Cd toxicity in human, animal, and poultry: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:4588–4604
Maret W, Moulis JM (2013) The bioinorganic chemistry of cadmium in the context of its toxicity. Met Ions Life Sci 11:1–29
Zhou T, Jia X, Chapin RE, Maronpot RR, Harris MW, Liu J, Waalkes MP, Eddy EM (2004) Cadmium at a non-toxic dose alters gene expression in mouse testes. Toxicol Lett 154(3):191–200
Ogawa Y, Itoh M, Hirai S, Suna S, Naito M, Qu N, Terayama H, Ikeda A, Miyaso H, Matsuno Y (2012) Cadmium exposure increases susceptibility to testicular autoimmunity in mice. J Appl Toxicol 33(7):652–660
Zhu M, Miao S, Zhou W, Elnesr SS, Dong X, Zou X (2021) MAPK, AKT/FoxO3a and mTOR pathways are involved in cadmium regulating the cell cycle, proliferation and apoptosis of chicken follicular granulosa cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 214:112091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112091
Ren YP, Shao WH, Zuo LJ (2019) Mechanism of cadmium poisoning on testicular injury in mice. Oncol Lett 18(2):1035–1042
Medina MF, Arrieta MC, Villafae MN, Klyver SMR, González ME (2017) Early signs of toxicity in testes and sperm of rats exposed to low cadmium doses. Toxicol Ind Health 33(7):576–587
Abdelrazek HMA, Helmy SA, Elsayed DH, Ebaid HM, Mohamed RM (2016) Ameliorating effects of green tea extract on cadmium induced reproductive injury in male Wistar rats with respect to androgen receptors and caspase-3. Reprod Biol 16(4):300–308
Pant N, Upadhyay G, Pandey S, Mathur N, Saxena DK, Srivastava SP (2003) Lead and cadmium concentration in the seminal plasma of men in the general population: correlation with sperm quality. Reprod Toxicol 17(4):447–450
Marettova E, Maretta M, Legath J (2015) Toxic effects of cadmium on testis of birds and mammals: a review. Anim Reprod Sci 155:1–10
Niki E (2014) Role of vitamin E as a lipid-soluble peroxyl radical scavenger: in vitro and in vivo evidence. Free Radic Biol Med 66:3–12
Arita M, Sato Y, Arai H, Inoue K (1998) Binding of alpha-tocopherylquinone, an oxidized form of alpha-tocopherol, to glutathione-S-transferase in the liver cytosol. FEBS Lett 436(3):424–426
Boldyrev AA, Bulygina ER, Volynskaia EA, Kurella EG, Tiulina OV (1995) The effect of hydrogen peroxide and hypochlorite on brain Na K-ATPase activity. Biokhimiia 60(10):1688–1696
Fang J, Yin H, Yang Z, Tan M, Wang F, Chen K, Zuo Z, Shu G, Cui H, Ouyang P, Guo H, Chen Z, Huang C, Geng Y, Liu W (2021) Vitamin E protects against cadmium-induced sub-chronic liver injury associated with the inhibition of oxidative stress and activation of Nrf2 pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111610
Adi PJ, Burra SP, Vataparti AR, Matcha B (2016) Calcium, zinc and vitamin E ameliorate cadmium-induced renal oxidative damage in albino Wistar rats. Toxicol Rep 3:591–597
Bhuvaneswaridevi C, Kirankumari K (2017) Ameliorating effect of vitamin-E against cadmium (Cd) induced brain oxidative damage in albino rats. Int J Adv Res 5(7):1214–1223
Amanpour P, Khodarahmi P, Salehipour M (2020) Protective effects of vitamin E on cadmium-induced apoptosis in rat testes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393(3):349–358
Kanter M, Aksu B, Akpolat M, Tarladacalisir TY, Aktas C (2009) Vitamin E protects against oxidative damage caused by cadmium in the blood of rats. Eur J Gen Med 6(3):154–460
Dadgar Z, Abdali N, ElyasiIrai A, Salehian Z (2016) The consequence of vitamin E exposure on in vitro cadmium toxicity in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Int Biol Biomed J 2(1):21–30
Duan L, Li J, Ma P, Yang X, Xu S (2017) Vitamin E antagonizes ozone-induced asthma exacerbation in Balb/c mice through the Nrf2 pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 107:47–56
Zhu Y, Li J, Wu Z, Lu Y, You H, Li R, Li B, Yang X, Duan L (2015) Acute exposure of ozone induced pulmonary injury and the protective role of vitamin E through the Nrf2 pathway in Balb/c mice. Toxicol Res 5(1):268–277
