Abstract
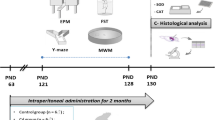
The present study focused on affective and cognitive behaviors in male Wistar rats, following direct and unique exposure to nickel chloride (NiCl2), as well as the possible involvement of oxidative stress. The rats were exposed to NiCl2 (300 μM), by intracerebral administration of 2 μL of this metal at the right hippocampus, using the stereotaxic approach. Five days after the surgery, a battery of behavioral tests was performed, including the open-field test (OFT) and elevated plus maze test (EPM) to assess the state of anxiety-like behavior and forced swimming test (FST) for depressive-like behavior. Y-maze and Morris Water Maze (MWM) were used to evaluate working memory and spatial learning. Thereafter, oxidative stress markers of the hippocampus were evaluated. The results confirm that NiCl2 exerts anxiogenic effects in both anxiety tests and depressogenic effects in the FST. In addition, MWM and Y-maze data show that NiCl2 causes memory and spatial learning disorders. The biochemical assay results showed that intrahippocampal injection of NiCl2 increased the levels of nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation (p < 0.001), while the activities of catalase and superoxide dismutase were significantly decreased in the hippocampus (p < 0.01). Overall, these results suggest that NiCl2 causes affective and cognitive disorders and oxidative stress in rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turna Demir F, Yavuz M (2020) Heavy metal accumulation and genotoxic effects in levant vole (Microtus guentheri) collected from contaminated areas due to mining activities. Environ Pollut 256:113378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113378
Zhen H, Jia L, Huang C, Qiao Y, Li J, Li H et al (2020) Long-term effects of intensive application of manure on heavy metal pollution risk in protected-field vegetable production. Environ Pollut 263:114552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114552
Gorini F, Muratori F, Morales MA (2014) The role of heavy metal pollution in neurobehavioral disorders: a focus on autism. Rev J Autism Dev Disord 1(4):354–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40489-014-0028-3
Lamtai M, Chaibat J, Ouakki S, Zghari O, Mesfioui A, El Hessni A et al (2018) Effect of chronic administration of nickel on affective and cognitive behavior in male and female rats: possible implication of oxidative stress pathway. Brain Sci 8(8):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8080141
Souza-Talarico JN, Marcourakis T, Barbosa F, Moraes Barros SB, Rivelli DP, Pompéia S et al (2017) Association between heavy metal exposure and poor working memory and possible mediation effect of antioxidant defenses during aging. Sci Total Environ 575:750–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.121
Lamtai M, Chaibat J, Ouakki S, Berkiks I, Rifi E-H, Hessni AE et al (2018) Effect of chronic administration of cadmium on anxiety-like, depression-like and memory deficits in male and female rats: possible involvement of oxidative stress mechanism. J Behav Brain Sci 08:240. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbbs.2018.85016
Lamtai M, Zghari O, Ouakki S, Marmouzi I, Mesfioui A, El Hessni A, Ouichou A (2020) Chronic copper exposure leads to hippocampus oxidative stress and impaired learning and memory in male and female rats. Toxicol Res 36(4):359–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-020-00043-4
Lamtai M, Azirar S, Zghari O, Ouakki S, El Hessni A, Mesfioui A, Ouichou A (2020) Melatonin ameliorates cadmium-induced affective and cognitive impairments and hippocampal oxidative stress in rat. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02247-z
Zambelli B, Uversky VN, Ciurli S (2016) Nickel impact on human health: an intrinsic disorder perspective. Biochim Biophys Acta 1864(12):1714–1731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.09.008
Zdrojewicz Z, Popowicz E, Winiarski J (2016) Nickel - role in human organism and toxic effects. Pol Merkur Lekarski 41(242):115–118
Bahadir Z, Ozdes D, Bulut VN, Duran C, Elvan H, Bektas H, Soylak M (2013) Cadmium and nickel determinations in some food and water samples by the combination of carrier element-free coprecipitation and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Toxicol Environ Chem 95(5):737–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2013.812730
Cameron KS, Buchner V, Tchounwou PB (2011) Exploring the molecular mechanisms of nickel-induced genotoxicity and carcinogenicity: a literature review. Rev Environ Health 26(2):81
