Abstract
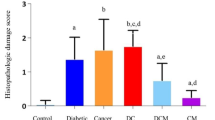
In this study, the effect of metformin on boron levels and oxidative brain damage in rats due to diabetes and prostate cancer was investigated for the first time. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and the amount of DNA were investigated as tissue oxidative and toxic damage parameters. In Copenhagen rats, Dunning prostate cancer was induced using high metastatic MAT-Lylu cells and diabetes was induced by single dose of streptozotocin (STZ) injection. Metformin was administered for 14 days after diabetes and prostate cancer induced. The rats were divided into six groups as follows: control group, diabetic group (D), cancer group (C), diabetic + cancer (DC) group, cancer + metformin (CM) group, diabetic + cancer + metformin (DCM) group. At the end of the experiment, brains were removed. Significant decrease of brain boron levels and significant elevation of MPO activity and DNA levels were observed in D, C, and DC groups as compared to control group. The effect of diabetes induction on the brain boron levels was much more than prostate cancer induction. The administration of metformin with CM and DCM obviously declined MPO activity and increased brain boron levels almost near to control group level. In conclusion, this study shows that the protective effect of metformin against brain damage in STZ-induced diabetic rats with Dunning prostate cancer may also be related to increased boron levels. The boron levels may be a novel indicator of reduced toxic and oxidative stress. Furthermore, the distribution and mechanism of action of boron should be clarified.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC (2010) Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. Diabetes Care 33(7):1674–1685. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-0666
Kim HJ, Lee SJ, Chun KH, Jeon JY, Han SJ, Kim DJ, Kim YS, Woo JT, Nam MS, Baik SH, Ahn KJ, Lee KW (2018) Metformin reduces the risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes: an analysis based on the Korean National Diabetes Program Cohort. Medicine 97:e0036. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000010036
Kuo YJ, Sung FC, Hsieh PF, Chang HP, Kun-Ling Wu KL, Wu HC (2019) Metformin reduces prostate cancer risk among men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a nation wide population-based cohort study. Cancer Med 8:2514–2523. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2025
Zaidi S, Gandhi J, Joshi G, Smith NL, Khan SA (2019) The anticancer potential of metformin on prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 22(3):351–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-018-0085-2
Navone N, Logothetıs CJ, Von-Eschenbach AC, Troncoso P (1999) Model systems of prostate cancer: uses and limitations. Cancer Metastasis Rev 17:361–371
Pienta KJ, Abate-Shen C, Agus DB, Attar RM, Chung LWK, Greenberg NM, Hahn WC, Isaacs JT, Navone NM, Peehl DM, Simons JW, Solit DB, Soule HR, VanDyke TA, Weber MJ, Wu L, Vessella RL (2008) The current state of preclinical prostate cancer animal models. Prostate 68(6):629–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20726
Tennant TR, Kim H, Sokolof M, Rinker-Schaeffer CW (2000) The Dunning model. Prostate 43(4):295–302
Yıldırım S, Altun S, Gumushan H, Patel A, Djamgoz MBA (2012) Voltage-gated sodium channel activity promotes prostate cancer metastasis in vivo. Cancer Lett 323(1):58–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2012.03.036
Bugan I, Karagoz Z, Altun S, Djamgoz MBA (2016) Gabapentin, an analgesic used against cancer-associated neuropathic pain: effects on prostate cancer progression in an in vivo rat model. BCPT. 118(3):200–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12484
Hunter JM, Nemzer BV, Rangavaila N, Bita A, Rogoveanu OC, Neamtu J, Scorei IR, Bejenaru LE, Rau G, Bejenaru C, Dan MG (2019) The fructoborates: part of a family of naturally occurring sugar-borate complexes-biochemistry, physiology, and impact on human health: a review. Biol Trace Elem Res 188(1):11–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1550-4
Nielsen FH, Eckhert C (2020) Boron Adv Nutr 11:461–462. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmz110
Pizzorno L (2015) Nothing boring about boron. Integr Med 14:35–48
Nielsen FH (2014) Update on human health effects of boron. J Trace Elem Med Biol 28:383–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.06.023