Carlson BA, Tobe R, Yefremova E, Tsuji PA, Hoffmann VJ, Schweizer U, Gladyshev VN, Hatfield DL, Conrad M (2016) Glutathione peroxidase 4 and vitamin E cooperatively prevent hepatocellular degeneration. Redox Biol 9:22–31
Ma J, Jin G (2019) Epidermal growth factor protects against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through activating Nrf2 signaling pathway. Free Radical Res 53(3):313–323
Zhai J, Li Z, Zhang H, Ma L, Li X (2020) Coptisine ameliorates renal injury in diabetic rats through the activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway. Archiv für Experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie 393(1):57–65
El-Demerdash FM, Yousef MI, Kedwany FS, Baghdadi HH (2004) Cadmium-induced changes in lipid peroxidation, blood hematology, biochemical parameters and semen quality of male rats: protective role of vitamin E and β-carotene. Food Chem Toxicol 42(10):1563–1571
Nazimabashir MV, Prabu SM (2014) Protective role of grape seed proanthocyanidins against cadmium induced hepatic dysfunction in rats. Toxicol Res 3(2):131–141
Johnsen SG (1970) Testicular biopsy score count–a method for registration of spermatogenesis in human testes: normal values and results in 335 hypogonadal males. Hormones 1(1):2–25
Belsey MA, Moghissi KS, Eliasson R, Paulsen CA, Gallegos AJ, Prasad MR (1980) Laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and semen-cervical mucus interaction. Press Concern, Singopore, p 58
Yu W, Xu Z, Gao Q, Xu Y, Dai Y (2020) Protective role of wogonin against cadmium induced testicular toxicity: involvement of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic pathways. Life Sci 258:118192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118192
Bashir N, Kalist S, Shagirtha V, Miltonprabu S (2018) The molecular and biochemical insight view of grape seed proanthocyanidins in ameliorating cadmium-induced testes-toxicity in rat model: implication of PI3K/Akt/Nrf-2signaling. Biosci Rep 39(1):1–20
Prabu M, Shagirhta K, Muthumani M (2010) The protective role of S-allylmercaptocysteine against cadmium induced changes in sperm characteristics and testicular oxidative damage in rats. J Pharm Res 3(11):2717–2721
Hossein AM, Fariba Z, Arash S, Mehdi A, Majid S, Morteza K, Abazar Y, Rafieh AM (2014) Saffron improves epididymal sperm parameters in rats exposed to cadmium. Nephrourol Mon 6(1):12125. https://doi.org/10.5812/numonthly.12125
Jahan S, Khan M, Ahmed S, Ullah H (2014) Comparative analysis of antioxidants against cadmium induced reproductive toxicity in adult male rats. Syst Biol Reprod Med 60(1):28–34
Cupertino MdC, Novaes RD, Santos EC (2017) Cadmium-induced testicular damage is associated with mineral imbalance, increased antioxidant enzymes activity and protein oxidation in rats. Life Sci 175:23–30
Bonda E, Włostowski T, Krasowska A (2004) Testicular toxicity induced by dietary cadmium is associated with decreased testicular zinc and increased hepatic and renal metallothionein and zinc in the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus). Biometals 175(6):615–624
Elnesr SS, Elwan HAM, Xu QQ, Xie C, Dong XY, Zou XT (2019) Effects of in ovo injection of sulfur-containing amino acids on heat shock protein 70, corticosterone hormone, antioxidant indices, and lipid profile of newly hatched broiler chicks exposed to heat stress during incubation. Poult Sci 98(5):2290–2298
Elwan H, Elnesr SS, Xu Q, Xie C, Dong X, Zou X (2019) Effects of in ovo methionine-cysteine injection on embryonic development, antioxidant status, igf-i and tlr4 gene expression, and jejunum histomorphometry in newly hatched broiler chicks exposed to heat stress during incubation. Animals 9(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9010025
Kheradmand A, Alirezaei M, Dezfoulian O (2015) Biochemical and histopathological evaluations of ghrelin effects following cadmium toxicity in the rat testis. Andrologia 47(6):634–643