Das KK, Das SN, Dhundasi SA (2008) Nickel, its adverse health effects & oxidative stress. Indian J Med Res 128(4):412–425
Ulrich Harréus MD P, Baumeister P, Kleinsasser N, Reiter M, Bachmeier B, Matthias C (2007) Genotoxic effects of metals on human salivary gland tissue and lymphocytes as detected by the Comet assay. Toxicol Environ Chem 89(2):205–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772240601012804
Xu S-C, He M-D, Zhong M, Zhang Y-W, Wang Y, Yang L et al (2010) Melatonin protects against Nickel-induced neurotoxicity in vitro by reducing oxidative stress and maintaining mitochondrial function. J Pineal Res 49(1):86–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00770.x
He M-D, Xu S-C, Zhang X, Wang Y, Xiong J-C, Zhang X et al (2013) Disturbance of aerobic metabolism accompanies neurobehavioral changes induced by nickel in mice. NeuroToxicology 38:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2013.05.011
He M-D, Xu S-C, Lu Y-H, Li L, Zhong M, Zhang Y-W et al (2011) L-carnitine protects against nickel-induced neurotoxicity by maintaining mitochondrial function in Neuro-2a cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 253(1):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.03.008
Xu S-C, He M, Zhong M, Li L, Lu Y, Zhang Y et al (2015) The neuroprotective effects of taurine against nickel by reducing oxidative stress and maintaining mitochondrial function in cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 590:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.01.065
Ijomone OM, Olatunji SY, Owolabi JO, Naicker T, Aschner M (2018) Nickel-induced neurodegeneration in the hippocampus, striatum and cortex; an ultrastructural insight, and the role of caspase-3 and α-synuclein. J Trace Elem Med Biol 50:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2018.05.017
Bannerman DM, Rawlins JNP, McHugh SB, Deacon RMJ, Yee BK, Bast T et al (2004) Regional dissociations within the hippocampus—memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28(3):273–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2004.03.004
Godsil BP, Kiss JP, Spedding M, Jay TM (2013) The hippocampal–prefrontal pathway: the weak link in psychiatric disorders? Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23(10):1165–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.10.018
Tang M, Huang H, Li S, Zhou M, Liu Z, Huang R et al (2019) Hippocampal proteomic changes of susceptibility and resilience to depression or anxiety in a rat model of chronic mild stress. Transl Psychiatry 9(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0605-4
Fatehyab S, Hasan M, Hasan MZ, Anwar J (1980) Effect of nickel on the levels of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin in different regions of the rat brain. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 47(4):318–320
Jia C, Roman C, Hegg CC (2010) Nickel sulfate induces location-dependent atrophy of mouse olfactory epithelium: protective and proliferative role of purinergic receptor activation. Toxicol Sci 115(2):547–556. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfq071
Liapi C, Zarros A, Theocharis S, Voumvourakis K, Anifantaki F, Gkrouzman E et al (2011) Short-term exposure to nickel alters the adult rat brain antioxidant status and the activities of crucial membrane-bound enzymes: neuroprotection by L-cysteine. Biol Trace Elem Res 143(3):1673–1681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-011-9006-0
Wu L, Gong W, Shen S-P, Wang Z-H, Yao J-X, Wang J et al (2017) Multiple metal exposures and their correlation with monoamine neurotransmitter metabolism in Chinese electroplating workers. Chemosphere 182:745–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.112
Cenini G, Lloret A, Cascella R (2019) Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: from a mitochondrial point of view. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 20:127–256. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2105607
Ferry B, Gervasoni D, Vogt C (2014) Stereotaxic neurosurgery in laboratory rodent. Springer Paris, Paris. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-2-8178-0472-9
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Burlington, MA: Academic, London Retrieved from http://site.ebrary.com/id/10360087
Durand M, Berton O, Aguerre S, Edno L, Combourieu I, Mormède P, Chaouloff F (1999) Effects of repeated fluoxetine on anxiety-related behaviours, central serotonergic systems, and the corticotropic axis axis in SHR and WKY rats. Neuropharmacology 38(6):893–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3908(99)00009-X