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Cigerci IH, Fatih Fidan A, Eryavuz A (2010) The effects of dietary boric acid and borax supplementation on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant activity, and DNA damage in rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 24(3):161–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2010.01.003
Daugherty A, Dunn JL, Rateri DL, Heinecke JW (1994) Myeloperoxidase, a catalyst for lipoprotein oxidation, is expressed in human atherosclerotic lesions. J Clin Invest 94(1):437–444. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI117342
Malle E, Furtmüller PG, Sattler W, Obinger C (2007) Myeloperoxidase: a target for new drug development? Br J Pharmacol 152(6):838–854. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0707358
Unubol M, Yavasoglu I, Kacar F, Guney E, Omurlu IK, Ture M, Kadikoylu G, Bolaman Z (2015) Relationship between glycemic control and histochemical myeloperoxidase activity in neutrophils in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr 7:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-015-0115-3 eCollection 2015
Grimes JA, Fraser SP, Stephence GJ, Downing JE, Laniado ME, Foster CS, Abel PD, Djamgoz MB (1995) Differential expression of voltage-activated Na+ currents in two prostatic tumour cell lines: contribution to invasiveness in vitro. FEBS Lett 369(2- 3):290–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(95)00772-2
Mossine V, Chopra P, Mawhinney TP (2008) Interaction of tomato lycopene and ketosamine against rat prostate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 68(11):4384–4391. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0108
Kuru R, Yilmaz S, Tasli PN, Yarat A, Sahin F (2019) Boron content of some foods consumed in Istanbul, Turkey. Biol Trace Elem Res 187:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1319-9
Hatcher JT, Wilcox LV (1950) Colorimetric determination of boron using carmine. Anal Chem 22:567–569. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60040a017
Wei H, Frenkel K (1991) In vivo formation of oxidized DNA bases in tumor promoter-treated mouse skin. Cancer Res 51:4443–4449
Burton K (1956) A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 62(2):315–323. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0620315
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Pernicova I, Korbonits M (2014) Metformin--mode of action and clinical implications for diabetes and cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10:143–156. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2013.256
An H, He L (2016) Current understanding of metformin effect on the control of hyperglycemia in diabetes. J Endocrinol 228(3):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-15-0447
Rena G, Hardie DG, Pearson ER (2017) The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia 60:1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z
Bayrak BB, Koroglu P, Bulan Karabulut O, Yanardag R (2021) Metformin protects against diabetes–induced heart injury and dunning prostate cancer model. Hum Exp Toxicol 40:297–309. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120947452
Koroglu P, Karabulut-Bulan O, Bugan I, Turkyilmaz IB, Altun S, Yanardag R. The protective effect of metformin against testicular damage in diabetes and prostate cancer model. Biologia (in press)
Li W, Chaudhari K, Shetty R, Winters A, Gao X, Hu Z, Ge WP, Sumien N, Forster M, Liu R, Yang SH (2019) Metformin alters locomotor and cognitive function and brain metabolism in normoglycemic mice. Aging Dis 10(5):949–963. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2019.0120
Sanadgol N, Barati M, Houshmand F, Hassani S, Clarner T, Shahlaei M, Golab F (2020) Metformin accelerates myelin recovery and ameliorates behavioral deficits in the animal model of multiple sclerosis via adjustment of AMPK/Nrf2/mTOR signaling and maintenance of endogenous oligodendrogenesis during brain self-repairing period. Pharmacol Rep 72(3):641–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-019-00019-8
Moreira PI (2014) Metformin in the diabetic brain: friend or foe? Ann Transl Med 2(6):54,1–54,3. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2014.06.10
Ghasemi AS, Taghartapeh MR, Soltani A, Mahon PJ (2019) Adsorption behavior of metformin drug on boron nitride fullerenes: thermodynamics and DFT studies. J Mol Liq 275(1):955–967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.11.124
Khaliq H, Juming Z, Ke-Mei P (2018) The physiological role of boron on health. Biol Trace Elem Res 186(1):31–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1284-3