Townsend DM, Tew KD, Tapiero H (2003) The importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed Pharmacother 57:145–155
Liu Z, Yang Q, Zhang C (2011) Study on antioxidant activity of proanthocyanidins from peanut skin. Adv Mater Res 197–198:1582–1586
AlkhedaideAdel AZS, Sabry A (2016) Protective effect of grape seed extract against cadmium-induced testicular dysfunction. Mol Med Rep 13(4):3101–3109
Klaudia J, Marian V (2011) Importance of iron chelation in free radical-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Curr Pharm Des 17(31):3460–3473
Wang Y, Fang J, Leonard SS (2004) Cadmium inhibits the electron transfer chain and induces reactive oxygen species. Free Radical Biol Med 36(11):1434–1443
Valko M, Jomova K, Rhodes CJ (2016) Redox- and non-redox-metal-induced formation of free radicals and their role in human disease. Arch Toxicol 90(1):1–37
Jie L, Qian SY, Guo Q (2008) Cadmium generates reactive oxygen- and carbon-centered radical species in rats: insights from in vivo spin-trapping studies. Free Radical Biol Med 45(4):475–481
Matović V, Buha A, Ðukić-Ćosić D (2015) Insight into the oxidative stress induced by lead and/or cadmium in blood, liver and kidneys. Food Chem Toxicol 78:130–140
Wang J, Zhang H, Zhang T (2015) Molecular mechanism on cadmium-induced activity changes of catalase and superoxide dismutase. Int J Biol Macromol 77:59–67
Olamudathir KF, Suru SM, Fafunso MA, Obioha UE, Faremi TY (2008) Protective roles of onion and garlic extracts on cadmium-induced changes in sperm characteristics and testicular oxidative damage in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 46(12):3604–3611
Aitken RJ, Curry BJ (2011) Redox regulation of human sperm function: from the physiological control of sperm capacitation to the etiology of infertility and DNA damage in the germ line. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(3):367–381
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, El-Deiry WS, Fulda S, Gottlieb E, Green DR, Hengartner MO, Kepp O, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lipton SA, Lu X, Madeo F, Malorni W, Mehlen P, Nuñez G, Peter ME, Piacentini M, Rubinsztein DC, Shi Y, Simon HU, Vandenabeele P, White E, Yuan J, Zhivotovsky B, Melino G, Kroemer G (2012) Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ 19(1):107–120
Barrett WC, DeGnore JP, King S (2015) Regulation of PTP1B via glutathionylation of the active site cysteine 215. Biochemistry 38(20):6699–6705
Eder K, Siebers M, Most E, Scheibe S, Weissmann N, Gessner DK (2017) An excess dietary vitamin E concentration does not influence Nrf2 signaling in the liver of rats fed either soybean oil or salmon oil. Nutr Metab 14(1):1–15
Böhm V (2018) Vitamin E. Antioxidants 7(3):44
Lee GY, Han SN (2018) The role of vitamin E in immunity. Nutrients 10(11):1614
Al-Attar AM (2011) Antioxidant effect of vitamin E treatment on some heavy metals-induced renal and testicular injuries in male mice. Saudi J Biol Sci 18(1):63–72
Fiego DP, Santoro P, Macchioni P, Mazzoni D, Piattoni F, Tassone F, De Leonibus E (2004) The effect of dietary supplementation of vitamins C and E on the α-tocopherol content of muscles, liver and kidney, on the stability of lipids, and on certain meat quality parameters of the longissimus dorsi of rabbits. Meat Sci 67(2):319–327
Mohamed D, Saber A, Omar A, Soliman A (2014) Effect of cadmium on the testes of adult albino rats and the ameliorating effect of zinc and vitamin E. Br J Sci 72(111):72–79
Shi X, Fu L (2019) Piceatannol inhibits oxidative stress through modification of Nrf2-signaling pathway in testes and attenuates spermatogenesis and steroidogenesis in rats exposed to cadmium during adulthood. Drug Des Dev Ther 13:2811–2824
Taguchi K, Kensler TW (2020) Nrf2 in liver toxicology. Arch Pharmacal Res 43(3):337–349
Liu Z, Xiang Y, Sun G (2013) The KCTD family of proteins: structure, function, disease relevance. Cell Biosci 3(45):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-3-45