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open : closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14(3):149–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(85)90031-7
Rodgers RJ, Haller J, Holmes A, Halasz J, Walton TJ, Brain PF (1999) Corticosterone response to the plus-maze: high correlation with risk assessment in rats and mice. Physiol Behav 68(1–2):47–53
Walf AA, Frye CA (2007) The use of the elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in rodents. Nat Protoc 2(2):322. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.44
Carobrez AP, Bertoglio LJ (2005) Ethological and temporal analyses of anxiety-like behavior: the elevated plus-maze model 20 years on. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29(8):1193–1205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.04.017
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229(2):327–336
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47(4):379–391
Mandillo S, Tucci V, Hölter SM, Meziane H, Banchaabouchi MA, Kallnik M et al (2008) Reliability, robustness, and reproducibility in mouse behavioral phenotyping: a cross-laboratory study. Physiol Genomics 34(3):243–255. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.90207.2008
Morris RGM (1981) Spatial localization does not require the presence of local cues. Learn Motiv 12(2):239–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/0023-9690(81)90020-5
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11(1):47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4
D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP (2001) Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Research. Brain Res Rev 36(1):60–90
Camkurt MA, Fındıklı E, İzci F, Kurutaş EB, Tuman TC (2016) Evaluation of malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase and catalase activity and their diagnostic value in drug naïve, first episode, non-smoker major depression patients and healthy controls. Psychiatry Res 238:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.01.075
Chao CC, Hu S, Molitor TW, Shaskan EG, Peterson PK (1992) Activated microglia mediate neuronal cell injury via a nitric oxide mechanism. J Immunol 149(8):2736–2741
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Beyer WF, Fridovich I (1987) Assaying for superoxide dismutase activity: some large consequences of minor changes in conditions. Anal Biochem 161(2):559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90489-1
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05016-3
Majercikova Z, van Weering H, Scsukova S, Mikkelsen JD, Kiss A (2012) A new approach of light microscopic immunohistochemical triple-staining: combination of Fos labeling with diaminobenzidine-nickel and neuropeptides labeled with Alexa488 and Alexa555 fluorescent dyes. Endocr Regul 46(4):217–223
Rivas-Arancibia S, Hernández-Zimbrón LF, Rodríguez-Martínez E, Borgonio-Pérez G, Velumani V, Durán-Bedolla J (2013) Chronic exposure to low doses of ozone produces a state of oxidative stress and blood-brain barrier damage in the hippocampus of rat. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 04(11):24–29. https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2013.411A2004
Sampath D, Sathyanesan M, Newton S (2017) Cognitive dysfunction in major depression and Alzheimer’s disease is associated with hippocampus–prefrontal cortex dysconnectivity. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 13:1509–1519. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S136122
Kahloula K, Adli DEH, Slimani M, Terras H, Achour S (2014) Effet de l’exposition chronique au nickel sur les fonctions neurocomportementales chez les rats Wistar pendant la période de développement. Toxicol Anal Clin 26(4):186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxac.2014.09.056
Bockaert J, Bécamel C (2017) Contrôle de l’anxiété par les récepteurs de la sérotonine 5-HT2c de la strie terminale - Une explication des effets anxiogènes des inhibiteurs sélectifs de la recapture de la sérotonine (ISRS) ? Médecine/Sciences 33(1):87–89. https://doi.org/10.1051/medsci/20173301015
Undurraga J, Baldessarini RJ (2017) Direct comparison of tricyclic and serotonin-reuptake inhibitor antidepressants in randomized head-to-head trials in acute major depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Psychopharmacol 31(9):1184–1189. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881117711709
Nee DE, D’Esposito M (2018) The representational basis of working memory. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 37:213–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/7854_2016_456