Kuru R, Yılmaz S, Balan G, Alev Tuzuner B, Tasli PN, Akyuz S, Yener Ozturk F, Altuntas Y, Yarat A, Sahin F (2019) Boron-rich diet may regulate blood lipid profile and prevent obesity: a non-drug and self-controlled clinical trial. JTEMB. 54:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.04.021
Uluisik I, Karakaya HC, Koc A (2018) The importance of boron in biological systems. J Trace Elem Med Biol 45:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.10.008
Demirdogen RE (2020) Relationship among blood boron level, diabetes mellitus, lipid metabolism, bone metabolism and obesity: can boron be an efficient indicator for metabolic diseases. Health Sci J 14(1):689. https://doi.org/10.36648/1791-809X.14.1.689
Kot FS (2009) Boron sources, speciation and its potential impact on health. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 8:3–28
Nielsen FH, Meacham SL (2011) Growing evidence for human health benefits of boron. JEBCAM. 16:169–180. https://doi.org/10.1177/2156587211407638
Hunt CD (1998) Regulation of enzymatic activity. Biol Trace Elem Res 66:205–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783139
Penland JG (1994) Dietary boron, brain function, and cognitive performance. Environ Health Perspect 102:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.94102s765
Nielsen FH, Penland JG (2006) Boron deprivation alters rat behaviour and brain mineral composition differently when fish oil instead of safflower oil is the diet fat source. Nutr Neurosci 9:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/10284150600772189
Kelly GS (1997) Boron: a review of its nutritional interactions and therapeutic uses. Altern Med 2:48–56
Meacham S, Karakas S, Wallace A, Altun F (2010) Boron in human health: evidence for dietary recommendations and public policies. Open Miner Process J 3:36–53. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874841401003010036
Warrington K (1923) The effect of boric acid and borax on the broad bean and certain other plants. Ann Bot 37:629–672. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a089871
Nielsen FH, Hunt CD, Mullen LM, Hunt JR (1987) Effect of dietary boron on mineral, estrogen, and testosterone metabolism in postmenopausal women. FASEB J 1:394–397
Hunt CD (2010) Boro. In: Coates PM, Blackman MR, Cragg GM, Levine M, Moss J, White JD (eds) Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 55–65
Coban FK, Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Demirel HH, Hazman O (2015) Boron attenuates malathion-induced oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 38(4):391–399. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2014.974109
Data availability (data transparency)
Not applicable
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Armagan Begüm Özel: investigation, methodology, resources, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, visualization. Eda Dagsuyu: methodology, resources, writing-review and editing, visualization. Pınar Koroglu Aydın: methodology, resources. Ilknur Bugan: methodology, resources. Omur Karabulut Bulan: methodology, resources, supervision. Refiye Yanardag: conceptualization, methodology, resources, writing-review and editing, supervision. Aysen Yarat: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, resources, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experiments were carried out according to the guiding principles in the use of experimental animals and approved by the Istanbul University Animal Care and Use Committee (2014/28 - ethics committee decision number)
Ethics Approval (include appropriate approvals or waivers)
The ethical approval was obtained Istanbul University Animal Care and Use Committee (2014/28 - ethics committee decision number).
Consent to participate (include appropriate statements)
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication (include appropriate statements)
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• The first study on the brain boron level in metformin treated rats in diabetes and prostate cancer model.
• Metformin’s protective effect against brain tissue may also be related to increasing boron levels.
• Increased brain boron level is an important factor to reduce oxidative stress.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozel, A.B., Dagsuyu, E., Aydın, P.K. et al. Brain Boron Level, DNA Content, and Myeloperoxidase Activity of Metformin-Treated Rats in Diabetes and Prostate Cancer Model. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 1164–1170 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02708-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02708-z