De Haan JB (2011) Nrf2 activators as attractive therapeutics for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 60(11):2683–2684
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S (2007) Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47(1):89–116
Zhang M, An C, Gao Y (2013) Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase II antioxidant enzymes in neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol 100(1):30–47
Yang SH, Yu LH, Li L, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Long M, Li P, He JB (2018) Protective mechanism of sulforaphane on cadmium-induced sertoli cell injury in mice testis via Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway. Molecules 23(7):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071774
Yang SH, Li P, Yu LH, Li L, Long M, Liu MD, He JB (2019) Sulforaphane protect against cadmium-induced oxidative damage in mouse leydigs cells by activating Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 20(3):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030630
He L, Li P, Yu LH, Li L, Yang SH (2017) Protective effects of proanthocyanidins against cadmium-induced testicular injury through the modification of Nrf2-Keap1 signal path in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 57:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.11.002
Nazima B, Manoharan V, Miltonprabu S (2015) Grape seed proanthocyanidins ameliorates cadmium-induced renal injury and oxidative stress in experimental rats through the up-regulation of nuclear related factor 2 and antioxidant responsive elements. Biochem Cell Biol 93(3):210–226
Goven D, Boutten A, Leçon-Malas V, Boczkowski J, Bonay M (2009) Prolonged cigarette smoke exposure decreases heme oxygenase-1 and alters Nrf2 and Bach1 expression in human macrophages: roles of the MAP kinases ERK(1/2) and JNK. FEBS Lett 583(21):3508–3518
Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I, Yamamoto M, Nabeshima Y-i (1997) An Nrf2/Small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236(2):313–322
Alam J, Stewart D, Touchard C, Boinapally S, Choi AM, Cook JL (1999) Nrf2, a Cap’n’Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem 274(37):26071–26078
Feng Z, Liu Z, Li X, Jia H, Sun L, Tian C, Jia L, Liu J (2010) α-Tocopherol is an effective phase II enzyme inducer: protective effects on acrolein-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Nutr Biochem 21(12):1222–1231
Funding
This work was supported by National key research and development project (2018YFD0501800), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2018NZ0002, 2019YFQ0012), and Sichuan beef cattle innovation team of National modern agricultural industry technology system (SCCXTD-2020–13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhuo Chen, Zhicai Zuo, Kejie Chen, Zhuangzhi Yang, Fengyuan Wang, and Jing Fang designed and performed experiments, collected and analyzed data, and wrote the paper. Hengmin Cui, Hongrui Guo, Ping Ouyang, Zhengli Chen, Chao Huang, Yi Geng, Wentao Liu, and Huidan Deng performed experiments. All authors contributed discussions and interpretations.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The experimental animals and procedures were implemented in accordance with the agreement approved by the Animal Care and the Ethics Committee of Sichuan Agricultural University (Approval No:2012–024, Chengdu, China).
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
The authors confirm that the work described has not been published before.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Zuo, Z., Chen, K. et al. Activated Nrf-2 Pathway by Vitamin E to Attenuate Testicular Injuries of Rats with Sub-chronic Cadmium Exposure. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 1722–1735 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02784-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02784-1