Lalonde R (2002) The neurobiological basis of spontaneous alternation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26(1):91–104
Ijomone OM, Okori SO, Ijomone OK, Ebokaiwe AP (2018) Sub-acute nickel exposure impairs behavior, alters neuronal microarchitecture, and induces oxidative stress in rats’ brain. Drug Chem Toxicol 41(4):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2018.1437173
Henriksson J, Tallkvist J, Tjälve H (1997) Uptake of nickel into the brain via olfactory neurons in rats. Toxicol Lett 91(2):153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(97)03885-X
Milner B, Squire LR, Kandel ER (1998) Cognitive neuroscience and the study of memory. Neuron 20(3):445–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80987-3
Eichenbaum H (2001) The hippocampus and declarative memory: cognitive mechanisms and neural codes. Behav Brain Res 127(1–2):199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(01)00365-5
MacDonald CJ, Lepage KQ, Eden UT, Eichenbaum H (2011) Hippocampal “time cells” bridge the gap in memory for discontiguous events. Neuron 71(4):737–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.07.012
Topal A, Atamanalp M, Oruç E, Halıcı MB, Şişecioğlu M, Erol HS et al (2015) Neurotoxic effects of nickel chloride in the rainbow trout brain: Assessment of c-Fos activity, antioxidant responses, acetylcholinesterase activity, and histopathological changes. Fish Physiol Biochem 41(3):625–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0033-1
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis 12(5):913–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0756-2
Mazereeuw G, Herrmann N, Andreazza AC, Khan MM, Lanctôt KL (2015) A meta-analysis of lipid peroxidation markers in major depression. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:2479–2491. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S89922
Hall ED, Detloff MR, Johnson K, Kupina NC (2004) Peroxynitrite-mediated protein nitration and lipid peroxidation in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 21(1):9–20. https://doi.org/10.1089/089771504772695904
Kaehler ST, Singewald N, Sinner C, Philippu A (1999) Nitric oxide modulates the release of serotonin in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res 835(2):346–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01599-1
Lorrain DS, Hull EM (1993) Nitric oxide increases dopamine and serotonin release in the medial preoptic area. Neuroreport 5(1):87–89
Segovia G, Porras A, Mora F (1994) Effects of a nitric oxide donor on glutamate and GABA release in striatum and hippocampus of the conscious rat. Neuroreport 5(15):1937–1940
Sanna MD, Monti M, Casella L, Roggeri R, Galeotti N, Morbidelli L (2015) Neuronal effects of a nickel-piperazine/NO donor complex in rodents. Pharmacol Res 99:162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2015.06.004
Wegener G, Volke V, Rosenberg R (2000) Endogenous nitric oxide decreases hippocampal levels of serotonin and dopamine in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 130(3):575–580. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0703349
Perry JJP, Shin DS, Getzoff ED, Tainer JA (2010) The structural biochemistry of the superoxide dismutases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1804(2):245–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.11.004
Sheng Y, Abreu IA, Cabelli DE, Maroney MJ, Miller A-F, Teixeira M, Valentine JS (2014) Superoxide dismutases and superoxide reductases. Chem Rev 114(7):3854–3918. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr4005296
Misra M, Rodriguez RE, Kasprzak KS (1990) Nickel induced lipid peroxidation in the rat: correlation with nickel effect on antioxidant defense systems. Toxicology 64(1):1–17
Ates B, Orun I, Talas ZS, Durmaz G, Yilmaz I (2008) Effects of sodium selenite on some biochemical and hematological parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792) exposed to Pb2+ and Cu2+. Fish Physiol Biochem 34(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-007-9146-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee (Local Institutional Research Committee).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Brouzi, M.Y., Lamtai, M., Zghari, O. et al. Intrahippocampal Effects of Nickel Injection on the Affective and Cognitive Response in Wistar Rat: Potential Role of Oxidative Stress. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 3382–3392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02457-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02457-5